The global space logistics market size is expected to be valued at $4 billion in 2030, and is projected to reach $19.8 billion by 2040, growing at a CAGR of 17.3% from 2030 to 2040.
Space logistics includes the transportation of cargo and material to, from, and within space as well as the capacity to sustain manned and robotic operations. In addition, space logistics refers to the aspects of space operations that deal with the acquisition, design & development, storage, distribution, evacuation, maintenance, movement, and disposal of space material as well as the evacuation, movement, and hospitalization of individuals in space.

Since the first space launch, governments and space agencies have been involved in space exploration. Currently, the emphasis is on cooperative human and robotic expeditions, close-by asteroids, Mars, and locations outside of solar system. The innovation that results from space exploration is crucial for creating new fields in space science and technology. As the advantages of space exploration and innovation, more nations and non-governmental organizations are interested in participating in these activities. An increasing number of space exploration missions such as Jupiter Icy Moon Explorer, SpaceX Starship, dearMoon, Asteroid explorer returns to Earth, and others are expected to create demand for space management and exploration during the forecast period.
Any piece of equipment or debris left in space by humans is known as space trash or space debris. It can be used to describe large objects such as spacecraft that have failed or failed and were left in orbit after their missions. It can also include tiny objects such as paint flecks or debris that have dropped off missiles. Space debris will endanger both present and future space operations. Over the past ten years, numerous efficient strategies for removing space debris have been put forth, and several of these have either undergone ground testing or parabolic flight experiments.
In June 2022, Space logistics company D-Orbit announced a $2 million contract with the European Space Agency to upgrade the production of its ION Satellite Carrier. It was the latest win for the Italian firm with ambitious plans to offer a wide range of satellite services from active debris removal to space-based cloud computing. Under the contract, ESA will fund D-Orbit’s campaign to improve the performance and reduce the cost of ION, the vehicle that transports cubesats and microsatellites from the point where a large rocket drops them off to their desired orbital destinations. Such developments are anticipated to drive the growth of the market during the forecast period.
The need for satellite networks and services for commercial purposes has grown significantly in recent years. The satellite manufacturing industry has also benefited from the arrival of businesses such as Google and Facebook with commercial services that need satellite bandwidth and networks. Hundreds of additional small satellites such as nanosatellites, picosatellites, and CubeSats must be developed and launched to fulfill the rise in demand for commercial space applications. For instance, Lockheed Martin Corporation was granted a $4.9 billion contract in June 2021 to develop a trio of missile-warning satellites for the U.S. Space Force. Such an increasing number of satellites is expected to create demand for space management and logistics in the near future, which is expected to boost the growth of the market.
Increase in space exploration missions and rise in space stations, increasing demand for LEO-based satellite services, and growing investment by private companies are the major factors that propel the space logistics market growth. However, the high involved, the heightened emissions due to the rising number of space launches, and interoperability issues are the major factors that hamper the growth of the space logistics market. Furthermore, new plans for space tourism, and concerns over space debris are the factors that are expected to offer growth opportunities for the market during the forecast period.
