Table Of Contents
- The economic landscape of the consumer goods industry in Q4 2024
- Funding statistics of leading global CG companies in Q4 2024
- Regional dynamics driving the growth of the industry in Q4 2024The consumer goods industry observed prominent growth across multiple regions in Q4 2024. According to the above-mentioned graph, the U.S. consumer goods industry showcased consistent growth in this quarter, with a projected market output of $1,680 billion. The increased employment in the sector generated a revenue of 3.76 million, highlighting its contribution to bringing economic stability. Technological advancements in electrical equipment and electronics drove growth in non-durable goods, particularly in smart devices and renewable energy products. Additionally, the North American furniture market, valued at $49.09 billion in Q4 2024, benefited from a recovering housing market and increasing consumer interest in home decor.
- Supply chain developments impacting the consumer goods industry
- Key challenges and solutions in the landscape of consumer goods in Q4 2024In the fourth quarter of 2024, the global consumer goods industry faced significant challenges, particularly in the APAC region due to labor shortages and supply chain disruptions. Companies like Unilever and Nestle S.A. addressed these challenges by investing in near-shoring strategies and enhancing partnerships with local suppliers. They also utilized digital technologies such as AI for better demand forecasting. In the U.S., rising inflation pressured operational costs, prompting brands like Coca-Cola to implement cost-cutting measures and diversify product offerings. Meanwhile, European firms focused on sustainability amid strict regulations, while Latin American companies improved employee relations to minimize labor strikes. These market-specific challenges promote the need for adaptive strategies in global supply chain management, emphasizing technology, cost-efficiency, sustainability, and employee relations to reduce risks and sustain growth.
- The bottom line

Roshan Deshmukh

Koyel Ghosh
Consumer Goods Industry: Key Insights and Performance Trends in Q4 2024

In the fourth quarter of 2024, the consumer goods industry showed robust performance, bouncing back from several economic challenges. Companies adapted to changing market conditions and consumer preferences by implementing new strategies to tackle issues such as supply chain problems and rising costs. The industry experienced a steady recovery as businesses adjusted to ongoing economic challenges. Many companies adopted digital technologies and sustainable practices to cater to environmentally conscious consumers. Moreover, there was a notable rise in direct-to-consumer sales and personalized marketing efforts, reflecting changing shopping habits. In Q4 2024, the consumer goods sector demonstrated resilience, emphasizing innovation and responsiveness to consumer demands.
This newsletter attempts to highlight key trends and significant changes in the consumer goods sector during the fourth quarter of 2024. It examines sales across different sectors, analyzes how global and regional companies adapted to new challenges. The study also identifies solutions for overcoming them and maintaining a competitive edge.
The economic landscape of the consumer goods industry in Q4 2024
As mentioned in the above-provided graph, the consumer goods industry experienced a mixed economic environment in Q4 2024, exhibiting a real GDP growth of 1.7% across advanced economies. Due to resilient consumer spending, the U.S. economy surpassed expectations, achieving a GDP growth of 2.6%. There was a rise in demand for essential goods and premium products, which created growth opportunities for companies in the sector. However, high interest rates made it difficult for consumers to spend on non-essential items. In 2025, sluggish growth is expected, raising concerns about potential impacts on consumer behavior and long-term market trends.
