Table Of Contents
- Dominance of Semi-Autonomous Ships
- Comparative Analysis of Autonomous vs. Traditional Shipping Costs
- Initial Investment
- Operational Costs
- Safety and Insurance
- New Business Models to Offer Promising Avenues
- Case Study: World's First Electric Autonomous Cargo Ship by Yara International Takes to the Water
- Key Technologies Shaping the Landscape
- Navigation and Control Systems
- Sensor Technologies
- Communication Systems
- Closing Section

Lalit Janardhan Katare

Koyel Ghosh
Autonomous Shipping Revolution: Transforming the Global Trade Industry

The maritime industry is undergoing a revolutionary transformation with the advent of autonomous ships. Autonomous ships, also known as unmanned or crewless vessels, are equipped with advanced navigation and control systems that allow them to operate without direct human intervention. Autonomous ships, or Maritime Autonomous Surface Ships (MASS), represent a significant technological advancement in maritime transport. Worldwide, there were more than 1,100 autonomous ships in 2022 operated by over 53 organizations. These vessels work alongside manned ships with minimal autonomous-specific regulation.
Autonomous ships leverage advanced technologies like AI, sensors, and GPS to navigate and operate with reduced human intervention. For instance, in February 2023, The NYK Group started working on creating crewed autonomous ships which will enhance crew operations through advanced automation technology and remote shore-based support. These ships aim to improve safety and efficiency in maritime operations by integrating human capabilities, such as flexibility and the ability to process ambiguous information, with machine advantages like high information-processing capacity and consistent objectivity. This synergy allows crewed autonomous ships to handle situations beyond human processing capacity, offering support that addresses human limitations.
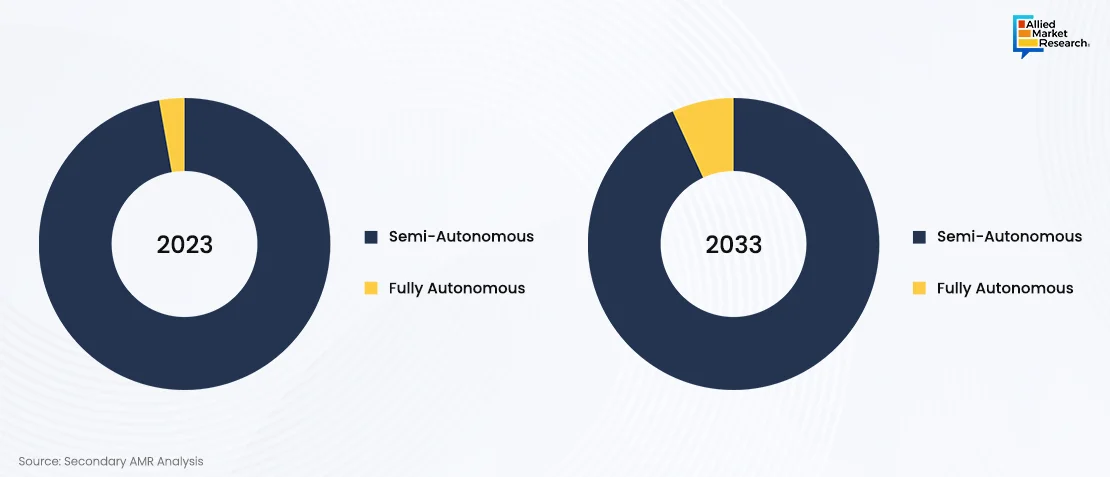
Dominance of Semi-Autonomous Ships
Semi-autonomous ships currently dominate the autonomous ships sector, capturing over 95% of market share in 2023, primarily due to several practical advantages over fully autonomous vessels. Semi-autonomous technology allows for a gradual transition from traditional crewed operations to autonomous capabilities, mitigating concerns around technological reliability and regulatory compliance. For example, L3Harris autonomous vessel team tackled the challenge of distinguishing between different types of vessels on the water, each with its own right-of-way status under COLREGS. By utilizing sensor data, the USV can identify the type of vessel it is encountering and respond appropriately. The system considers the paths and types of nearby vessels to predict their movements accurately, ensuring safe and efficient navigation.
Comparative Analysis of Autonomous vs. Traditional Shipping Costs
Initial Investment
Investing in autonomous ships requires substantial capital for advanced technology, sensors, AI systems, and retrofitting existing vessels to accommodate autonomous operations. In contrast, traditional shipping involves lower upfront costs as it relies on conventional crewed ships without the need for extensive technological retrofitting. In May 2024, Orca AI secured $23 million in fresh funding to advance autonomous shipping. The funding round was spearheaded by OCV Partners and Mizmaa Ventures, bringing Orca AI's total raised capital to nearly $40 million.
Operational Costs
Autonomous ships offer potential savings in operational costs through enhanced fuel efficiency. These vessels can optimize routes and speed, thereby reducing fuel consumption. AI-driven predictive maintenance also minimizes downtime, although maintenance costs for technology upkeep are incurred. In comparison, traditional ships face higher operational expenses due to crew wages, regular maintenance of crewed ship systems, and sometimes higher fuel costs resulting from less efficient operations.
Safety and Insurance
Autonomous ships, at the same time, mitigate risks associated with human error but raise concerns about the reliability of AI systems. Bureau Veritas has established various guidelines to ensure the safety and reliability of autonomous ships. These guidelines address key areas such as risk and technology assessment, the functionality of autonomous systems, and their reliability. Since 2022, Bureau Veritas has offered a design approval and survey scheme specifically for unmanned autonomous vessels under 500 GRT, classified under the class notation USV.
New Business Models to Offer Promising Avenues
New business models in the autonomous ships sector are set to transform maritime operations, creating significant opportunities for growth and profitability. These innovative models capitalize on advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, Internet of Things, and data analytics to optimize fleet management and operational efficiency. For instance, in February 2024, Sea Machines received a significant investment boost from Emerald Technology Ventures. This cleantech venture capital leader joined forces with Nabtesco Technology Ventures (NTV), Chevron Technology Ventures, RKKVC, Level 2 Ventures, and IMC Ventures in a $12 million funding round to expand its footprint across the world.

