Table Of Contents
- Emerging Innovations Shaping the Future of EV Charging Software
- Technological challenges
- Cybersecurity risks
- Regulatory and policy constraints
- Infrastructure and investment challenges
- Consumer adoption and awareness
- Technological Breakthroughs Shaping the Landscape
- Smart charging and load management
- Integration with renewable energy sources
- Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology
- AI and ML
- Blockchain Technology
- Case Study: Successful Migration of 3,500 EV Charging Points for Eneco eMobility
- Strategic Recommendations
- Closing Lines

Onkar Sumant

Koyel Ghosh
Empowering Electric Mobility: Driving the Future with EV Charging Software Innovation

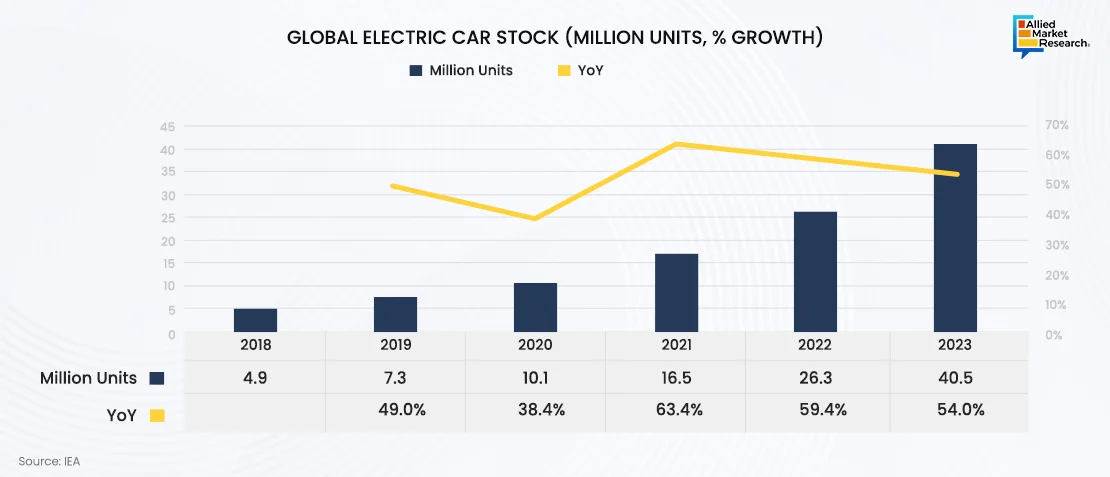
The global EV Charging Software Market is set for robust expansion, fueled by the rapid rise in EV adoption. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the number of electric cars on the road reached 40.5 million in 2023, a 53% increase over the previous year. This surge in EV ownership is creating a substantial demand for advanced charging infrastructure and, consequently, sophisticated software solutions to manage this infrastructure efficiently.
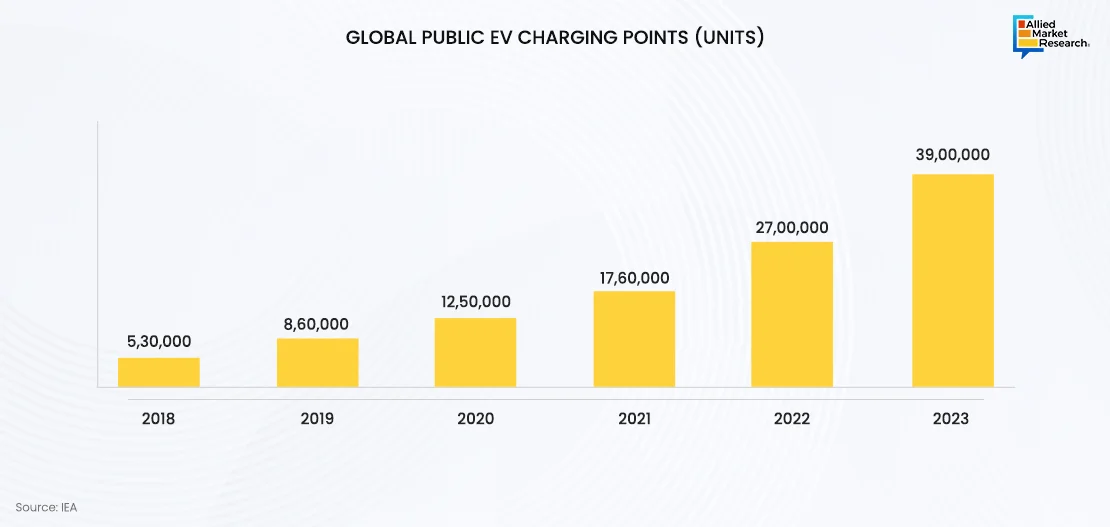
Government initiatives play a pivotal role in driving EV Charging Software growth. For instance, in March 2023, the European Union announced plans to install 3.5 million public charging points by 2030, under its “Fit for 55” package aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Such regulatory measures encourage the development and deployment of comprehensive EV charging software solutions that can support large-scale charging networks.