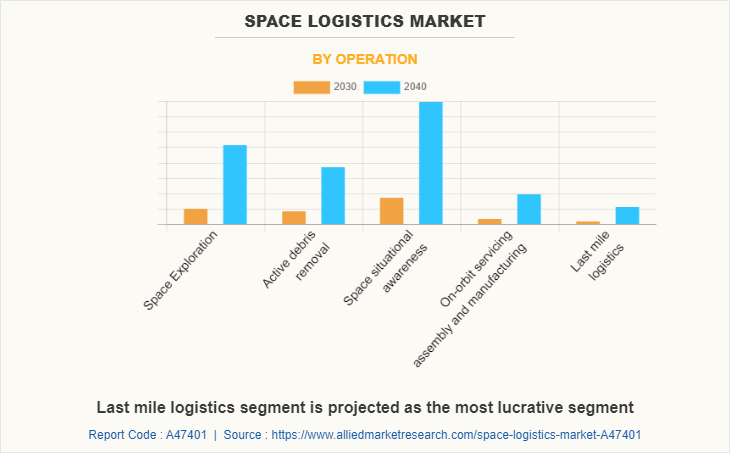
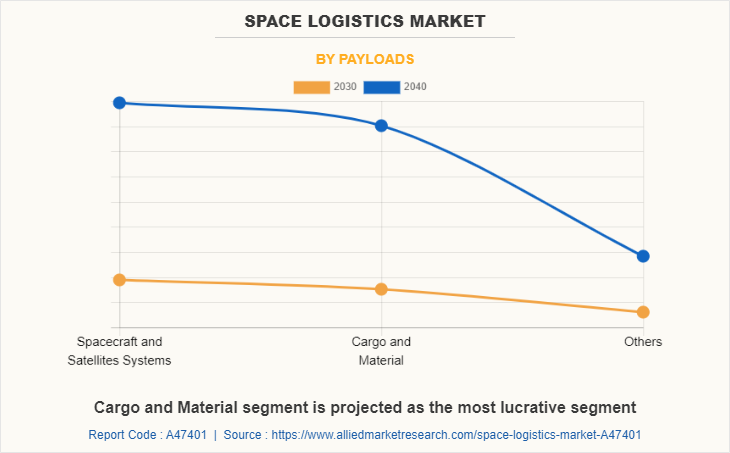
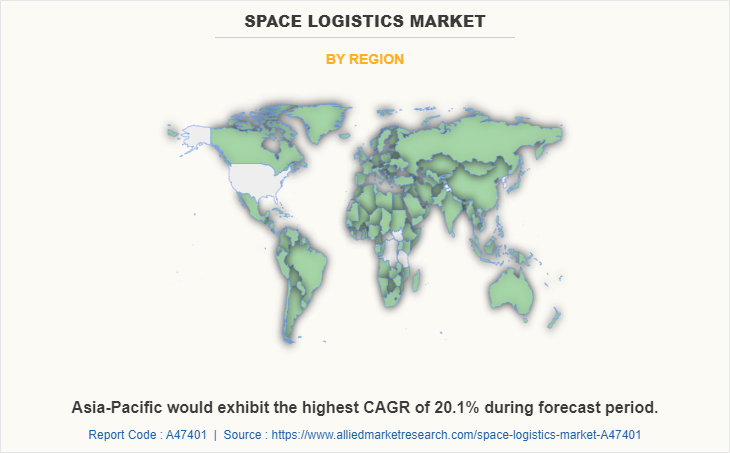
The space logistics market segmentation is based on the operation, payloads, and region. By operation, it is categorized into space exploration, active debris removal, space situational awareness, on-orbit servicing, assembly, and manufacturing, and last mile logistics. By payloads, it is divided into spacecraft and satellite systems, cargo and material, and others. By region, the market is analyzed across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA.
Some leading companies profiled in the space logistics market report comprises ArianeGroup, ATOMOS SPACE, Deutsche Post DHL Group, D-Orbit SpA, EXOLAUNCH GmbH, Exotrail, Impulse Space, Inc., Launcher Inc., Momentus Space, Northrop Grumman, Space Machines Company Pty Ltd., and Yusen Logistics Co., Ltd.
The leading companies are adopting strategies such as partnership, contract, agreement, and expansion to strengthen their market position. In September 2022, Yusen Logistics Co., Ltd. expanded & opened a new warehouse and distribution center located near the federal road B10, in a region that is continuously developing into an important logistics hub for light industry. In addition, in December 2020, Deutsche Post DHL Group entered into a partnership with D-Orbit to jointly tackle terrestrial challenges and leverage galactic opportunities. DHL & D-Orbit worked together to set up logistics for ION Satellite Carrier.
