Table Of Contents
- Evolution of Warehousing and Distribution Logistics
- Impact of E-commerce on Warehousing & Distribution
- Key Technologies Shaping the Future of Warehousing
- Streamlining Warehousing with Advanced Automation and Robotics
- The below graph depicts the process of warehousing automation
- Investment Driving the Logistics Industry Growth
- Case Study: Walmart’s Alphabot: Designing Material Handling System with Simulation
- Problem Statement: Walmart, the world’s largest retailer by revenue, was looking for an automation technology that would help complete orders faster and at a lower cost in the company’s fast-growing online grocery business. They wanted to evaluate Alert Innovation’s Goods-to-Person (GTP) concept, Alphabot, that could automate online grocery at the store level by using autonomous mobile robots capable of operating in all three dimensions within a multilevel storage structure. Alphabot robots, or “bots”, are self-driving vehicles that can gather items in ambient, chilled, and frozen temperature zones in a high-density storage system and bring them to associates that pick individual items to build a customer’s order. Alert Innovation presented Alphabot as a technology that would make the in-store fulfilment of online orders faster and more efficient.
- Proposed Solution: To model Alphabot’s behaviour and operations in a computer simulated environment, with real world complexity and variability, MOSIMTEC chose AnyLogic material handling simulation software for the project. MOSIMTEC’s and AnyLogic’s abilities to dynamically build facility layouts from data inputs, without accessing the development environment for each layout change, would help cut model development time significantly and enable faster evaluation of multiple Alphabot configurations. AnyLogic also offered unparallel ease of deployment, so that multiple Walmart engineers could run the material handling design model, without the need to install additional software or purchase developer’s licenses. AnyLogic was also selected because the Alphabot system would require extensive control algorithms. AnyLogic’s ability to integrate with Java eliminated excessive time spent translating algorithm ideas back and forth between a propriety scripting language and a format that programmers would be comfortable with.
- Outcome: The initial material handling design model helped estimate the equipment needed to meet different turn-around-time goals, supporting the business case for wider deployment of Alphabot. The simulation model quantified system performance capability under unconstrained demand conditions to benchmark its limits. The model showed that Alphabot would be able to pick 95% of online grocery orders in less than eight minutes, with an average pick time to be under five minutes.
- Conclusion
- Driven by the rapid adoption of technology and the evolving demands of consumers, the future of warehousing and distribution logistics looks promising indeed. Automation, AI, IoT, blockchain, autonomous vehicles, and AR/VR are transforming the way goods are stored, moved, and delivered, leading to greater efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction. However, businesses should properly deal with issues such as high upfront costs, system integration, workforce adaptation, and cybersecurity risks. To stay competitive, adopting these technologies is essential. Companies that invest in innovation and the future of warehousing and logistics are expected to be better equipped to thrive in the rapidly changing supply chain landscape.

Lalit Janardhan Katare

Koyel Ghosh
The Future of Warehousing: Embracing Technology for Efficient Distribution Logistics

Warehousing and distribution logistics are key to the global supply chain. They help store, move, and deliver products from manufacturers to consumers, keeping everything running smoothly. However, the rapid advancement of technology and the evolving demands of consumers have spurred significant changes in these areas. This article delves into the future of warehousing and distribution logistics, focusing on how emerging technologies are transforming operations, improving efficiency, and reshaping the entire supply chain landscape.
Evolution of Warehousing and Distribution Logistics
Traditionally, warehousing involved storing goods in large facilities until they were needed for distribution, with manual processes relying on physical labor and basic machinery. Distribution logistics focused on transporting these goods to final destinations via trucks, trains, ships, and planes. In the early 20th century, mechanization began with the introduction of forklifts, conveyors, and other equipment in warehouses. This era also witnessed the development of advanced logistics management practices, such as just-in-time (JIT) inventory and centralized distribution centers.
