Table Of Contents
- Construction Drones: Go-to Tools for Construction Firms
- Sensors Equipped in Construction Drones
- Advanced Technologies to Play a Significant Role
- Current Level of Adoption
- Barriers to Adoption of Construction Drones
- Early Adopters
- Future Capabilities and Applications
- Utilizing Drone Technology to its Full Potential
- Risks Associated with Construction Drones
- Future Outlook

Sonia Mutreja

Pooja Parvatkar
Construction Drones: Revolutionizing the Construction Industry

Construction drones—also referred to as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs)—have gained high traction in construction firms as they provide real-time data and elevate safety standards. These drones are equipped with sensors, cameras, and other advanced technologies to capture aerial data for surveying, mapping, inspection, and monitoring on construction sites.
With the help of construction drones, inspecting hard-to-reach areas or optimizing construction sites have become easier that were earlier hard to access or even track. Thus, the use and impact of drones in construction is likely to continue to grow as the domain grows.
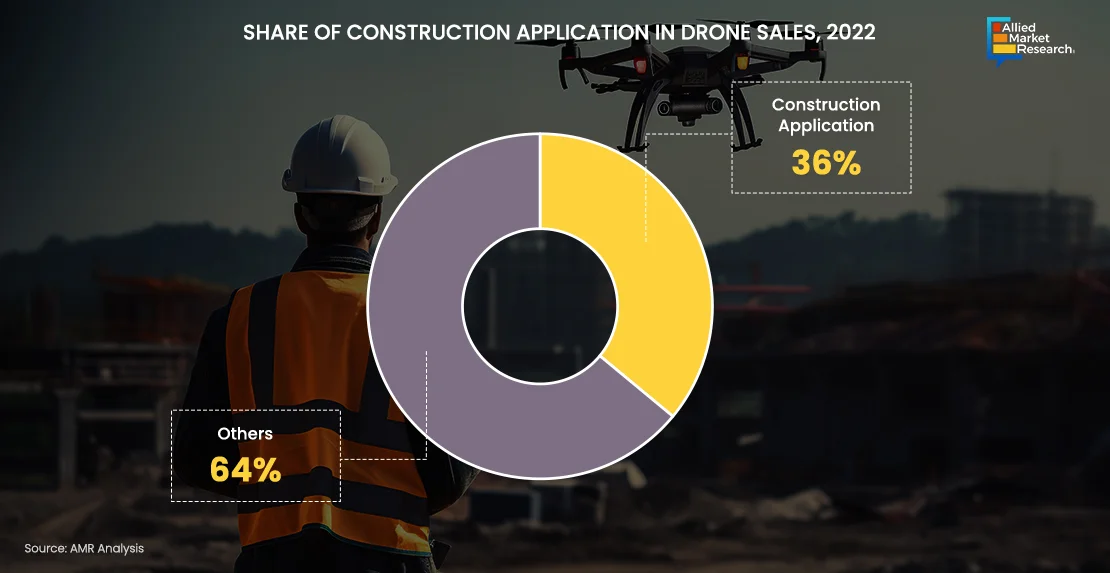
Construction Drones: Go-to Tools for Construction Firms
Drones are equipped with flight control systems, including gyroscopes, accelerometers, GPS receivers, and altimeters, which enable them to maintain stability, navigate, and maneuver in the air. Operators use remote controllers or mobile devices to control the drone’s flight path, altitude, and speed.
Sensors Equipped in Construction Drones
Furthermore, sensors and imaging technologies, such as cameras, light detection and ranging (LiDAR), thermal sensors, and multispectral sensors are installed in construction drones to capture high-resolution images, 3D point clouds, thermal data, and other data about the construction site and its surroundings. This aerial data that is captured is transmitted wirelessly to ground control stations or stored onboard. In some cases, drones may process data in real time using onboard processing capabilities.

Once data is captured, it is processed and analyzed using specialized software tools. This may involve stitching together aerial images to create ortho mosaic maps, generating 3D models of the construction site, extracting measurements and topographic information, or identifying anomalies and defects through image analysis algorithms. The processed data is subsequently used to generate reports, maps, and visualizations that provide valuable insights to construction project stakeholders for project planning, design optimization, progress tracking, quality control, and safety monitoring.
Thus, drones facilitate real-time data collection, help to gain valuable insights into construction projects, and make informed decisions to improve productivity, safety, and project outcomes.
Advanced Technologies to Play a Significant Role
Key players operating in the market are on the quest to develop new technologies and features to improve their product offerings. Advanced technologies such as global navigation satellite systems (GNSS), global positioning systems (GPS), geographical information systems (GIS), Internet of Things (IoT), thermal imaging, and artificial intelligence (AI) are being integrated into drones. For instance, in June 2020, Parrot SA—a France-based drone developer—launched a new drone, ANAFI USA, which is built for firefighters, first responders, search & rescue teams, security agencies, surveying, and inspection professionals. The drone is especially designed for the U.S. Army. Other companies such as Dà-Ji?ng Innovations Science and Technology Co., Ltd. (DJI), SenseFly, and Trimble Inc. have also been adopting strategies to obtain a strong foothold in the industry. In November 2023, Trimble and Skydio announced a collaboration to enhance drone technology and features such as accurate data capture, data visualization, and data analytics. The focus is to address the needs of critical infrastructure industries in their surveying, mapping, and inspections.
Current Level of Adoption
The adoption of construction drones has been steadily increasing, with many construction companies and engineering firms incorporating drones into their operations. While adoption levels may vary depending on factors such as region, industry segment, and company size, drones are being used in various contexts across the construction industry.