Increase in space exploration missions and rise in space stations
A space station is a kind of space housing because it can sustain a crew aboard in orbit for a long duration of time. An artificial spacecraft is called an orbital station or orbital space station. Without the ability to support life, space cannot expand steadily. It also implies the requirement for building space stations. A rise in the development of space stations such as Starlab, Lunar Gateway, and Orbital Reef among others is anticipated to create demand for space logistics to provide cargo, accessories, or fuel to space stations. This factor led to drive the growth of the market.
Moreover, space exploration has resulted in the research and construction of more dependable and efficient propulsion systems and spacecraft, lowering the possibility of system failure and increasing mission success rates. For instance, in February 2021, the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) announced that it is exploring the possibility of developing a new propulsion technology to fuel spacecraft for its future deep space missions. In addition, in January 2021, ISRO issued an invitation for “expression of interest” for the design and modeling; simulation and analysis; testing, and qualification of a 100W Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (RTEG) without radioisotope, an alpha source thermoelectric propulsion technology. Such developments in space propulsion systems pushed organizations and market players to develop space logistics systems for space missions to provide logistics services including life extension services and on-orbit assembly and manufacturing. Such an increase in space exploration missions is expected to drive the growth of the market during the forecast period.
Increasing demand for LEO-based satellite services
The demand for internet connections via fixed and mobile broadband networks is increasing dramatically. Despite network expansions and enhancements, only around half of the world's households have access to fixed broadband services. With the development of LEO constellations, satellite broadband services are projected to increase broadband penetration. Owing to the constellations of several hundred LEO spacecraft, global broadband internet might be accessible from everywhere on the planet. In addition, local service providers will be able to expand their networks in terms of service range and geographic reach, allowing local services to be supplied over a global network. Such a rise in the demand for LEO-based spacecraft and missions is expected to create demand for spacecraft logistics systems.
Furthermore, satellites are primarily mass-produced to meet customer demand for high-speed internet connectivity almost anywhere, including aircraft, cruise ships, and remote spots throughout the world. SpaceX, OneWeb, and Boing are among the companies proposing and building LEO satellite networks to provide global high-speed internet connectivity. LEO satellites are widely used for communications, military reconnaissance, spying, and other imaging applications. For instance, in July 2021, Inmarsat announced the launch of around 150 satellites into LEO to enhance its existing telecommunications capabilities. The increased bandwidth provided by Inmarsat's LEO satellites might be useful for congested sea routes or crowded aviation corridors. There is an increasing requirement to make sure that activities are managed properly and responsibly as LEO activity increases. This growing number of LEO satellites is expected to create demand for space logistics systems, which is anticipated to drive the growth of the global market.
High cost involved
Carrier rockets are developed using sophisticated technologies and modern materials that are both strong and light, such as aerospace-grade aluminum or titanium. The cost of a carrier rocket is increased by the adoption of advanced technology and modern hardware, which limits carrier rocket development. For instance, Virgin Galactic's successful launch into space in July 2021 was valued at $841 million. The spaceship was launched into orbit using Virgin Galactic's passenger rocket aircraft VSS Unity. The hefty expenses of developing a carrier rocket prevent new manufacturers from entering the market. The high costs related to carrier rocket act as a challenge to the growth of space exploration over the forecast timeframe.
Moreover, the initial cost for launch services is very high. A launch service can roughly cost $1 million to $100 million. Initially, the space activities and launching services were either controlled by the government & military or by the space agencies formed by the government. The market was monopolized as there were lesser to no other players in the market. The industry still has a few players in the market that are largely concentrated in the U.S. and European regions. The initial cost associated with providing launch services is anticipated to hamper the space logistics market growth.
Furthermore, the launch services and logistics and space management service provider need to invest hugely to procure the infrastructure and supporting activities required for the launch or transport of materials or cargo. This factor is anticipated to hinder the growth of the market.