By the late 20th and early 21st centuries, warehousing underwent a significant transformation with the rise of automation. Automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS), robotics, and warehouse management systems (WMS) streamlined operations, reduced manual labor, and enhanced efficiency. Globalization further complicated supply chains, increasing the demand for more efficient warehousing and distribution logistics.
Impact of E-commerce on Warehousing & Distribution
Globally, the e-commerce sector has increased significantly over the past few years. The COVID-19 pandemic led to a big rise in online shopping because of lockdowns. With physical stores closed, retailers focused on improving their online presence to meet this growing demand. Moreover, with rapid urbanization, there is growing demand for ready-to-eat and frozen foods such as canned foods, frozen pizzas, salads and pre-cooked chicken from developing countries. The growing demand for groceries, daily needs products, consumer goods and others has resulted in online retailers investing heavily in the development of their warehousing and logistics capabilities.
For instance, in recent years, the warehousing and logistics market in India has experienced substantial growth, driven by increasing purchasing power and the rising popularity of online shopping, particularly in Tier 1 and Tier 2 cities. To address the expanding demand, e-commerce companies are increasingly adopting the hub-and-spoke model. This approach involves a centralized distribution hub and multiple spoke distribution centers located throughout various parts of the cities, optimizing their delivery networks.

However, the logistics industry in India is still in its infant stage; for example, logistics cost in India is significantly higher, accounting for approx. 14% of GDP, which is much higher when compared to other large economies. On the contrary, to tackle the logistics issue, the government is emphasizing especially on the development of its road and rail infrastructure. For instance, in 2022, the country inaugurated its western and eastern dedicated freight corridors to enable the free flow of goods. Similarly, the government is investing heavily in promoting long-haul goods transportation, which is capable of transporting bulk cargo via utilization of intermodal transportation.
Key Technologies Shaping the Future of Warehousing
Automation and robotics are revolutionizing warehousing, with technologies like automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and robotic arms reducing human intervention, minimizing errors, and increasing throughput. Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS) further enhance efficiency by optimizing space utilization, reducing retrieval times, and improving inventory accuracy while lowering labor costs. Collaborative robots (cobots) work alongside humans, assisting with tasks like picking and packing, making them ideal for dynamic environments.
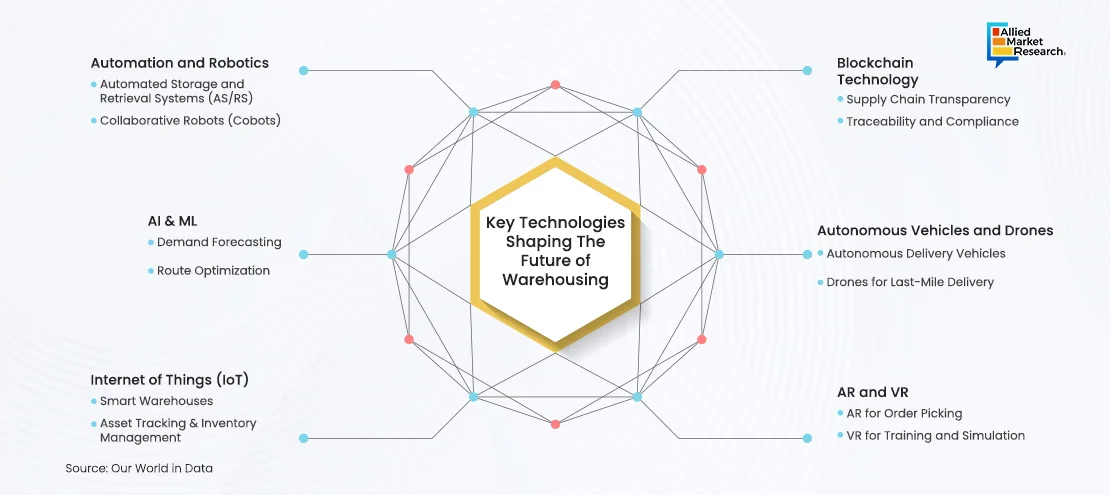
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are transforming warehousing through data-driven decision-making and predictive analytics. AI-powered demand forecasting helps optimize inventory levels, while route optimization algorithms reduce fuel consumption and delivery times by analyzing traffic patterns and weather conditions. The Internet of Things enhances visibility and asset tracking in smart warehouses, where sensors monitor conditions like temperature and equipment performance. IoT devices like RFID tags provide real-time tracking, improving inventory management and order accuracy.
