Grid Forming Inverters Market Research, 2033
The global grid forming inverters market size was valued at $0.7 billion in 2023, and is projected to reach $1.5 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 8.2% from 2024 to 2033.

Market Introduction and Definition
Grid forming inverters are a crucial component in modern power systems, especially in the context of renewable energy integration and the transition towards more resilient and decentralized power grids. Grid forming inverters operate by using advanced control algorithms that enable them to mimic the behavior of a traditional synchronous generator. They can maintain grid stability by adjusting their output in response to changes in load or generation. This includes controlling the voltage and frequency of the grid, providing inertia, and supporting fault ride-through capabilities. The ability to form a grid independently is what distinguishes them from grid following or grid supporting inverters, which require an existing grid to operate.
One of the primary applications of grid forming inverters is in the integration of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind. These renewable sources are inherently variable and intermittent, which pose challenges for maintaining grid stability. Grid forming inverters can smooth out these fluctuations by providing virtual inertia and regulating voltage and frequency, thereby facilitating a higher penetration of renewables. In remote or off-grid areas, they enable the creation of standalone power systems that can reliably supply electricity without the need for a traditional grid connection.
Microgrids are localized grids that can operate independently or in conjunction with the main power grid. They are becoming increasingly popular for enhancing energy security, reducing emissions, and improving resilience against grid failures. Grid forming inverters are integral to the operation of microgrids because they allow these systems to function autonomously. They can synchronize distributed energy resources, manage power flows, and ensure stable operation even when disconnected from the main grid. This capability is particularly valuable in critical infrastructure applications such as hospitals, military bases, and data centers where uninterrupted power supply is essential.
Key Takeaways
- The grid forming inverters industry covers 20 countries. The research includes a segment analysis of each country in terms of value for the projected period in the grid forming inverters market statistics.
- The study integrated high-quality data, professional opinions and analysis, and critical independent perspectives. The research approach is intended to provide a balanced view of the global grid forming inverters market overview and to assist stakeholders in making educated decisions to achieve their growth objectives.
- Over 3, 700 product literature, annual reports, industry statements, and other comparable materials from major industry participants were reviewed to gain a better understanding of the grid forming inverters market report.
- The grid forming inverters market share is highly fragmented, with several players including ABB, Schneider Electric, Siemens, GENERAL ELECTRIC, SMA Solar Technology AG, Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., Delta Electronics, Inc., Enphase Energy, Hitachi Energy Ltd., and Eaton. Also tracked key strategies such as acquisitions, product launches, mergers, and expansion of the players operating in the grid forming inverters market growth.
Segment Overview
The grid forming inverters market is segmented into type, power rating, application, and region. By type, the market is classified into micro inverters, central inverters, and string inverters. By power rating, the market is categorized into below 50 KW, 50-100 KW, above 100 KW. By application, the market is fragmented into wind power plants, solar PV plants, electric vehicles, and energy storage system. Region-wise, the market is studied across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA.
Key Market Dynamics
Increase in renewable energy integration is expected to drive the growth of the grid-forming inverters market. The integration of renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, is reshaping the landscape of modern power systems. As these clean energy technologies become prevalent, the role of grid-forming inverters has become increasingly critical in maintaining grid stability and reliability. One of the primary drivers behind the growing need for grid-forming inverters is the variability and intermittency associated with renewable energy sources. Solar power generation depends on sunlight, which varies throughout the day and is affected by weather conditions. Similarly, wind power generation is contingent on wind patterns, which can be unpredictable and fluctuating. These characteristics can lead to significant fluctuations in power output, posing challenges for grid stability. Grid-forming inverters help mitigate these challenges by providing dynamic support to the grid, ensuring a steady and reliable power supply even when renewable energy output varies. According to the International Energy Agency, global renewable capacity additions could potentially reach 550 GW in 2024. The increase is primarily driven by the rapid deployment of residential and commercial PV installations, assuming the swift implementation of recent policies and incentives. The growth of utility-scale onshore wind and solar PV projects hinges on the speed of permitting, construction, and timely grid connection for projects currently under development.
