Table Of Contents
- Industry Trends and Market Dynamics
- Auto Industry: The Global Analysis
- Autonomous Technology and Cybersecurity Update
- Global AV Adoption
- Cybersecurity Is a Top Priority:
- Truck as a Service: The Next Step toward Zero-Emission Fleets
- Surge in Mergers and Acquisitions Transforming the Landscape of Transport and Logistics
- Strong Performance in the Air Freight Sector
- Global Electric Vehicle Demand Forecast
- Verdict in 2024 and the Outlook for 2025

Lalit Janardhan Katare

Koyel Ghosh
Automotive and Transportation Industry: 2024 Review and Future Outlook

The Automotive and Transportation industry played an important role in driving global connectivity and economic growth in 2024 through innovative mobility solutions. It covered the design, production, and operation of vehicles and transport infrastructure across land, air, and water. Significant advancements were made in electric vehicles, powered by state-of-the-art batteries, which supported sustainability efforts. Autonomous vehicles made notable progress, using AI, machine learning, and advanced sensors for self-driving capabilities. IoT and 5G-powered connected systems enhanced navigation, diagnostics, and infotainment in vehicles. Smart manufacturing technologies, including robotics and 3D printing, streamlined production processes. Intelligent traffic management systems contributed to improved urban mobility. Additionally, renewable energy transit systems and high-speed rail projects redefined sustainable, efficient, and safe transportation, shaping the future of the industry.
Industry Trends and Market Dynamics
The automotive industry has been undergoing a significant transformation, driven by shared mobility, connectivity, and feature upgrades. In 2024, these advancements continued to reshape the market, contributing to a projected 30% increase in the industry’s revenue pool, potentially adding $1.5 trillion by 2030. Traditional revenue sources like car sales and aftermarket services, which grew from $3.5 trillion in 2015 to an estimated $5.2 trillion by 2030, saw accelerated growth, with annual rates rising to 4.4% from 3.6% in the 2010-2015 period.
Key drivers in 2024 included on-demand mobility services and data-driven offerings. Connectivity and autonomous technologies turned vehicles into personalized platforms, enabling activities like media consumption during transit. The increasing reliance on software-driven innovations demanded systems capable of frequent updates. Shared mobility solutions, such as car-sharing and e-hailing, gained wider acceptance in 2024, offering shorter lifecycles and boosting consumer awareness of new technological advancements. This growth spurred a stronger demand for upgradeable features in both shared and private vehicles, fueling ongoing innovation in the sector.
Auto Industry: The Global Analysis
Autonomous Technology and Cybersecurity Update
In 2024, advancements in autonomous driving technology continued to shape the global automotive industry, particularly in the ride-sharing sector. While progress was notable, the adoption of autonomous vehicles remained slower than earlier predictions. However, experts anticipate that by 2030, several million AVs will be in use for ride-sharing services worldwide, reflecting steady but gradual growth in this transformative technology.