Blockchain technology offers transparency and traceability in supply chains, reducing fraud and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. Autonomous vehicles and drones are expected to revolutionize distribution logistics, enabling faster, more efficient delivery. Lastly, Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality are being used for warehouse training, maintenance, and order picking, improving accuracy and productivity.
Streamlining Warehousing with Advanced Automation and Robotics
Warehouse automation is the implementation of technologies that are capable of making warehouse operations and processes more streamlined and efficient. Warehousing automation allows for automating tedious and time-consuming human tasks with the combined use of robotics, machines and software applications. Warehousing automation can handle the tasks from when the inventory arrives in a warehouse till the time it is dispatched, thus helping in increased productivity, improved safety, reduced labor cost and enhanced accuracy. An automated warehouse uses machines to store and retrieve items, move them around, sort them, and prepare them for shipping. This system helps make the most of warehouse space by using vertical storage, which is hard for people or forklifts to reach. To tackle the ever-growing demand for warehouse automation and robotics, global companies are investing heavily in the development of warehouse robotics technology.
On March 6, 2024, LG introduced new robots called the LG CLOi CarryBot. These robots can explore complex warehouse areas on their own and are designed to carry different payloads. They can also load and unload inventory faster than humans. Furthermore, the company also unveiled its plan for the development of an advanced AMR platform for autonomous navigation in robots, which will utilize modern hardware design, advanced fleet management systems, and the latest generation of Wi-Fi capabilities to further develop inventory management and optimize distribution and scheduling in modern warehouses.
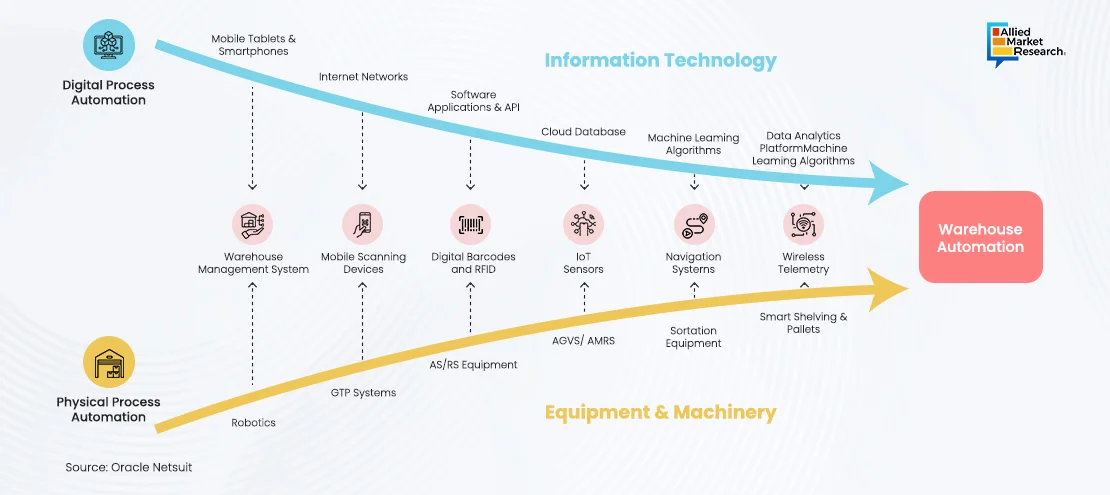
The below graph depicts the process of warehousing automation
The warehousing and distribution industry is growing because of the high demand from e-commerce. People want faster deliveries and returns, so companies are either building their own systems or using third-party services to speed things up. Since COVID, labor shortages have increased as workers moved away from cities. Wages for warehouse workers have risen, partly because many workers are older and younger people prefer other jobs. To address these issues, warehouses are focusing more on automation.