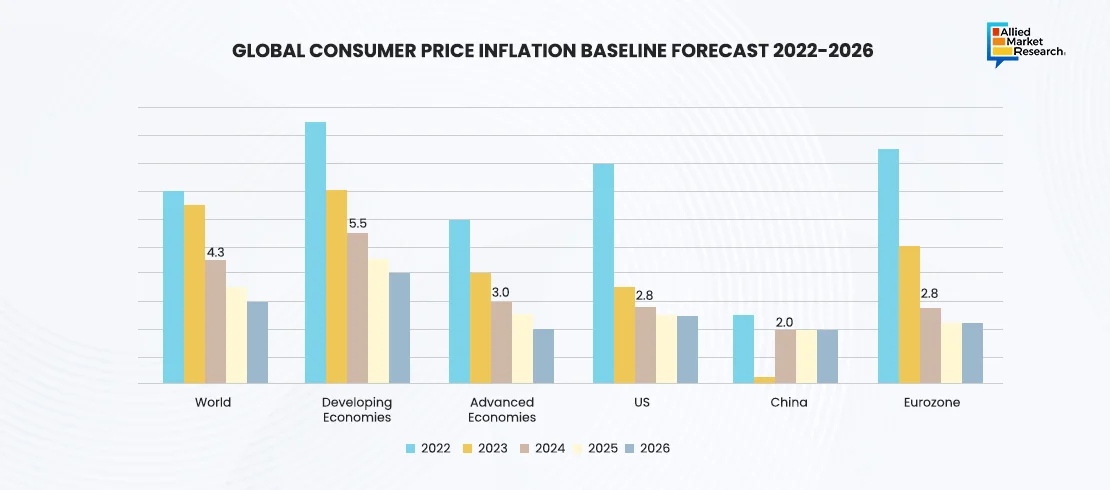
On the other hand, the European region slowly recovered from the downturn in 2023 with some persisting challenges as well. Germany, the region’s largest economy, witnessed no growth in 2024, hindering the demand for consumer goods. This indicates that there was economic stagnation, caused by weak exports and declined investments, leading to reduced market potential. In Japan, GDP growth for 2024 was modest at 1.2%. However, rising wages and tax reforms helped boost consumer purchasing power, which is expected to lead to robust growth in the consumer goods domain in 2025. The quarter emphasized the need for customized strategies to tackle region-specific challenges.
Funding statistics of leading global CG companies in Q4 2024
In the fourth quarter of 2024, the global consumer goods industry saw significant funding activities, especially in the beauty and fashion sectors. Here are some key highlights:
In November 2024, Our Legacy, a Swedish fashion brand announced an investment of up to $25 million from LVMH Luxury Ventures, indicating strong interest from investors in established fashion labels.
Also in November 2024, Southern California-based Vuori announced an impressive $825 million investment led by General Atlantic and Stripes, boosting its valuation to $5.5 billion. This investment, structured as a secondary tender offer, highlights Vuori’s rapid growth in the athleisure market.
Similarly, in October 2024, UK biotech skincare brand Reome secured $1.4 million in seed funding from Rianta Capital, showcasing investor confidence in innovative skincare solutions.
In parallel, In October 2024, the luxury womenswear brand With Nothing Underneath secured £2.5m in investment from Pembroke VCT and JamJar Investments to support international growth and expand its UK retail presence. This investment indicates a positive outlook for niche fashion brands.
Moreover, in October 2024, luxury fashion platform Cult Mia raised an additional $2 million, bringing its total funding to $5 million. This round included existing investors like Fuel Ventures, Morgan Stanley, and H&M Group Ventures, indicating significant support for its global growth and emphasizing the role of digital platforms in the luxury market.
Regional dynamics driving the growth of the industry in Q4 2024
The consumer goods industry observed prominent growth across multiple regions in Q4 2024. According to the above-mentioned graph, the U.S. consumer goods industry showcased consistent growth in this quarter, with a projected market output of $1,680 billion. The increased employment in the sector generated a revenue of 3.76 million, highlighting its contribution to bringing economic stability. Technological advancements in electrical equipment and electronics drove growth in non-durable goods, particularly in smart devices and renewable energy products. Additionally, the North American furniture market, valued at $49.09 billion in Q4 2024, benefited from a recovering housing market and increasing consumer interest in home decor.
On the other hand, European consumer goods markets faced challenges due to a sluggish economic recovery, particularly in Germany, where weak exports and low investment are the main factors that hindered regional growth. However, certain segments, such as leather goods benefited from strong demand for luxury items, reflecting evolving consumer preferences. The trend of premiumization supported resilience in other countries, especially in France and Italy, where high-quality and artisanal products performed well.
