Table Of Contents
- Flying IoT Revolutionizing the Construction Industry
- Rapid Urbanization Unlocking Opportunities for the Construction Industry
- Vital Role of IoT in Meeting Key User Needs in Construction
- Recent Breakthroughs Building the Future of the Construction Industry
- Pioneers of IoT in Construction
- Exploring the Potential Applications of IoT
- Constructing a Brighter Future

Sonia Mutreja

Akshata Tiwarkhede
Exploring the Transformative Potential of IoT in Construction

The construction industry, often regarded as traditional, is experiencing a technological revolution driven by the Internet of Things (IoT)—a network of interconnected devices—facilitating data collection and exchange. Deploying IoT in the construction sector enables the integration of digital technologies in physical infrastructure, revolutionizing how projects are planned, executed, and managed.
In practical terms, IoT applications in construction are making significant headway. For example, sensors embedded in construction equipment help to monitor performance metrics in real time. This enables predictive maintenance and reduces downtime in businesses. According to a study by McKinsey & Company, predictive maintenance enabled by IoT can reduce maintenance costs by up to 25% and unplanned downtime by up to 50%, which highlights the advantage of IoT in construction.
Moreover, IoT-enabled construction sites are becoming increasingly common, with sensors deployed to monitor environmental conditions, equipment utilization, and worker safety. These data-driven insights help project managers make informed decisions and mitigate risks at construction sites, thus increasing productivity. Research by PwC in 2022 indicated that the adoption of IoT in construction increased productivity by up to 14% and reduced project delays by up to 12%.
Flying IoT Revolutionizing the Construction Industry
Drones are not just viewed as aerial vehicles but serve as an advanced IoT tool that will play a pivotal role in shaping the construction industry. These tools enhance the efficiency and precision of construction processes, as they exhibit the ability to capture high-resolution images, conduct aerial inspections, and generate accurate topographical maps.
Prior to the advent of drones, site inspection was carried out on-foot and data was obtained using traditional methods such as manned aerial vehicles. Moreover, initially, the applications of IoT in construction were limited, primarily focusing on basic monitoring and control functions. However, the introduction of construction drones equipped with AI and robotics facilitated construction tasks such as bricklaying, concrete pouring, and steel beam placement autonomously owing to rapid technological advancements. Further advancements in drone technology will enable real-time monitoring and control of construction processes, enabling project managers to track progress and identify potential issues along with monitoring construction materials, equipment utilization, and worker activity. For instance, the Norwegian Public Roads Administration is targeting a zero-fatality goal by 2024 with the aim to construct the safest road network. To achieve this goal, the agency plans to use vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) drones for surveying, which are also expected to cut down the field time and save cost. These autonomous drones could work collaboratively with humans to increase efficiency and productivity on construction sites. Thus, the maturity level of IoT in construction continues to rise, offering potential opportunities for innovation and driving the industry toward a more connected and sustainable future.
Rapid Urbanization Unlocking Opportunities for the Construction Industry
Exponential increase in population in the developing and developed economies such as India, China, Mexico, Brazil, France, the UK, and the U.S. has resulted in rapid urbanization, which is shaping the future of construction and infrastructure industries. According to the UN report 2021, around 68% of the world population is expected to live in urban areas by 2050.
Urban Population to Boost the Construction Industry
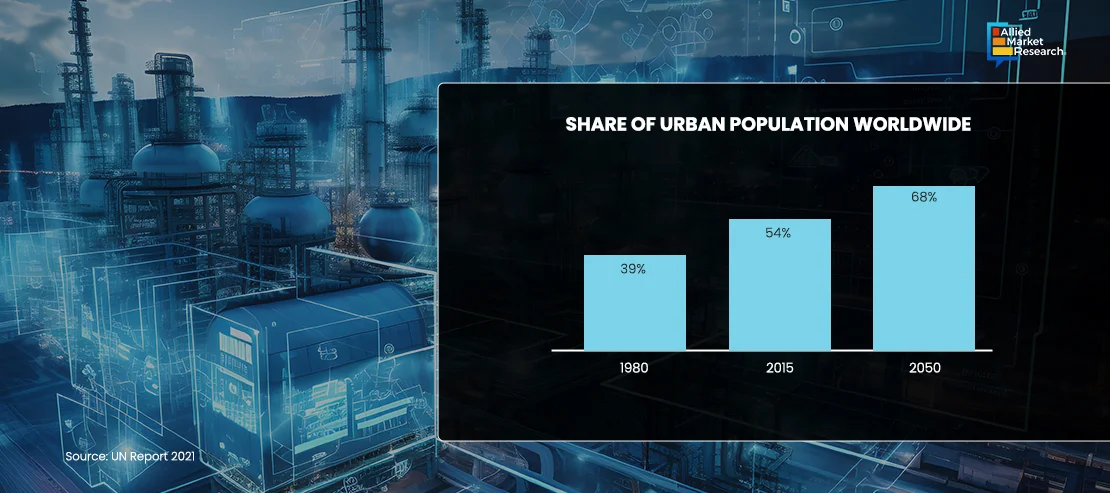
This is expected to increase residential construction activities globally, which, in turn, will foster the need for surveying, monitoring, and surveillance of construction sites, thereby fostering the adoption of IoT in construction industry.
Key User Needs Addressed by IoT in Construction Sector

