Table Of Contents

Yerukola Eswara Prasad

Koyel Ghosh
Understanding the Demand Prospects of Water Treatment

Process water is broadly defined as water used in industry, manufacturing processes, power generation, municipal, and similar applications. The specific process water requirements of various industries and plants vary significantly. Therefore, it is manufactured using a range of process water technologies tailored to the feed water characteristics and the desired final water quality and volume. Process water treatment is mainly used in pharmaceutical & cosmetics, food & beverage, and chemical & petrochemical industries. It is found in factories where products are manufactured. Process water is used as rinse water for cleaning products or installations, cooling water for cooling installations, and as product water for drinks and food. Moreover, biocides and disinfectants are intensively used in cooling towers. According to AMR, the global process water treatment market is expected to register a CAGR of 7.0% from 2020 to 2030.
To put it simply, process water is water that is used in a variety of manufacturing processes, including boiler make-up water, cooling tower make-up water, coating and plating, rinsing and spraying, washing and many others. Municipal or ground water supplies often contain dissolved minerals which can cause a multitude of problems that can affect product quality and manufacturing costs. For processing the water, various equipment and chemicals are used, depending on the application served. Water needs to be potable in nature when used as a drinking water source in the municipal sector and related activities in the industrial sector. On the other hand, municipal wastewater, like that from the industrial sector, needs to be treated to remove sewage and other particulates before being released into water bodies.
Rapid urbanization has presently increased the need for municipal water treatment to cater to the growing demand for drinking water and sanitation services. Water is essential for various end-user industries, including chemical, pharmaceutical, food & beverages, and metal processing, where it is integral to production, material processing, and cooling applications. The rising global population, coupled with economic development, is driving increased demand for municipal and industrial water treatment. Additionally, end-user industries such as oil & gas, food & beverages, paper & pulp, personal care & chemicals, and metal processing have witnessed substantial investments due to economic growth in both developed and developing countries. For example, China held a 40% share of global textile exports in 2019, largely due to ongoing private sector investments, particularly in the textile industry. As investment and industrial activities are expanding now, the demand for effective water treatment solutions is also growing, addressing challenges like scaling, corrosion, wastewater disposal, and microbiological control.
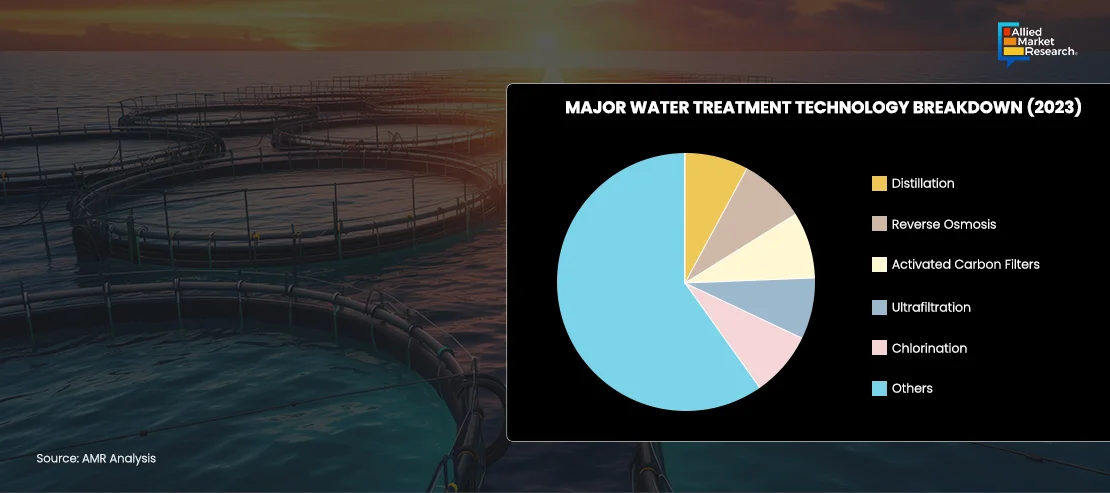
As shown in the above figure, distillation and reverse osmosis are the most common methods of water filtration process used globally. Distilled water is used in cosmetics manufacturing, laboratory experiments, canned goods production, and for various automotive purposes. Distilled water is also used to sterilize medical equipment and surfaces. The distillation systems market is gaining traction due to encouragement by numerous governments and stringent laws imposed on emission of wastewater. The government has imposed and cleared the regulations for purification of wastewater, which is augmenting the demand for distillation systems. For instance, IF (a U.K. based company) in May 2024 launched a new distillation system-based water purification technology. According to the company, this product uses a miniature vapor compression distillation without consumable parts or added chemicals. This approach highlights the company's innovative strategies and positions it to gain a strong competitive edge in the market.
Increasing investments for establishing water treatment facilities
An increase in investments in wastewater treatment facilities refers to the growth in allocation of financial resources toward the development, expansion, or improvement of infrastructure and technologies used for treating and managing wastewater. This increase in investments is driven by several factors, including growth in environmental concerns, stricter regulations, population growth, urbanization, and recognition of the importance of water resource management. Investments in wastewater treatment facilities result in enhanced water quality by removing pollutants, contaminants, and pathogens from wastewater before it is discharged into the environment. This helps protect water bodies, ecosystems, and public health, as well as ensures the availability of safe water for various purposes, including drinking, agriculture, and industry. Furthermore, properly treated wastewater minimizes the adverse impact on the environment and reduces pollution of surface water, groundwater, and soil. Investments in wastewater treatment facilities contribute to the preservation of aquatic ecosystems, biodiversity, and overall ecological balance by removing pollutants and harmful substances.