Emerging Innovations Shaping the Future of EV Charging Software
Integration with renewable energy sources: The integration of charging solutions with renewable energy sources helps in minimizing the carbon footprint of EV charging. For example, Tesla’s Solar Charging initiative, announced in March 2023, combines solar power with EV charging, offering a sustainable and cost-effective solution for EV owners.
Advancements in smart charging technology: Smart charging technology, which enables dynamic adjustment of charging based on real-time data, is gaining traction. This technology not only optimizes energy consumption but also enhances grid stability. In January 2024, Sainsbury's launched Smart Charge, an ultra-rapid EV charging service in the UK, utilizing Kempower technology. With over 750 bays planned across more than 100 locations by the end of 2024, Smart Charge aims to address common EV driver frustrations such as broken chargers and insufficient bays, while enhancing convenience by allowing drivers to shop during charging. This initiative supports Sainsbury's commitment to reducing carbon emissions and improving EV infrastructure reliability and accessibility.
Interoperability and standardization efforts: Ensuring interoperability between different charging networks and software platforms is essential for EV Charging Software growth. In January 2024, the US Joint Office of Energy and Transportation partnered with Linux Foundation Energy (LF Energy) to develop an open-source reference implementation for EV charging infrastructure using the EVerest project. This collaboration aims to solve compatibility and reliability issues in EV charging by standardizing communications protocols, enhancing interoperability, and avoiding vendor lock-in, with a focus on maintaining long-term hardware support.
Expansion of public charging infrastructure: Governments and private companies are increasingly investing in expanding public charging infrastructure. In January 2024, the US administration announced $623 million in funding for electric vehicle charging infrastructure, targeting disadvantaged communities and freight trucks across 22 states and Puerto Rico. This investment aims to address range anxiety and enhance EV adoption by establishing charging stations in underserved areas, including tribal lands, poorer urban regions, and rural stretches. The funds will support various projects, including high-capacity chargers for battery-electric trucks, as well as specific use cases like charging stations at libraries, apartments, and electric scooters and bikes.
Supportive government policies, technological advancements, and strategic investments are collectively shaping the future of the EV Charging Software industry, establishing it as a key element within the broader EV ecosystem.
Addressing Constraints in EV Charging Software: Despite the promising growth prospects, the EV charging software industry faces several challenges and constraints that could hinder its development. These challenges range from technological issues to regulatory hurdles and market dynamics that need to be addressed to ensure sustained growth.
Technological challenges
One of the primary technological challenges is interoperability. With a myriad of EV models and charging stations from different manufacturers, ensuring seamless communication and operation across various platforms remains a significant hurdle. For instance, many EV owners face difficulties traveling long distances due to the lack of standardized charging protocols and incompatible software systems. This challenge was highlighted in a report by the International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT) in February 2023, which called for greater efforts toward standardization to enhance user experience and efficiency.
Cybersecurity risks
As EV charging infrastructure becomes more integrated with smart grids and IoT technologies, the risk of cyberattacks increases. Hackers can potentially disrupt charging operations, steal personal data, or manipulate grid interactions. A notable incident occurred at EV charging stations in 2022, with a Russian station and three UK stations targeted, displaying prank messages. Shell subsequently patched a vulnerability that could have exposed millions of charging logs across its network. This incident highlighted the vulnerabilities in the current systems and the urgent need for enhanced security protocols.
Regulatory and policy constraints
Regulatory and policy environments can also pose significant constraints. While many governments are actively promoting EV adoption and charging infrastructure development, inconsistent policies and regulatory frameworks across different regions often hold the potential to create market fragmentation and operational inefficiencies. For example, differing regulations on charging station installations and energy tariffs between the US and the European Union can complicate the operations of companies operating in both markets.
