Table Of Contents
- Bracing up in the Battlefield
- From Destruction to Development: Drone’s Shifting Perspective
- Drone Delivery: The Sky is no Longer the Limit
- Drone Delivery is Developing, yet Challenges Persist
- Funding to Furnish the Future
- Developments in Drone Technology
- Foreseeing a Future with Drones Dominating the World

Lalit Janardhan Katare

Akshata Tiwarkhede
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV): Revolutionizing the Skies

An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), or drone, is an autonomously programmed aircraft without a human onboard. It has emerged as a transformative force in modern aviation, witnessing increased penetration in industries ranging from agriculture to defense, albeit accompanied by regulatory and privacy considerations.
Bracing up in the Battlefield
The last decade has witnessed significant evolution of combat UAVs characterized by rapid advancements in technology and capabilities. From as simple as remote-controlled aircraft to sophisticated autonomous systems, UAVs have undergone significant transformations, reshaping the military & defense sector.
The Queen Bee: In 1935, the British introduced DH.82B Queen Bee—the mother of all drones—which was the first reusable, radio-controlled, pilotless aircraft that exhibited the capacity to travel a maximum distance of 300 miles at over 100 mph and could fly as high as 17,000 feet. Retired in 1947, Queen Bees served as target drones in the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force.
Scout Drone: One of the earliest notable UAVs was the Israeli-made "Scout" drone, which saw operational use during the 1982 Lebanon War. This reconnaissance drone demonstrated the potential of unmanned aircraft in providing real-time intelligence without risking human lives. Subsequent conflicts, such as the Gulf War and the war in Afghanistan, further underscored the value of drones in modern warfare, leading to increased investment and technological innovation in this field.

Autonomous Flying Wing Technology Demonstrator: In July 2022, a flight trial of Autonomous Flying Wing Technology Demonstrator—an indigenous high-speed flying-wing UAV—was carried out by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), India, from the Aeronautical Test Range, Chitradurga, Karnataka. This high-speed UAV showcased the capability of landing autonomously, which was accomplished without the support of ground radars or a pilot, thus demonstrating a groundbreaking achievement.
Furthermore, in the same year, during the aftermath of Hurricane Ida in the U.S., drones were deployed extensively for various purposes, including photography, surveying, and disaster response. They provided crucial real-time data to aid in assessing the extent of damage, identifying areas in need of immediate assistance, and facilitating effective disaster relief efforts. Thus, regulatory bodies around the world have focused on developing guidelines and regulations to govern the safe and responsible operation of UAVs in civilian airspace. Thus, as technology matures, the applications of drones are likely to expand in the military domain.
From Destruction to Development: Drone’s Shifting Perspective
While drones were introduced as a weapon a century ago, today they stand as a powerful tool to shape the future of aviation. Civilian and commercial sectors have recognized the potential of this device for various tasks, including aerial photography, surveying, mapping, infrastructure inspection, wildlife monitoring, and disaster response.
The advent of UAVs has marked a significant milestone by serving as a ubiquitous solution that reduces human efforts and mitigates errors. They enhance accuracy, efficiency, and safety of the tasks such as inspecting infrastructure, crop health monitoring, or delivering medical supplies to remote areas, which were once labor-intensive and error-prone. Thus, the versatility and agility of this technology have paved the way for a wide range of applications across different industries.