Drones are majorly applicable in aerial surveying and mapping of construction sites, providing high-resolution imagery, 3D models, and topographic data to inform site planning, design, and earthwork operations. They are employed to monitor progress on construction projects by capturing aerial images and videos at regular intervals. This data is used to track construction activities, assess project milestones, and identify potential delays or issues. Furthermore, they are utilized for asset management purposes, including inventory management, tracking equipment and materials, and conducting audits of cranes, scaffolding, and temporary structures.
Drones in the construction industry are used for environmental monitoring and compliance assessments, including monitoring erosion control measures, tracking vegetation clearance, and assessing impacts on sensitive habitats. They are further being deployed for emergency response and disaster management purposes to assess damage, conduct search and rescue operations, and support disaster relief efforts in the aftermath of natural disasters or emergencies.
Barriers to Adoption of Construction Drones
Complex and evolving regulations governing drone operations, airspace restrictions, and privacy concerns may pose barriers to adoption. This is attributed to the fact that compliance with regulatory requirements, obtaining necessary permits and licenses, and navigating bureaucratic processes can be time-consuming and costly for construction companies. Initial investment costs associated with purchasing drones, sensors, software, and training personnel can be prohibitive for some construction firms, especially smaller companies with limited budgets. Moreover, regular maintenance, software updates, and insurance renewal, incur addition cost, thus limiting the adoption of drones.
In addition, integrating drones in existing construction workflows and systems may present technical challenges, especially for companies with outdated or incompatible technology infrastructure. Lack of interoperability between drones and construction management software platforms could impede seamless data sharing and collaboration. Resistance to adopting new technologies due to skepticism, fear of job displacement, and cultural barriers to innovation as well as changing traditional work practices within the construction industry may further slowdown the adoption of drones.
Moreover, lack of awareness about the capabilities and potential benefits of construction drones among construction professionals, project stakeholders, and regulatory agencies hinders the adoption.
Early Adopters
Several industries and applications are likely to represent early adopters of drone technology due to their alignment with the capabilities and benefits offered by drones. These early adopters may include construction & engineering, surveying & mapping, architecture & urban planning, infrastructure inspection, environmental monitoring & conservation, disaster response & emergency management, mining & quarrying, and agriculture & precision farming.

Future Capabilities and Applications
Drones equipped with AI and robotics autonomously perform construction tasks such as bricklaying, concrete pouring, and steel beam placement. These autonomous drones could work collaboratively with humans to increase efficiency and productivity on construction sites. Future technology may be capable of providing real-time monitoring and control of construction processes, enabling project managers to track progress and identify potential issues along with monitoring construction materials, equipment utilization, and worker activity.
Drones could play a vital role in disaster response and recovery efforts by rapidly assessing damage, identifying hazards, and aiding in search and rescue operations. These drones could provide valuable data to emergency responders and help expedite recovery efforts in the aftermath of natural disasters or other emergencies.
As drone technology continues to evolve, it may become increasingly customizable and adaptable to specific project requirements. This could include the ability to modify drone configurations, payloads, and software to suit different construction tasks and environments, maximizing versatility and effectiveness.
Overall, the future capabilities and applications of drones hold tremendous promise for revolutionizing the construction industry and enhancing efficiency, safety, sustainability, and innovation in construction processes and projects. Continued investment in research and development, collaboration among stakeholders, and adaptation to emerging technologies will be key to realizing this potential.
Utilizing Drone Technology to its Full Potential
Drones have immense potential in several applications that are a result of the benefits that they provide:
- Improved Battery Life and Energy Efficiency: Longer flight times and increased energy efficiency enable drones to cover larger areas and perform more tasks without frequent recharging.
- Enhanced Payload Capacity: Drones with high payload capacity can carry heavy equipment and sensors, expanding their utility for various construction applications.
- Advanced Sensors and Imaging Technology: The integration of high-resolution cameras, LiDAR, thermal imaging, and other sensors can provide more detailed and accurate data for surveying, mapping, and monitoring purposes.
Risks Associated with Construction Drones
Drone technology offers numerous benefits, including increased efficiency, enhanced safety, and improved data collection. However, several risks and concerns need to be addressed to ensure its safe and effective use.
Drones operating in construction sites pose safety risks to workers and bystanders due to potential collisions or falling objects. Stringent safety protocols have been implemented, including designated no-fly zones, operator training, and geofencing, to prevent drones from entering restricted areas.
Furthermore, drones equipped with cameras raise privacy concerns as they can inadvertently capture images or footage of individuals without consent. Establishment of clear policies regarding drone use and data collection, obtaining consent when necessary, and ensuring compliance with local privacy regulations are essential.
Future Outlook
Construction drones have emerged as transformative assets in the construction sector, offering real-time data collection, safety enhancements, and critical insights for project management. Despite encountering hurdles such as regulatory complexities and initial investment barriers, their adoption is steadily rising. With ongoing advancements in technology, including improvements in battery life, payload capacity, and sensing capabilities, drones hold significant potential for further revolutionizing the industry. Addressing concerns such as safety risks and privacy considerations will be essential to ensure their effective and responsible use. Overall, the future outlook for construction drones appears promising, contingent upon continued investment and collaboration within the industry.
For further insights, get in touch with AMR analysts.