Also, Rolls-Royce and Sea Machines announced a strategic partnership in September 2021 to advance smart ships and autonomous ship control solutions. This collaboration is part of Rolls-Royce's PS 2030 strategy, which plans to position Rolls-Royce Power Systems as a broad solutions provider in the maritime industry. Under the agreement, Rolls-Royce Power Systems and Sea Machines will collaborate on the development and commercialization of both fully and semi-autonomous vessel control systems.
Case Study: World's First Electric Autonomous Cargo Ship by Yara International Takes to the Water
Introduction

Norway has unveiled the Yara Birkeland, the world's first all-electric and autonomous cargo vessel, marking a significant leap toward sustainable maritime transport. This modern initiative aims to revolutionize cargo shipping by replacing 40,000 diesel-powered truck journeys annually, significantly reducing NOx and CO2 emissions.
Background

The Yara Birkeland project, a collaborative effort between chemical production company Yara and maritime technology firm Kongsberg, was unveiled in 2017. This vessel marks a significant advancement in maritime technology. It is specifically designed to transport chemicals and fertilizers from Yara's production facility in Prosgrunn to nearby towns. The vessel, which measures 80 meters in length, is powered by a 6.8-mWh battery pack and has a carrying capacity of up to 3,200 tons, reaching a top speed of 15 knots.
Objectives and Implementation
The primary objective of the Yara Birkeland was to create a sustainable and efficient transport solution, reducing the environmental impact of Yara's logistical operations. The vessel made its debut with a short-crewed trip to Oslo, with plans to commence commercial operations in 2022. Over a two-year period, the ship went to testing to achieve certification as an autonomous vehicle. Kongsberg was tasked with integrating advanced sensors and autonomous navigation systems into the vessel. The pathway to full autonomy will include phases of remote operation, ensuring safety and reliability before transitioning to completely autonomous voyages.
Challenges
The development of the Yara Birkeland faced several challenges, including the integration of autonomous navigation technology and the development of a sustainable power source. While the ship is currently powered by a substantial battery pack, Yara is also exploring the use of ammonia, produced during its fertilizer manufacturing, as a zero-carbon fuel source. Despite the potential of ammonia as a diesel alternative, its production and application present technical and logistical hurdles that must be overcome.
Outcomes
The successful debut of Yara Birkeland marks a remarkable achievement in the maritime industry. By replacing traditional vessels with an electric vessel, Yara made a substantial environmental gain, aligning with global sustainability goals. The project demonstrates the viability of electric and autonomous shipping, setting a precedent for future advancements in the industry.
Key Technologies Shaping the Landscape
The autonomous ships industry encompasses a wide range of technologies. These technologies can be broadly categorized into navigation and control systems, sensor technologies, and communication systems.
Navigation and Control Systems
This system includes Autonomous Navigation Systems (ANS) that utilize artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to process data from a multitude of sensors. These sensors collect information about the ship’s environment, including its position, the presence of obstacles, and other navigational hazards. On January 17, 2022, the Japanese ferry Soleil was the world's first vessel to complete a fully autonomous voyage, including departure from and arrival at the dock. The Soleil navigated a 240 Kms journey between the ports of Shinmoji and Iyonada in seven hours.
Sensor Technologies
Sensor technologies are fundamental to the operation of autonomous ships, providing therequired data needed for navigation, obstacle detection, and environmental understanding. These technologies include radar, LiDAR, cameras, optical sensors, and sonar systems, each contributing uniquely to the ship's awareness and operational capabilities.
Communication Systems
Communication technology in autonomous ships is essential for seamless operations, encompassing ship-to-ship and ship-to-infrastructure interactions. These technologies include short-range communication systems like VHF and AIS for immediate, local exchanges, and long-range systems such as satellite communications for global connectivity. A notable development is the Maritime Autonomous Surface Ships (MASS) protocol. For example, the Rolls-Royce and Intel partnership have advanced remote operations, which enables the ships to communicate and navigate efficiently, operating the integration of robust communication frameworks in autonomous maritime technology.
Closing Section
The landscape of autonomous ships is evolving rapidly, transitioning from a futuristic concept to a pivotal innovation in maritime transportation. Looking ahead in the autonomous shipping industry, the potential for fully autonomous vessels is immense. Effective implementation, emphasizing enhanced operational efficiency and safety, is expected to bring significant advancements to maritime logistics. However, active stakeholder engagement, clear regulatory frameworks, and advanced technological integration are necessary.
Allied Market Research sees the huge potential of autonomous ships in the automotive & transportation industry. By using AMR's advanced tools and methods, companies can get valuable insights into industry trends, new technologies, and regulatory updates. This approach helps businesses in the autonomous shipping sector to tailor their services to meet the changing industry demands. AMR also helps companies find new demand and unmet needs, encouraging targeted innovation and strategic actions. Using AMR's expertise, companies can improve operations, increase efficiency, and make significant progress in maritime transportation. For further information, reach out to our expert team today