They have further revolutionized aerial cinematography and photography, enabling filmmakers, photographers, and content creators to capture breathtaking aerial shots that were previously inaccessible or prohibitively expensive. Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and stabilization systems have become indispensable tools in the entertainment industry. Furthermore, they are increasingly used for inspecting critical infrastructure such as bridges, power lines, pipelines, and wind turbines. By conducting aerial inspections, they can identify structural defects, corrosion, and other issues more quickly and cost-effectively than traditional methods, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. In addition, in emergency situations, UAVs equipped with thermal imaging cameras and other sensors can assist search and rescue teams in locating missing people, assessing disaster areas, and coordinating relief efforts. They provide valuable situational awareness and support emergency responders in their lifesaving missions. Drones equipped with LiDAR technology are also used for creating detailed 3D maps of urban areas, terrain, and infrastructure. These maps are valuable for urban planning, disaster preparedness, navigation, and simulation applications. Moreover, they play a vital role in environmental research and conservation efforts by monitoring wildlife population, tracking deforestation, mapping ecosystems, and assessing the impact of climate change. They enable scientists and conservationists to collect data over large areas with greater accuracy and efficiency. Law enforcement agencies, border patrols, and private security firms utilize this device on a large scale for surveillance, monitoring, and reconnaissance purposes. Drones equipped with cameras, infrared sensors, and other surveillance equipment provide aerial surveillance capabilities for enhancing public safety and security. Additionally, the companies such as Amazon, UPS, and DHL are exploring the use of UAVs for package delivery in urban and remote areas. Delivery drones promise faster delivery times and lower carbon emissions compared to traditional delivery methods, although regulatory and logistical challenges remain to be addressed.
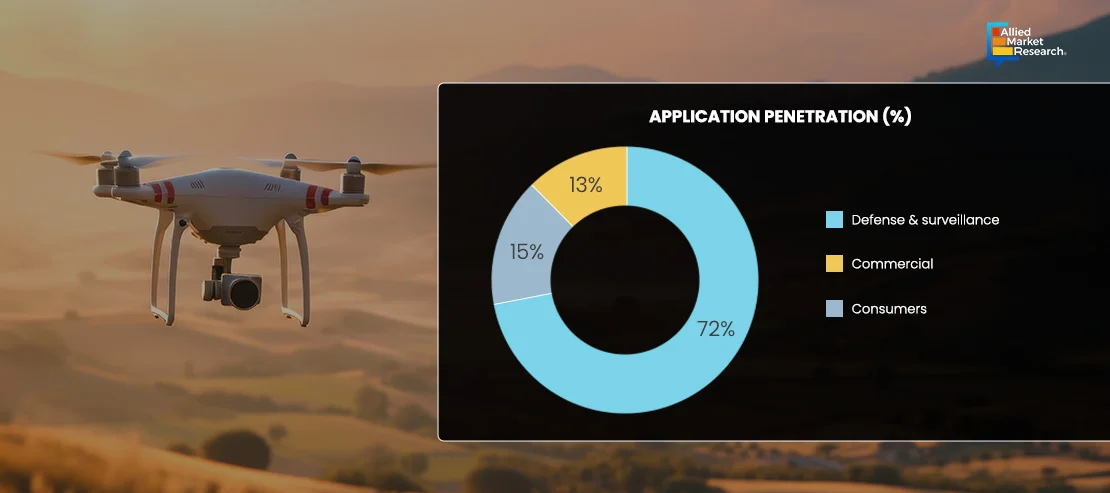
Drone Delivery: The Sky is no Longer the Limit
While earlier drones were primarily used for military-grade operations, they are now within reach of civilians due to rapid technological advancements. The adoption of drones equipped with GPS and a 4K camera indicate the potential of drones to revolutionize the delivery industry. According to a report by McKinsey & Company—an American multinational strategy and management consulting firm—more than 2,000 drone deliveries were completed globally by early 2022. CNBC, the world leader in business news and real-time financial market coverage, reported in May 2023 that Wing—a subsidiary of Google parent Alphabet—has completed 330,000 drone deliveries. Adam Woodworth, the CEO of Wing, further added that “The service area that we cover there is between 70,000 and 100,000 people and it’s a relatively sort of geographically constrained location. If you look at metrics from last year, we were seeing on the order of about 1,000-plus deliveries a day to that sort of one snapshot of the planet.” Thus, e-commerce giants continue to be invested in leveraging delivery UAVs to focus on improving last-mile delivery, reducing delivery time, and providing better user experience.