Investment Driving the Logistics Industry Growth
Manufacturers with extensive financial and technical resources are expected to maintain a competitive edge by meeting the industry's evolving demands. Leading players are prioritizing technological innovation and the adoption of advanced technologies to stay ahead. On June 19, 2024, SCLA and PPLC Superport & Industrial Co., LTD. signed an MOU focused on enhancing Cambodia's logistics sector. The partnership aims to train 300 Cambodian trainees in Singapore, who will return with expertise in business operations, technology, and global supply chains, contributing to sustainable urban growth in Cambodia through advanced logistics and multimodal transportation systems.
Similarly, on June 26, 2024, Yusen Logistics inaugurated its largest pharmaceutical warehousing facility in Gembloux, Wallonia, Belgium. This 40,000-square-meter facility incorporates cutting-edge technologies like automated packaging centres and mobile robots, designed to fully automate operations and support major pharmaceutical companies in storing and exporting vaccines and drugs globally. On April 17, 2024, YCH expanded its presence in North Asia with a new logistics hub at Fukuoka airport in Japan. This strategic investment aims to enhance regional network capabilities and support operations in China and South Korea, adhering to high quality and regulatory standards while facilitating duty-free operations.
Additionally, on February 13, 2024, DHL Group announced a $200 million investment in its life sciences and logistics segment, funding the construction of a new 13 million square foot facility in Pennsylvania to expand its North American presence. The facility will be strategically located near major pharmaceutical manufacturers and research institutes to better serve a diverse customer base. Furthermore, in July 2023, DHL Group committed approximately $550 million to Latin America, addressing growing demand across various sectors including e-commerce, healthcare, and technology. This phased investment, planned through 2028, is expected to enhance DHL's regional presence, integrate warehouse automation and robotics, and support the decarbonization of its fleet with sustainable alternatives.
Case Study: Walmart’s Alphabot: Designing Material Handling System with Simulation
Problem Statement: Walmart, the world’s largest retailer by revenue, was looking for an automation technology that would help complete orders faster and at a lower cost in the company’s fast-growing online grocery business. They wanted to evaluate Alert Innovation’s Goods-to-Person (GTP) concept, Alphabot, that could automate online grocery at the store level by using autonomous mobile robots capable of operating in all three dimensions within a multilevel storage structure. Alphabot robots, or “bots”, are self-driving vehicles that can gather items in ambient, chilled, and frozen temperature zones in a high-density storage system and bring them to associates that pick individual items to build a customer’s order. Alert Innovation presented Alphabot as a technology that would make the in-store fulfilment of online orders faster and more efficient.
The retailer wanted to evaluate the feasibility of the Alphabot concept, and its suitability for Walmart, prior to making a financial commitment toward product development. Alert Innovation had already made some static spreadsheet calculations for the project, however, both Alert Innovation and Walmart agreed that the spreadsheets could not be relied upon due to system complexity and variability in demand and execution. Before making a financial commitment and deploying the system in a Walmart store, it was decided to task MOSIMTEC, a simulation consulting firm, with designing a material handling simulation model for an independent technology feasibility assessment. The goal of this initial modelling assessment was to:
- Understand the throughput and turnaround time capabilities of the Alphabot® system during peak customer demand periods and assess service levels.
- Understand any potential performance weaknesses of the Alphabot® system with realistic demand data and variability.
- Identify the best configuration of the racking structure, automated bots, and each-picking workstations required for a variety of store profiles.
- Compare the capital expenditure requirements predicted by the model vs. the business case spreadsheets.
- Use model throughput and turn-around-time results to compare the proposed performance of Alert Innovation’s Alphabot with other industry leading Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (ASRS) and Goods-to-Person (GTP) technologies.