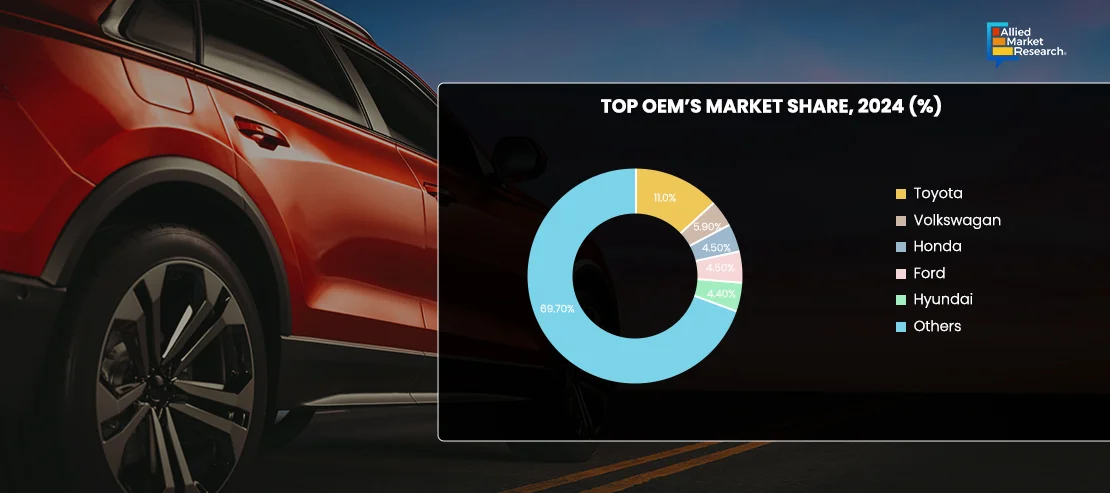
Global AV Adoption
By 2030, up to 10% of new car sales globally are projected to feature Level 3 (L3) or higher autonomy, enabling drivers to take their hands off the wheel in certain conditions. By 2040, over one-third of new cars could be L3, while fully autonomous Level 4+ (L4+) vehicles are expected to make up 14% of new sales—slightly down from earlier forecasts of 17%. In 2024, China solidified its position as the global leader in autonomous vehicle (AV) development, with 16 cities permitting driverless cars on public roads and 19 companies actively working on AV technology. By 2040, nearly half of all new car sales worldwide are expected to be L3 or higher, with China predicted to dominate, achieving 90% penetration in L3+ vehicles. Europe is projected to reach 79% market penetration, while the U.S. is expected to follow with 65%.
Waymo and GM Cruise Automation Remain Market Leaders in the U.S
In 2024, Waymo and GM's Cruise Automation remained the market leaders in autonomous vehicle technology in the U.S. Waymo operated a fleet of 800 vehicles across Phoenix, San Francisco, and Los Angeles and stood out as the only autonomous taxi operator in the country collecting fares. Earlier in the year, Google, Waymo’s parent company, invested $5 billion to support its expansion efforts, allowing the company to continue testing vehicles and plan fleet expansions in Austin and Atlanta.
Meanwhile, GM’s Cruise Automation faced challenges in 2024. Its operations were paused in October after one of its vehicles was involved in a pedestrian accident in California. Although Cruise Automation resumed operations in Phoenix and Texas later in the year, it has not yet regained permission to test its autonomous vehicles in California.
Cybersecurity Is a Top Priority:
Cybersecurity was ranked as the leading external concern for global automotive companies, in 2024. A notable cyberattack in June targeted CDK, a technology provider for the automotive industry, disrupting thousands of U.S. auto dealerships and underscoring the severe impact of such incidents on the sector.
Cyberattacks inflicted an estimated $11.8 billion in damages on the automotive industry during the first half of the year, reflecting the escalating threats. Additionally, researchers from the University of California, Irvine, and the University at Buffalo tested vulnerabilities in LiDAR and other technologies used in autonomous vehicles, further highlighting the pressing need for stronger cybersecurity measures across the industry.
Truck as a Service: The Next Step toward Zero-Emission Fleets
In 2024, more than 95% of trucks on the road globally relied on diesel or gasoline engines. The traditional truck ownership model, combining purchase or lease options with select add-on services, remained a proven system for both OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers) and customers. Large fleet owners leveraged their expertise in managing vehicle life cycles, predicting residual values at retirement, handling emergency repairs, and maintaining strong ties with aftermarket service providers.
However, the transition to zero-emission (ZE) trucks gained momentum, driven by stricter regulations, long-term total cost of ownership (TCO) benefits, and the growing demand for sustainable transportation. For instance, the EU maintained its push toward a 45% reduction in road transport CO2 emissions by 2030 compared to 2019 levels. Achieving these targets required medium- and heavy-duty ZE trucks to comprise 15-20% of global sales by 2030. This shift significantly impacted the commercial vehicle ecosystem, with nearly half of the industry's projected profits by 2030 expected to come from new opportunities that did not exist in 2024.
OEMs began preparing for this shift by exploring new business models to capture emerging profit streams. The move toward ZE trucks—and eventually autonomous vehicles—encouraged the evolution of "Truck as a Service" (TaaS) models. While service bundles and solutions were already common in 2024, these new models demanded rethinking service offerings to promote ZE adoption and improve profitability.