Infrastructure and investment challenges
The expansion of EV charging infrastructure requires substantial investment, and financial constraints can slow down progress. Many regions, especially in developing countries, lack the necessary funds to build comprehensive charging networks. This disparity can limit the widespread adoption of EV charging software solutions. In March 2024, a report by BloombergNEF highlighted that while global investment in EV charging infrastructure reached record levels, significant gaps remain, particularly in less developed economies.
Consumer adoption and awareness
Consumer adoption and awareness also present another layer of challenge. Many potential EV owners are still skeptical about the reliability and convenience of EV charging solutions. This skepticism is often fueled by concerns over charging times, the availability of charging stations, and the overall cost of EV ownership. A survey conducted by Deloitte in July 2023 revealed that potential EV buyers cited a lack of charging infrastructure as a major barrier to purchase, indicating a need for increased consumer education and awareness efforts.
Addressing these challenges requires a coordinated approach involving technological innovation, regulatory alignment, increased investment, and consumer engagement to unlock the full potential of EV charging software.

Technological Breakthroughs Shaping the Landscape
The field of EV charging software is experiencing a wave of technological advancements that are driving its growth and enhancing the efficiency, reliability, and user-friendliness of charging solutions. These innovations play an important role in addressing the challenges associated with EV charging, thus paving the way for a more sustainable and robust EV infrastructure.
Smart charging and load management
One of the most significant advancements is the development of smart charging and load management systems. These technologies enable the dynamic adjustment of charging rates based on real-time data, such as electricity demand, grid capacity, and energy prices. For instance, Mitsubishi Motors, MC Retail Energy, Kaluza, and Mitsubishi Corporation launched a proof of concept (PoC) for smart EV charging in Japan in February 2024. The PoC aims to optimize charging times using a smartphone app connected to Kaluza's platform, reducing charging costs and creating a more appealing charging environment. This initiative builds on previous collaborations and initiatives by the companies to develop smart-charging services and reduce carbon emissions.

Integration with renewable energy sources
At the same time, the integration of EV charging infrastructure with renewable energy sources not only reduces the carbon footprint of EV charging but also promotes the use of clean energy. In April 2024, Maharashtra State Electricity Distribution Co. Ltd. (MSEDCL) EV charging stations in Pune, India will be powered by solar energy. A solar project will be set up in the area to generate green energy for charging. This initiative aims to supply power to all 18 charging stations in Pune City using solar power plants, promoting sustainable energy use in EV charging infrastructure.
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology
Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology is gaining momentum as a revolutionary advancement in EV charging software. V2G enables bidirectional energy flow between EVs and the grid, allowing EVs to store energy and feed it back into the grid during peak demand periods. In August 2022, Revel, Fermata Energy, and NineDot Energy launched New York's first Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) system at Revel's Red Hook warehouse. The bidirectional charging system allows EVs to charge and send stored energy back to Con Edison’s grid during peak demand, enhancing grid resilience. The project aims to manage energy use, support grid resilience, and decarbonization efforts, with plans to expand to more EV models.
AI and ML
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are playing a transformative role in enhancing the capabilities of EV charging software. These technologies are used to predict energy consumption patterns, optimize charging schedules, and provide personalized user experiences. In April 2024, Siemens introduced its AI-driven charging management platform, which takes recourse to ML algorithms to analyze vast amounts of data from charging sessions, weather conditions, and traffic patterns. This platform helps in predicting optimal charging times and locations, thereby improving the overall efficiency and convenience of EV charging.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is emerging as a promising solution for ensuring the security and transparency of EV charging transactions. It can facilitate peer-to-peer energy trading, secure payment systems, and transparent tracking of energy sources. In February 2024, Technology startup PowerPod is developing a blockchain-based decentralized EV charging network using peaq's community-run blockchain as its foundation. The initiative aims to address the lack of EV charging infrastructure by utilizing private chargers from existing EV owners, who will be rewarded for sharing their chargers. PowerPod is also creating a platform, app, and various hardware devices to facilitate these interactions and manage transactions and data via blockchain.
These technological advancements are essential in addressing the current limitations of the EV charging infrastructure and in promoting the widespread adoption of EVs. By leveraging smart charging, renewable energy integration, V2G, AI, and blockchain, the EV Charging Software industry is set to achieve greater efficiency, sustainability, and user satisfaction.