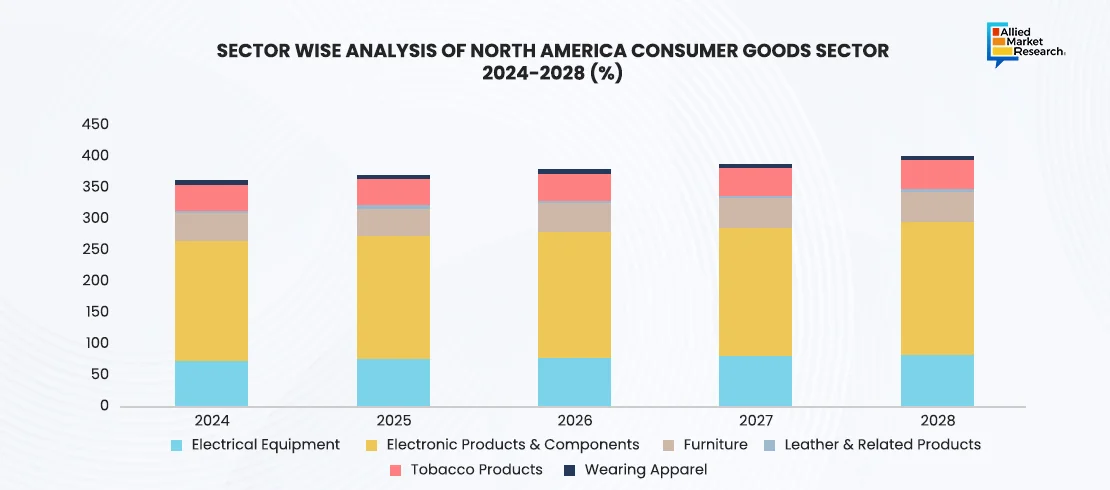
The Asia-Pacific region, driven by countries such as Japan and India, displayed contrasting dynamics. In Japan, gradual improvements in consumer purchasing power, supported by tax reforms and rising wages, boosted moderate growth in the electronics and durable goods sector. In contrast, the Indian market showed strong momentum in consumer durables, driven by urbanization and growing disposable incomes. The focus on affordability and innovation acted as prime drivers for the growth.
The Middle East and Africa witnessed steady growth in consumer goods, driven by urbanization and rising demand for durable products. Moreover, innovations in electrical equipment, particularly energy-efficient solutions gained huge popularity, aligning with the region's sustainable development goals. These developments showcase the adoption of environmentally friendly practices across the region.
In addition, Latin America experienced a slow recovery in consumer goods demand, constrained by macroeconomic challenges. However, durable goods markets, including furniture and electronics, benefited from localized manufacturing, and the rising middle-class consumption, especially in Brazil created growth opportunities for the region in Q4 2024.
Supply chain developments impacting the consumer goods industry
The consumer goods domain witnessed significant supply chain developments in Q4 2024. Persistent global uncertainties, such as geopolitical tensions and labor shortages, disrupted supply chain operations and resulted in increased storage costs due to excess inventory. Many companies incorporated digital technologies like AI and IoT to enhance resilience and efficiency. Additionally, sustainability initiatives gained traction as firms aimed to reduce emissions and ensure ethical sourcing. In the FMCG sector, companies in India planned to implement price increases of 2-4% to counter rising input costs, aligning with fluctuating consumer demand and market competition.
Key challenges and solutions in the landscape of consumer goods in Q4 2024
In the fourth quarter of 2024, the global consumer goods industry faced significant challenges, particularly in the APAC region due to labor shortages and supply chain disruptions. Companies like Unilever and Nestle S.A. addressed these challenges by investing in near-shoring strategies and enhancing partnerships with local suppliers. They also utilized digital technologies such as AI for better demand forecasting. In the U.S., rising inflation pressured operational costs, prompting brands like Coca-Cola to implement cost-cutting measures and diversify product offerings. Meanwhile, European firms focused on sustainability amid strict regulations, while Latin American companies improved employee relations to minimize labor strikes. These market-specific challenges promote the need for adaptive strategies in global supply chain management, emphasizing technology, cost-efficiency, sustainability, and employee relations to reduce risks and sustain growth.
The bottom line
In conclusion, the fourth quarter of 2024 was a dynamic period for the consumer goods industry, influenced by significant investments, strategic expansions, and notable growth rates. The report emphasizes key trends and transitions within the domain, examining sales across various categories and how global and regional players adapted to emerging challenges. It also evaluates the specific hurdles faced by certain sectors and presents effective solutions to overcome these issues, thereby enabling companies to gain competitive advantage in a rapidly changing market landscape.
To gain more insights into the evolving landscape of consumer goods, feel free to reach out to our industry analysts today!