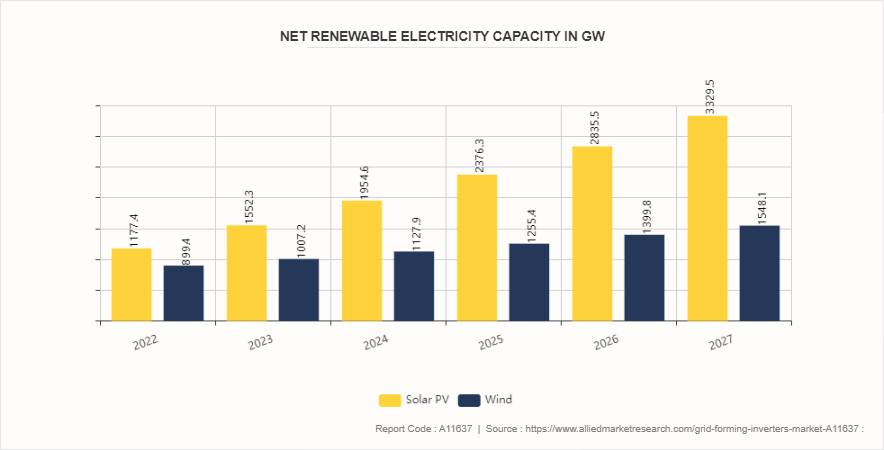
However, the high cost of grid-forming inverters and related infrastructure is expected to hinder the growth of the grid forming inverters market. The high initial costs associated with these advanced technologies present a significant barrier for many utilities and end-users. Grid-forming inverters are more complex and sophisticated compared to traditional grid-following inverters, requiring advanced components, control systems, and integration capabilities. This complexity translates into higher production costs, which are often passed on to consumers, making the initial investment substantial. For utilities, particularly those operating within tight budget constraints or in markets with regulated pricing, the high cost of grid-forming inverters can be a major deterrent. The capital expenditure required to deploy these inverters across the grid can strain financial resources, especially when combined with the costs of upgrading existing infrastructure to accommodate new technologies. This financial burden can be particularly challenging for smaller utilities or those in developing regions, where access to capital may be limited, and the financial viability of such investments is closely scrutinized.
The increase in deployment of microgrids is expected to provide more opportunities for the grid forming inverters market forecast. The expansion of microgrids, particularly in remote and off-grid areas, presents a substantial opportunity for the deployment and utilization of grid-forming inverters. Microgrids are localized power grids that can operate independently or in conjunction with the main electrical grid. They are increasingly being deployed to enhance energy resilience, integrate renewable energy sources, and provide reliable power in areas where traditional grid infrastructure is lacking or unreliable. The increasing deployment of microgrids driven by the need for energy resilience and reliability presents a significant market opportunity for grid-forming inverters. Natural disasters, extreme weather events, and other disruptions can severely impact traditional grid infrastructure, leading to prolonged power outages and significant economic losses. Microgrids, equipped with grid-forming inverters, offer a resilient solution by ensuring continuous power supply to critical infrastructure and communities during such events. This resilience is particularly important for remote and isolated areas, where restoring power through conventional means may take considerable time and resources. In January 2022, Ameresco Inc. revealed its contract to implement the Slemon Park Microgrid Project in Prince Edward Island, Canada, in collaboration with Prince Edward Island Energy Corporation. This initiative is slated for completion by the end of 2022 and features a 10 MW solar facility paired with DC-coupled energy storage, utilizing a shared interconnection setup.
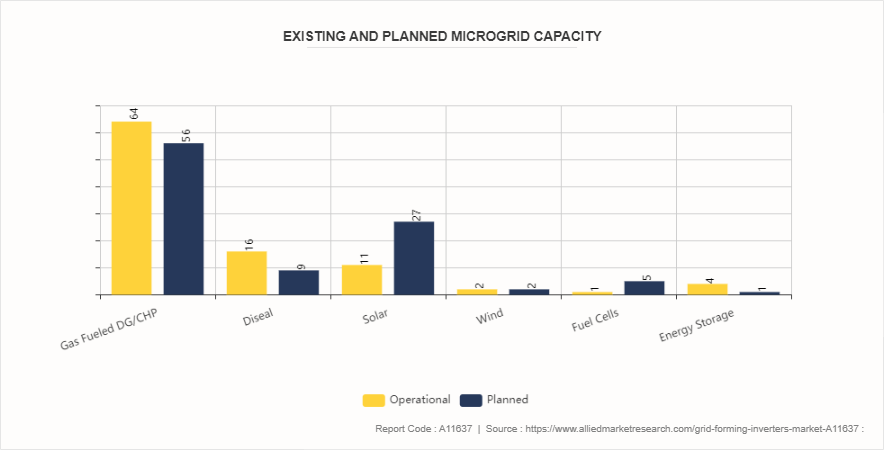
Regional Market Outlook
In North America, countries like the U.S. and Canada are integrating grid forming inverters to support renewable energy integration. These inverters enable seamless transitions between grid-connected and islanded operations, crucial for maintaining grid stability amid fluctuating renewable energy outputs. In Europe, nations such as Germany, Spain, and the United Kingdom are leveraging grid forming inverters to bolster their renewable energy capacities. These inverters help in maintaining voltage and frequency stability, which is essential as Europe transitions towards higher shares of wind and solar power.
In the Asia-Pacific region, countries such as China, Japan, and Australia are increasingly deploying grid forming inverters to bolster their power grid infrastructure. These inverters are crucial in managing the intermittency and variability inherent in renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power. By providing stable and reliable electricity supply, grid forming inverters help these countries to effectively integrate large-scale renewable energy generation into their grids. China, as one of the world's largest consumers of energy and a major player in renewable energy deployment, relies on grid forming inverters to enhance grid stability amidst the rapid expansion of wind and solar capacities. These inverters enable smooth transitions between grid-connected and islanded modes, ensuring continuous power supply even during fluctuations in renewable energy production.