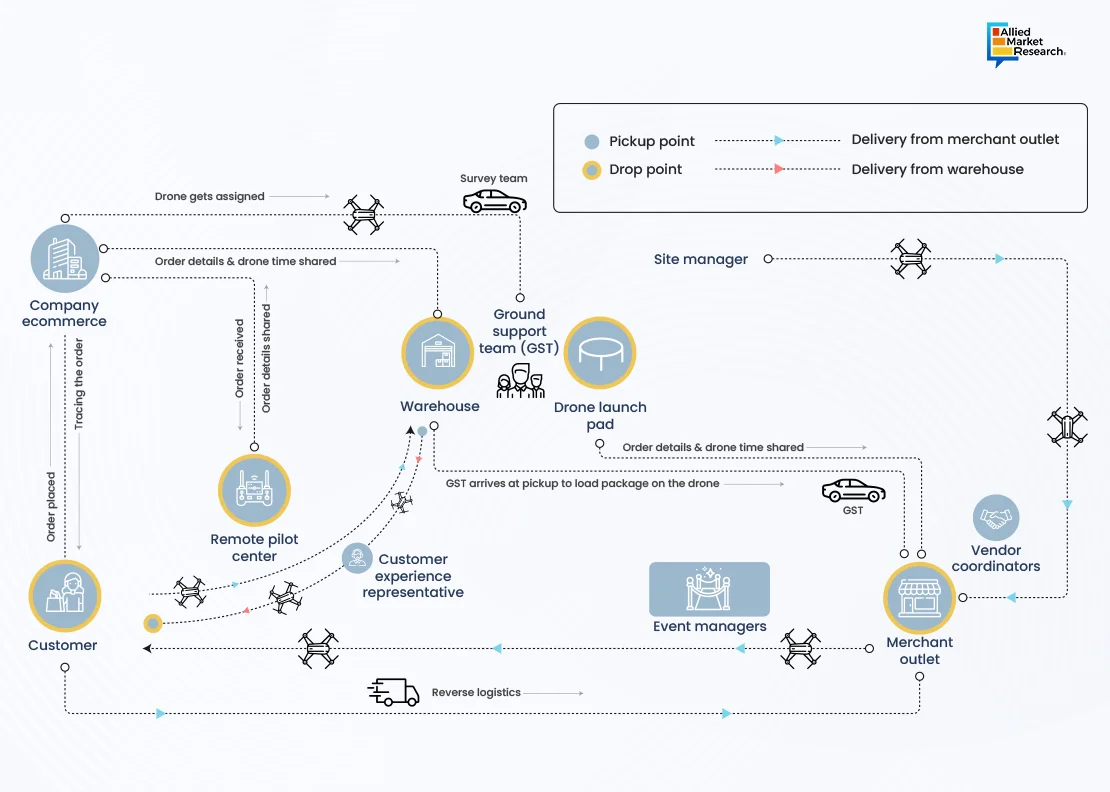
Drone Delivery is Developing, yet Challenges Persist
Although technological science has turned fiction into reality by facilitating deliveries through drones, products will still be brought to the doorstep of the buyer by a human, not a drone. Thus, despite their numerous benefits, UAVs pose various challenges and considerations that must be addressed.
Regulatory Compliance: Drone operations are subject to regulations and airspace restrictions imposed by civil aviation authorities. Pilots and operators must comply with registration, licensing, and operational requirements to ensure safe and legal drone flights.
Safety Concerns: Accidents and incidents involving drones can pose risks to people, property, and other aircraft. Mitigating safety risks requires implementing robust safety protocols, collision avoidance systems, and emergency procedures.
Privacy Issues: The proliferation of drones has raised concerns about privacy infringement and surveillance. Balancing the benefits of this device with privacy rights requires clear regulations, ethical guidelines, and public awareness campaigns.
Airspace Integration: Integrating UAVs into existing airspace systems presents technical and operational challenges, particularly in urban areas with dense air traffic. Developing systems for managing UAV traffic and ensuring safe coexistence with manned aircraft is essential for realizing the full potential of this technology.