Vital Role of IoT in Meeting Key User Needs in Construction
Enhanced Safety: IoT in construction can identify potential hazards and mitigate risks, ensuring a safer working environment by monitoring environmental conditions and equipment performance. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the construction industry consistently ranks among the highest in terms of workplace fatalities. However, IoT solutions are changing this landscape. For instance, wearable devices equipped with sensors can monitor workers' vital signs and detect signs of fatigue or overexertion, helping to prevent accidents and injuries. Research by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) suggests that IoT technologies have the potential to reduce construction-related accidents by up to 35%.
Improved Efficiency: Real-time data collection and analysis enable better resource allocation, task scheduling, and project management, leading to increased productivity and cost savings. For example, a study by McKinsey & Company found that IoT-enabled asset tracking systems can reduce material waste by up to 20% and improve equipment utilization by up to 25%. In addition, according to the Construction Industry Institute—a U.S.-established international consortium that focuses on improving the construction industry's performance and efficiency through research, collaboration, and best practices—adopting IoT technologies for project management can lead to a 15% increase in productivity and a 10% reduction in project costs.
Predictive Maintenance: IoT sensors can detect signs of equipment malfunction or deterioration before they occur, facilitating proactive maintenance and minimizing downtime. Research by Deloitte indicates that predictive maintenance enabled by IoT can reduce maintenance costs by up to 40% and increase equipment uptime by up to 50%.
Quality Control: By continuously monitoring materials and construction processes, IoT helps maintain quality standards and prevent defects. According to a report by Dodge Data & Analytics, construction projects using IoT-based quality control systems experience a 20% reduction in rework and defects.
Recent Breakthroughs Building the Future of the Construction Industry
Advancements in sensor technology, data analytics, and connectivity protocols have facilitated the penetration of more robust and scalable IoT solutions in the construction sector. For instance, in September 2022, Hexagon AB acquired iConstruct Pty Ltd., a developer of building information modelling software used in commercial, infrastructure, and industrial construction. The company’s flagship solution “iConstruct Pro” is a construction automation tool that enables integration, accessibility, and control of design and construction information held within different BIM models, combining all data into a single 3D model.
In June 2022, CalAmp entered into a partnership with Techmatics. The business will provide guaranteed Techmatics' Apollo electronic logging device (ELD) to commercial and public fleet operators through this agreement, enabling them to record and log the crucial data required for regulatory compliance. Apollo ELD is used for recording and logging crucial data related to vehicle operations and compliance with regulatory requirements. The Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) in the U.S., a third-party organization recognized by the Minister of Transport for Canada, and the Secretara de Comunicaciones y Transportes (SCT) for Mexico have all given their approval for the use of Apollo ELD in interstate and intrastate commerce throughout the U.S.
In March 2021, Oracle developed its new Oracle fusion cloud supply chain and manufacturing platform. The updates include IoT asset monitoring and IoT production monitoring capabilities that enable customers to monitor key characteristics of their assets and gain a full view of their production line output.
In October 2021, Hilti Corporation launched a new Jaibot, a semi-autonomous mobile ceiling drilling robot, for the construction industry. The Hilti Jaibot is used in the construction industry to tackle productivity, labor safety, and reduce labor shortage challenges. The main motto of the product launch was to digitize the construction sites.