Proposed Solution: To model Alphabot’s behaviour and operations in a computer simulated environment, with real world complexity and variability, MOSIMTEC chose AnyLogic material handling simulation software for the project. MOSIMTEC’s and AnyLogic’s abilities to dynamically build facility layouts from data inputs, without accessing the development environment for each layout change, would help cut model development time significantly and enable faster evaluation of multiple Alphabot configurations. AnyLogic also offered unparallel ease of deployment, so that multiple Walmart engineers could run the material handling design model, without the need to install additional software or purchase developer’s licenses. AnyLogic was also selected because the Alphabot system would require extensive control algorithms. AnyLogic’s ability to integrate with Java eliminated excessive time spent translating algorithm ideas back and forth between a propriety scripting language and a format that programmers would be comfortable with.
Walmart’s initial goal was to make a go/no-go decision about the Alphabot project launch. In seven weeks, MOSITMEC learned the system, designed control algorithms for bot decisions, built a material handling simulation, analyzed results, and presented findings to Walmart leadership.
In the final delivered model, Walmart managers could specify different inputs, like number of bots, their length, width, acceleration, and speed in different areas. Also, physical racking configurations, including number of aisles, levels, space between levels, and number of workstation tiers, along with other physical components of this system, were all configurable via model input parameters. Control logic parameters, covering selecting from various work assignment approaches or setting various thresholds, were exposed too and available for Walmart to run their own analysis.
Model input and output statistics were integrated in an Excel front-end so the users could easily configure and run the model. At this concept evaluation stage, MOSIMTEC incorporated basic 3D model animation that scaled based on the layout defined by the user within Excel. The output results in Excel included a summary report with key metrics, log files, scenario comparisons, charts, and graphs.
After completing the independent analysis of system capabilities, MOSIMTEC transitioned the AnyLogic material handling design model to Alert Innovation for long-term use in fine-tuning software control algorithms for eventual production deployment. Based on the outcome of Phase 1, Walmart proceeded with the Alphabot product development. Alert Innovation engineers used the Phase 1 model as the foundation for Phase 2 by increasing the level of detail and testing various control algorithms to simulate different system design alternatives. The enhancements made to the model took in:
- More bot-specific movement logic, including path planning, reservations, collision avoidance, and movement profiles, utilizing AnyLogic’s agent-based modeling and Java capabilities.
- Logic for separate temperature zones for shelf-stable, refrigerated, and frozen items in the storage system.
- Inventory tracking functionality within the racks to track every item in the system.
- Bot sequencing logic to help simulate robots sorting items on the desk.
With the updated material handling simulation model, engineers were able to validate the original system design assumptions and provide feedback to Alphabot product development teams.
Outcome: The initial material handling design model helped estimate the equipment needed to meet different turn-around-time goals, supporting the business case for wider deployment of Alphabot. The simulation model quantified system performance capability under unconstrained demand conditions to benchmark its limits. The model showed that Alphabot would be able to pick 95% of online grocery orders in less than eight minutes, with an average pick time to be under five minutes.
The initial model was later updated and expanded to understand the impact of various detailed design alternatives. The model helped Alert Innovation identify the design alternatives with the highest ROI and optimize system sizing for future deployments. Walmart and Alert Innovation launched a proof-of-concept pilot of Alphabot at a Walmart super center in Salem, New Hampshire in March 2019.
Conclusion
Driven by the rapid adoption of technology and the evolving demands of consumers, the future of warehousing and distribution logistics looks promising indeed. Automation, AI, IoT, blockchain, autonomous vehicles, and AR/VR are transforming the way goods are stored, moved, and delivered, leading to greater efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction. However, businesses should properly deal with issues such as high upfront costs, system integration, workforce adaptation, and cybersecurity risks. To stay competitive, adopting these technologies is essential. Companies that invest in innovation and the future of warehousing and logistics are expected to be better equipped to thrive in the rapidly changing supply chain landscape.
Allied Market Research explores warehousing and logistics industry, offering vendors detailed insights into the evolving field. Our curated reports cover technological advancements, market trends, and government initiatives, helping businesses integrate warehousing and transportation into their operations. To get more insights into the automotive and transportation domain, contact our specialists today!