Competitive Analysis
Key market players in the grid forming inverters market include ABB, Schneider Electric, Siemens, GENERAL ELECTRIC¸ SMA Solar Technology AG, Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., Delta Electronics, Inc., Enphase Energy, Hitachi Energy Ltd., and Eaton
Industry Trends
- In January 2022, Sungrow introduced its innovative 1+X central modular inverter at the World Future Energy Summit in Abu Dhabi. With an individual output capacity of 1.1MW, these inverters can be combined into configurations of up to eight units, achieving a total power output of 8.8MW. Additionally, the 1+X modular inverter includes a DC/ESS interface, enabling seamless integration with energy storage systems (ESS) .
- In May 2022, Fimer Spa, an Italy-based solar PV inverter manufacturer, provided 1 Mega Volt Ampere (MVA) inverters for a solar-plus-storage project in Gujarat, India. This project, which included an 18MWh battery energy storage system, was part of the Integrated Solar Energy Project in Modhera. Mahindra Susten Pvt. Ltd., an Indian solar PV engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) solution provider, executed the project, which was commissioned by Gujarat Power Corporation Limited (GPCL) , the state's utility company.
- As of 2022, India had an installed wind power capacity of 41.9 GW. However, the pace of new installations has slowed as the industry adjusts to the new wind power auction-based tariff determination method.
- In October 2022, Suzlon Group secured a new order from the Aditya Birla Group to develop wind power projects with a total capacity of 144.9 MW at sites in Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh. The contract includes the installation of approximately 69 wind turbine generators, each with a rated capacity of 2.1 MW, featuring Hybrid Lattice Tubular (HLT) towers. The projects are expected to be operational by the end of 2023.
Historic Trends Grid Forming Inverters Market
- Grid-forming inverters in the 2010s were primarily utilized in off-grid settings where connecting to a centralized power grid was either impractical or too expensive. These inverters played a critical role in supplying dependable electricity to remote areas, islands, and other locations where establishing conventional power infrastructure posed significant challenges.
- In 2015, the focus started shifting towards grid-tied applications as renewable energy penetration increased. Inverters began to play a crucial role in stabilizing grid voltage and frequency, especially with the rise of solar photovoltaic (PV) systems.
- In 2018, the advancements were made in grid-forming technology, driven by the need for better grid stability and resilience. This period saw the development of inverters capable of operating in grid-forming mode, where they can actively control voltage and frequency, mimicking the behavior of traditional synchronous generators.
- In 2021, the grid-forming inverter market has seen accelerated growth with increasing adoption in utility-scale renewable energy projects. Manufacturers are focusing on enhancing the efficiency, reliability, and scalability of grid-forming inverters to meet the demands of modern power grids.
Key Sources Referred
- International Energy Agency
- U.S. Department of Energy
- National Renewable Energy Laboratory
- Energy Central
- Solar Power World
Key Benefits For Stakeholders
- This report provides a quantitative analysis of the market segments, current trends, estimations, and dynamics of the grid forming inverters market analysis from 2024 to 2033 to identify the prevailing grid forming inverters market opportunities.
- The market research is offered along with information related to key drivers, restraints, and opportunities.
- Porter's five forces analysis highlights the potency of buyers and suppliers to enable stakeholders make profit-oriented business decisions and strengthen their supplier-buyer network.
- In-depth analysis of the grid forming inverters market segmentation assists to determine the prevailing market opportunities.
- Major countries in each region are mapped according to their revenue contribution to the global market.
- Market player positioning facilitates benchmarking and provides a clear understanding of the present position of the market players.
- The report includes the analysis of the regional as well as global grid forming inverters market trends, key players, market segments, application areas, and market growth strategies.
Grid Forming Inverters Market Report Highlights
| Aspects | Details |
| Market Size By 2033 | USD 1.5 Billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 8.2% |
| Forecast period | 2024 - 2033 |
| Report Pages | 300 |
| By Type |
|
| By Power Rating |
|
| By Application |
|
| By Region |
|
| Key Market Players | GENERAL ELECTRIC, SMA Solar Technology AG, Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., Hitachi Energy Ltd., Delta Electronics, Inc., Schneider Electric, Siemens, ABB, Eaton, Enphase Energy |
| | Others |
The global grid forming inverters market was valued at $0.7 billion in 2023, and is projected to reach $1.5 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 8.2% from 2024 to 2033.
Asia-Pacific is the largest regional market for grid forming inverters.
Energy storage systems is the leading application of grid forming inverters market.
The increase in deployment of microgrids are the upcoming trends of grid forming inverters market in the globe.
Key market players in the grid forming inverters market include ABB, Schneider Electric, Siemens, GENERAL ELECTRIC¸ SMA Solar Technology AG, Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., Delta Electronics, Inc., Enphase Energy, Hitachi Energy Ltd., and Eaton
Loading Table Of Content...