However, TaaS came with its challenges. In 2024, some OEMs struggled to find the right mix of services for different customer segments or mispriced their offerings, leading to market share losses. Others faced financial risks, as TaaS models often required OEMs to finance more assets, which stayed on their balance sheets. In some extreme cases, companies that failed to effectively manage these ecosystems saw investors withdraw support, resulting in financial instability or bankruptcy.
Surge in Mergers and Acquisitions Transforming the Landscape of Transport and Logistics
In the first half of 2024, the transport and logistics sector witnessed 86 mergers and acquisitions valued at $50 million or more—a 12% drop compared to the same period in 2023, marking a new industry low. Despite this decline in deal volume, total deal value rose to $42.5 billion, surpassing the previous two half-year periods. This growth was driven by an increase in the average deal size, which climbed to $494.7 million from $393.2 million in 2023. Notably, the first half of 2024 saw the announcement of 12 megadeals, each exceeding $1 billion in value. Financial investors showed renewed, albeit cautious, optimism, contributing 49% of the total deal value—up significantly from 36% in 2023.
Some of the key developments in the automotive sector are as follows:
- In December 2024, Japanese automakers Honda and Nissan initiated merger discussions to better compete with dominant global EV manufacturers. This potential consolidation aims to pool resources and expertise, enhancing their position in the evolving EV market.
- In December 2024, China's CATL announced plans to expand its battery-swapping services, introducing 1,000 new stations in 2024. This initiative seeks to offer EV owners a quicker alternative to traditional charging methods, potentially accelerating EV adoption by addressing concerns over charging times.
- In February 2024, Volkswagen Group invested $700 million in Chinese EV manufacturer XPeng, acquiring a 4.99% stake. This partnership focuses on developing mid-sized EVs for the Chinese market, leveraging XPeng's advanced technology to strengthen Volkswagen's position in the EV sector.
- In December 2024, Malaysian automaker Proton unveiled its inaugural electric vehicle, the e.MAS 7, marking a significant milestone in the company's history. Available in both basic and premium models, the e.MAS 7 is priced at 109,800 and 123,800 Malaysian ringgit, respectively. This launch aligns with Malaysia's broader strategy to increase EV and hybrid vehicle adoption, aiming for these vehicles to comprise 20% of new car sales by 2030.
- In November 2024, Volkswagen introduced the ID.Buzz, an electric van that combines retro design elements with modern electric mobility. The ID.Buzz is now available for pre-order, reflecting Volkswagen's commitment to expanding its electric vehicle lineup and appealing to consumers seeking sustainable yet stylish transportation options.
Strong Performance in the Air Freight Sector
The air cargo sector began 2024 on a strong note, recording 63.6 billion cargo ton kilometers (CTK) in Q1, a 13.2% year-on-year (YoY) rise. Growth was particularly robust in Asia & Oceania, the Middle East, and Africa, driven by booming e-commerce, demand for perishable goods, specialized freight like lithium batteries, and evolving supply chains. Disruptions in maritime shipping further bolstered air cargo demand, narrowing cost differences between sea and air freight.
Global air cargo capacity grew for the fourth consecutive quarter, with available cargo ton kilometers (ACTK) reaching 138.1 billion, fueled by a 24.3% YoY increase in belly-hold capacity as passenger services recovered. While growth slowed in Q2, May saw CTK and ACTK rise by 14.7% and 6.7%, respectively.
Air freight rates rebounded post-Lunar New Year, driven by demand from Asia & Oceania, particularly in e-commerce-driven fashion. Passenger traffic also surged, exceeding pre-pandemic levels with a 16.9% YoY increase in Q1.