Cybersecurity Risks: Like any connected device, UAVs are vulnerable to cybersecurity threats such as hacking, malware, and data breaches. Protecting them from cyberattacks requires implementing robust encryption, authentication, and intrusion detection mechanisms.
Environmental Impact: The proliferation of UAVs raises concerns about their environmental impact, including noise pollution, carbon emissions, and wildlife disturbance. Developing environment-friendly designs and promoting sustainable operational practices can help mitigate these impacts.
Public Acceptance: Building public trust and acceptance of drone technology is crucial for its widespread adoption. Educating the public about the benefits of this device, addressing misconceptions, and fostering dialogue between stakeholders can help alleviate concerns and promote positive approach toward it.
Funding to Furnish the Future
As the years progressed, investment in the drone industry surged, from approximately $300 million in 2014 to reaching a pinnacle in 2021 of nearly $3.5 billion. This substantial increase in funding is majorly attributed to the burgeoning demand for drones across a diverse array of applications, spanning military and defense operations, goods and parcel delivery services, as well as security and surveillance initiatives.
Although previous years witnessed rapid momentum, investments gradually plummeted by up to 50 in both 2022 and 2023 due to regulatory uncertainty surrounding drone operations, market saturation, and intensified competition, thereby posing barriers to entry for investors and limiting funding opportunities.
Despite these temporary setbacks, the drone industry is poised to continue its trajectory toward reshaping industries and driving progress in the years to come. For instance, in 2023, Aerodyne Group, a leading drone services provider based in Malaysia, secured a significant funding of $50 million. This investment, led by a consortium of investors, including Venture Capital firms and strategic partners, emphasized the growing interest and confidence in the drone industry. Aerodyne planned to utilize the funding to further expand its global operations, develop innovative drone technologies, and enhance its capabilities in aerial data analytics for various sectors, including infrastructure, energy, and agriculture. Thus, the widespread adoption of this technology in these sectors highlighted its transformative impact and increased investor interest.

Developments in Drone Technology
The future of UAVs holds immense promise, with continued advancements in technology, regulation, and applications.
Advanced Sensor Technologies: Future UAVs will be equipped with advanced sensors, artificial intelligence, and machine learning algorithms for enhanced perception, autonomy, and decision-making capabilities.
Urban Air Mobility: UAVs will play a significant role in the emerging field of urban air mobility, enabling on-demand passenger transportation, aerial taxis, and autonomous flying vehicles for urban mobility solutions.
Expanded Commercial Applications: UAVs will continue to find new applications across various industries, including construction, mining, environmental monitoring, telecommunications, and public safety.
Beyond Visual Line of Sight (BVLOS) Operations: Regulatory frameworks will evolve to enable BVLOS operations, allowing UAVs to fly beyond the operator's line of sight for long-range missions such as infrastructure inspection, delivery, and surveillance.
Collaborative Systems: Future UAVs will operate collaboratively with manned aircraft, ground vehicles, and infrastructure in integrated airspace systems, enabling seamless coordination and communication between diverse aerial platforms.
Sustainable Technologies: The development of lightweight materials, electric propulsion systems, and renewable energy sources will enhance the sustainability and environmental friendliness of UAVs, reducing their carbon footprint and ecological impact.
Global Connectivity: UAV networks will provide global connectivity and internet access to remote and underserved regions, bridging the digital divide and enabling socio-economic development in remote areas.
These advancements collectively will pave the way for a future where UAVs play an indispensable role in addressing societal challenges, driving innovation, and shaping the landscape of various industries.
Foreseeing a Future with Drones Dominating the World
UAVs represent a transformative technology with vast potential to revolutionize various industries and sectors. By addressing challenges, embracing innovation, and fostering responsible use, the power of UAVs can be harnessed to create a safer, more efficient, and sustainable future in the skies. For further insights, get in touch with AMR analysts.