Investments in wastewater treatment facilities drive research, development, and innovation in water treatment technologies. This leads to the discovery and adoption of more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly treatment processes and systems, improving overall water management practices. In recent years, the growth in industrialization and urbanization has resulted in high wastewater discharge and poor wastewater management has caused serious issues for the environment. Many treatment plants are currently grappling with stricter permit limits while dealing with the challenges of aging facilities and equipment. Governments focus and invest heavily in wastewater management services, to overcome these problems, and thus boost the growth of the wastewater treatment equipment market. Furthermore, enhancements to wastewater treatment infrastructure boost operational efficiency, enhance local environmental quality, create economic advantages, ensure reliable compliance, and elevate the community's quality of life. Cities and water authorities achieve these benefits without requiring upfront investments, potentially leading to long-term cost savings.
Increase in industrial waste discharge
Industrial water discharge has significant environmental impacts if not properly managed or treated, which is a common occurrence. Industrial wastewater often contains various pollutants, such as chemicals, heavy metals, oils, and organic compounds. These pollutants contaminate surface water, groundwater, and impact aquatic ecosystems and biodiversity when discharged into water bodies without appropriate treatment. Water pollution harms aquatic life, disrupts the natural balance of ecosystems, and affects human health if the contaminated water is used for drinking or irrigation. Furthermore, improper discharge or disposal of industrial wastewater leads to soil contamination. The pollutants in the wastewater seep into the soil, potentially affecting the quality of agricultural lands and posing risks to crops, plants, and groundwater resources if not addressed. Industrial water discharge containing pollutants has detrimental effects on fish populations and aquaculture operations. The discharge depletes oxygen levels in water bodies, disrupts the reproductive cycles of aquatic organisms, and introduces toxic substances that are harmful to fish and other aquatic species. It is crucial for industries to implement effective wastewater treatment and management practices to mitigate the negative impacts of increased industrial water discharge.
For mitigating such issues, various governments formulate regulations & guidelines in the industrial sector for effluent treatment. These government regulations for industrial wastewater discharge are designed to protect public health, the environment, and water resources by controlling the pollutants released by industries. These regulations vary by country but generally share common objectives and frameworks. For instance, the NPDES under the Clean Water Act regulates the discharge of pollutants from point sources, such as factories, into U.S. waters. In Germany, according to the federal Wastewater Charges Act (Abwasserabgabengesetz, AbwAG) and supplementary provisions of the Länder, charges must be paid for the discharge of wastewater containing certain contaminants and its corresponding limits into water bodies. According to Article 57, paragraph 1 of the Federal Water Act (WHG) discharges of wastewater into water bodies is only permissible if the pollution load of the wastewater is kept to the lowest level achievable by means of the best technology available. More detailed and specific requirements are set out in the Wastewater Ordinance (AbwV). In accordance with the EU laws, the Industrial Emissions Directive (2010/75/EU), also known as the IED, provide for a comprehensive licensing process that considers the impact of atmospheric emissions and water discharges from specified major industrial activities, waste management, and agriculture.
Government regulations for industrial wastewater discharge play an important role in safeguarding water quality and protecting ecosystems and public health. These regulations enforce standards, require proper treatment, and ensure ongoing monitoring and compliance by industries.
The Bottom Line
Water and wastewater treatment facilities are indispensable to modern society, playing an important role in protecting public health, preserving the environment, and ensuring sustainable access to clean water. Investing in advanced treatment technologies and infrastructure is essential to meet the increasing challenges posed by pollution, climate change, and resource scarcity. Furthermore, following strict regulatory standards and ongoing innovation are necessary for improving the efficiency and resilience of treatment systems. Finally, water and wastewater treatment facilities are needed to ensure sustainable development and a healthier future.
Allied Market Research delivers in-depth analysis of the expanding water treatment industry. Our reports provide up-to-date information on technological innovations, market trends, and relevant government policies. By staying informed about these developments, companies can make relevant choices and take advantage of new market opportunities. For expert advice on materials and chemicals related to water treatment, reach out to our team today!