A total of 8 developments were registered for year 2020, including acquisition, partnership, new product development, expansion, and others. Similarly, the years 2021, 2022, and 2023 registered 5, 3, and 1 developments, respectively.
The giants such as Advanced Opto-Mechanical Systems and Technologies Inc., Autodesk, Inc., CalAmp Corporation, Hexagon AB, Hilti Corporation, Oracle Corporation, Topcon Corporation, Triax Technologies, Inc., Pillar Technologies, Inc., and Trimble, Inc. contributed to these developments.
Thus, these developments collectively create a fertile environment for sustained market expansion, driving economic prosperity and fostering a culture of innovation and collaboration.
Navigating the Challenges
Interoperability: A number of manufacturers are involved in the development of IoT devices and systems and may use different communication protocols or standards. This lack of interoperability can hinder seamless integration and communication between devices, limiting the effectiveness of IoT solutions.
For instance, at a construction site, if sensors from different companies cannot understand the data transferred among them because they use incompatible "languages," it is tough to get a complete view of what is happening. By ensuring all devices can communicate using a common language or translator, data can be gathered and analyzed more effectively, making operations smoother and safer.
Data Privacy: IoT devices are vulnerable to cybersecurity threats, including malware, hacking, and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks. Weak security measures, unpatched vulnerabilities, and insecure communication channels can expose IoT systems to exploitation and compromise.
Deploying industrial IoT (IIoT) systems in manufacturing plants control crucial processes and machinery. A cyberattack on these systems could disrupt operations, damage equipment, or even endanger workers' safety. However, implementing robust security measures, regularly patching vulnerabilities, and securing communication channels can help mitigate these risks.
Pioneers of IoT in Construction
The current level of adoption of IoT in construction is steadily increasing, particularly in sectors such as infrastructure, commercial real estate, and industrial construction. Early adopters are leveraging IoT in construction to optimize processes, improve project outcomes, and gain a competitive edge.
A number of giants are adopting IoT in construction, especially in areas such as building roads, offices, and factories, which will help in driving innovation and shaping the trajectory of the construction industry. For example, Skanska—a multinational construction and development company—is using special sensors such as the "Sensidyne GilAir Plus" and "Lascar EL-USB-1" in its building sites to keep track of various parameters, including temperature, humidity, and air quality, which play a vital role during contraction activities, thus ensuring safety of workers and optimum use of resources.
The future of the construction industry is brighter with increasing penetration of smart gadgets. For instance, products such as "Google Nest Thermostat" and "Philips Hue Smart Bulbs" are gaining high traction for smart home automation. This not only makes life more convenient but also helps save energy and money on bills.
Thus, with continuous advancements in IoT, early adopters will remain at the forefront, driving the construction industry toward a smarter, more interconnected future.
Exploring the Potential Applications of IoT
The future potential of IoT in construction is vast, with experts forecasting continued growth and innovation in the coming years. Potential capabilities and applications include:
- Autonomous Construction: Integration of IoT with robotics and AI could lead to autonomous construction processes, reducing reliance on manual labor and enhancing efficiency.
- Smart Buildings: IoT-enabled buildings equipped with sensors and connected systems will enable predictive maintenance, energy optimization, and personalized user experiences.
- Digital Twins: IoT data can be used to create digital twins of construction projects, allowing for real-time monitoring, simulation, and optimization throughout the project lifecycle.
Constructing a Brighter Future
IoT has emerged as a catalyst for efficiently executing construction projects. The commitment of the construction industry to enhance customer experience through innovative solutions remains at the forefront with rapid advancements in technology. However, risks and concerns exist around data privacy, cybersecurity, and the ethical implications of IoT adoption in construction. These concerns must be addressed through robust security measures, regulatory frameworks, and industry best practices to build trust and confidence in the technology.
Contrarily, IoT has the power to transform the construction industry by offering unprecedented opportunities for safety, efficiency, and innovation. Thus, embracing IoT in construction sector can pave the way for a more connected and sustainable future and overcoming existing challenges.
For further insights, get in touch with AMR analysts.