Case Study: Successful Migration of 3,500 EV Charging Points for Eneco eMobility
Overview
In 2021, Eneco eMobility (Eneco), a leading Charge Point Operator (CPO) and E-Mobility Service Provider (EMSP) in the Netherlands, Belgium, and Germany, faced the challenge of upgrading and consolidating the software of 3,500 charge points. The need arose when their previous service provider decided to phase out its legacy platform. To enhance asset management, meet regulatory requirements, and ensure future scalability, Eneco chose to migrate to the GreenFlux platform.
Challenges
The migration project posed several significant challenges:
Diverse communication protocols: Eneco’s charge points included both G2 chargers using OCPP 1.5 SOAP and G3 chargers using OCPP 1.6 JSON. Additionally, there were customizations in the protocols from the early days of EV charging, complicating the integration process.
Secure communication: Ensuring secure data exchange between Eneco’s charge station SIM card providers and the GreenFlux backend platform was crucial to maintaining the integrity and security of the communication paths.
Project management: Coordinating the migration involved six different parties, necessitating efficient project management to meet deadlines and minimize disruptions.
Solutions
GreenFlux addressed these challenges through a series of strategic and technical measures:
Protocol accommodation: The GreenFlux platform is hardware-agnostic and capable of handling various OCPP versions, including 1.5 SOAP, 1.5 JSON, and 1.6 JSON. The team conducted extensive integration tests, customized communication paths, and established new channels to optimize communication across different charge point configurations.
Enhanced security: GreenFlux prioritized security by setting up private APN and VPN data connections with Eneco’s SIM card providers, ensuring secure data exchange without the need for physical SIM card changes. The platform's ISO27001 and 27002 certifications underscored its commitment to security.
Phased migration: To avoid a complete shutdown of charge points and inconvenience to EV drivers, GreenFlux executed the migration in phases. This approach ensured continuous service and minimized disruptions.
Efficient coordination: With over a decade of experience, GreenFlux effectively managed coordination among the six parties involved, overseeing the technical and logistical aspects from preparation to execution.
Results
The successful migration yielded several key benefits for Eneco:
Operational efficiency: The new platform streamlined the management of the entire network of charge points, enhancing overall efficiency.
Secure data communication: The use of private APN and VPN connections ensured robust data security.
Simpler asset management: Consolidating all charge points under the GreenFlux platform simplified asset management and monitoring.
Regulatory compliance: Eneco met the EU’s price transparency norms, allowing real-time data sharing and ad hoc payments for EV drivers.
Conclusion
The successful migration of 3,500 charge points demonstrated GreenFlux’s capability to handle large-scale, complex projects. The integration not only provided immediate operational benefits but also positioned Eneco for future growth and compliance with regulatory standards. This case exemplifies GreenFlux’s expertise in delivering customized solutions and efficient project management in the EV charging software sector.
Strategic Recommendations
- To succeed in the fast-changing EV charging software sector, stakeholders need strategic approaches that use new technology and solve current problems effectively.
- Invest in interoperability: Companies should focus on developing software solutions that are compatible with various charging station models and EV types. This will enhance user convenience and promote the growth of the landscape.
- Enhance cybersecurity: Implement robust cybersecurity measures to protect against potential threats. Regularly update software to address vulnerabilities and ensure data privacy.
- Leverage renewable integration: Integrate renewable energy sources into charging infrastructure to reduce carbon footprints and align with global sustainability goals. Promote projects that combine solar, wind, and EV charging solutions.
- Adopt AI and ML: Utilize AI and ML to optimize charging schedules, predict maintenance needs, and improve overall system efficiency. These technologies can provide personalized experiences and enhance operational efficiency.
- Promote consumer awareness: Educate potential EV owners about the benefits of advanced charging solutions. Highlight the convenience, cost savings, and environmental impact of using state-of-the-art charging software.
Closing Lines
The demand for EV charging software is expected to grow significantly, driven by technological innovations and supportive regulatory environments. By focusing on interoperability, cybersecurity, renewable integration, AI, and consumer education, stakeholders can capitalize on emerging opportunities and overcome existing challenges. Embracing these strategic recommendations ensures sustainable growth and a robust, user-friendly charging infrastructure.
Allied Market Research explores the expansive EV charging software industry, offering comprehensive analyses of technological advancements, market dynamics, and regulatory landscapes shaping the field. Our comprehensive reports offer stakeholders valuable insights on how EV charging software boosts efficiency, encourages electric vehicle adoption, and advances environmental sustainability. These insights help businesses seize opportunities, innovate, and promote eco-friendly practices in the EV charging industry.
Contact our experts today for a detailed analysis of what drives growth and investment opportunities in the EV charging software!