Global Electric Vehicle Demand Forecast
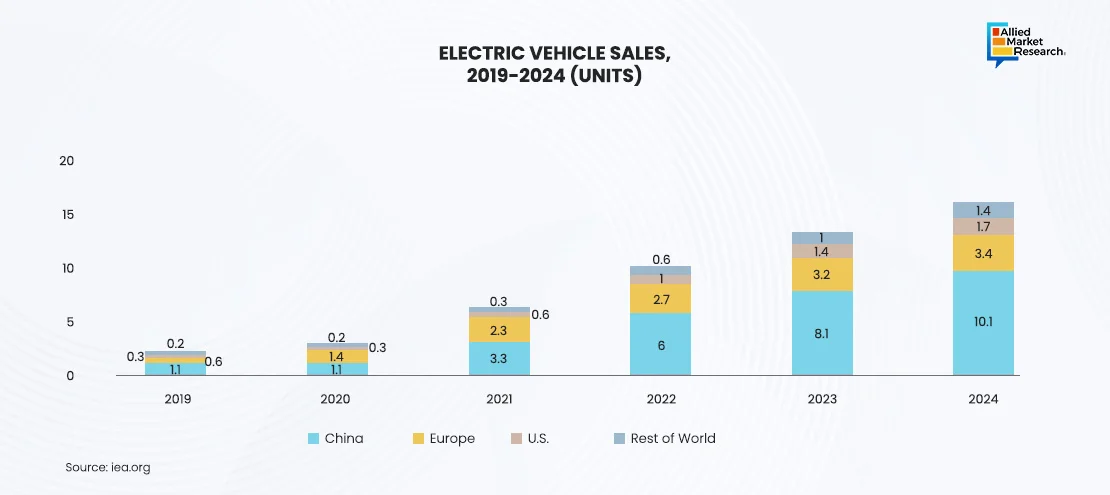
The global electric vehicle market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 29% over the next decade. EV sales, which stood at 2.5 million units in 2020, rose significantly to 16.6 million by 2024 and are projected to reach 31.1 million by 2030. EVs are expected to account for about 32% of total new car sales by the end of the decade. While global car sales took time to recover to pre-COVID-19 levels, achieving this milestone only in 2024, the rebound was gradual, primarily due to declining demand for internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. Despite the challenges of the pandemic, EV sales showed strong growth and captured a larger-than-expected share of the market during the recovery phase.
Looking ahead to 2030, China is expected to dominate the global EV market with a 49% share, followed by Europe at 27% and the U.S. at 14%. Regional EV market shares are predicted to vary significantly. China is likely to achieve a domestic EV market share of 48%, nearly double that of the U.S. at 27%. Europe is expected to reach 42%, with stronger growth in Northern and Western Europe, led by wealthier countries like the UK, Germany, France, and the Nordic nations, where infrastructure investments and incentives such as tax breaks and subsidies are driving adoption.
Verdict in 2024 and the Outlook for 2025
The automotive and transportation industry experienced notable shifts in 2024, with the market stabilizing after a post-pandemic surge. Global automotive sales grew by 1.9%, driven mainly by the rising demand for electric vehicles, especially in Europe. However, traditional automakers faced financial challenges due to increasing R&D and capital costs, highlighting the industry's focus on innovation and diversification. While EVs remained a growth driver, high costs and competition created hurdles, particularly in Europe, where production and affordability issues persisted.
The logistics sector also evolved, fueled by Asia's rapid growth and increased investment. The rise of start-ups intensified competition, with Asia expected to dominate global logistics by 2030, thanks to booming e-commerce. Looking ahead to 2025, the automotive industry is set to focus on electrified, connected, and autonomous vehicles. Shared mobility and regular upgrades are likely to shape consumer expectations, while logistics consolidation is anticipated to grow, especially in emerging markets like India and Southeast Asia.
For detailed insights on these trends, refer to our below trending reports in the automotive & transportation industry:
- https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/adas-market
- https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/automotive-regenerative-braking-system-market
- https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/golf-cart-market
- https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/automotive-scroll-e-compressor-market-A118662
- https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/mild-hybrid-vehicles-market-A123547
- https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/autonomous-logistics-vehicles-market-A136160
- https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/emergency-ambulance-vehicles-market-A135612
Reach out to our experts today for the latest insights and updates in the automotive and transportation industry!