New plans for Space Tourism
The concept of tourism has been around in the space industry for a long time. In the early 200s, the Russian Space Agency successfully facilitated orbital space tourism for seven people. The operations ceased in 2010. Since then, many industry players are toying with the idea of space tourism for recreational and leisure activities. Companies such as Virgin Galactic, Space Exploration Technologies, Blue Origin, Orion, and The Boeing Company, offer the chance to space tourism. Orbital space tourism and feasible lunar space tourism are anticipated to occur in the near future.
For instance, in March 2020, SpaceX signed a deal with a space tourism company to organize a trip orbiting the Earth for a handful of adventurous travelers. They are planning to send three tourists on a 10-day trip to the international space station sometime in late 2021. It’ll use its Falcon 9 rocket and its new Crew Dragon spacecraft. Such upcoming steps from the leading players are projected to provide numerous growth opportunities for the global space logistics market.
Key Benefits For Stakeholders
- This report provides a quantitative analysis of the market segments, current trends, estimations, and dynamics of the space logistics market analysis from 2030 to 2040 to identify the prevailing space logistics market opportunities.
- The market research is offered along with information related to key drivers, restraints, and opportunities.
- Porter's five forces analysis highlights the potency of buyers and suppliers to enable stakeholders make profit-oriented business decisions and strengthen their supplier-buyer network.
- In-depth analysis of the space logistics market segmentation assists to determine the prevailing market opportunities.
- Major countries in each region are mapped according to their revenue contribution to the global market.
- Market player positioning facilitates benchmarking and provides a clear understanding of the present position of the market players.
- The report includes the analysis of the regional as well as global space logistics market trends, key players, market segments, application areas, and market growth strategies.
Space Logistics Market Report Highlights
| Aspects | Details |
| Market Size By 2040 | USD 19.8 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 17.3% |
| Forecast period | 2030 - 2040 |
| Report Pages | 290 |
| By Operation |
|
| By Payloads |
|
| By Region |
|
| Key Market Players | Momentus Inc., D-Orbit SpA, Yusen Logistics Co., Ltd., ArianGroup, Northrop Grumman, Space Machines Company Pty Ltd, Deutsche Post DHL Group, Impulse Space, Inc., ATOMOS SPACE, EXOLAUNCH GmbH, Launcher Inc., Exotrail |
Analyst Review
The space logistics market is expected to witness remarkable growth in the future, owing to the growing investment by private companies. The key factors that drive the growth of the space logistics market are the increasing demand for LEO-based satellite services and increasing space exploration missions. However, the high cost involved in space logistics is anticipated to hinder the space logistics market growth. Furthermore, concerns over space debris are expected to provide remarkable growth opportunities for players operating in the space logistics market.
Private companies are increasingly involved in space exploration, and the number of collaborations between government and private space agencies as well as agreements and outsources, including sourcing of different electrical parts & ancillary equipment, robotic gadgets, and software development, have increased in recent years. Amazon and SpaceX have revealed plans to colonize the moon and Mars, accordingly. For instance, in February 2022, the CEO of SpaceX, Elon Musk announced SpaceX’s mega-rocket Starship that will one day take people and cargo to the moon, Mars, and other destinations in space. Such developments in space exploration by private companies are expected to enhance spacecraft manufacturing capabilities and create demand for space logistics and management during the forecast period.
However, interoperability is a smooth connectivity of information, disparate systems, products, and processes, or that permits their interconnection for the search of a common goal. Lack of interoperability causes problems in communication. A system that is flexible, robust, and open is globally optimized, interconnected, and interoperable. The challenges in communication require coordination mechanisms. If interoperability is not adopted in the early stages of the architecture, the technological challenges are expected to result in the failure of the system to yield any clear result. The interoperability issues hamper the space logistics market growth
The global space logistics market is expected to be valued at $4.02 billion in 2030, and is projected to reach $19.81 billion by 2040, registering a CAGR of 17.3% from 2030 to 2040
Some leading companies profiled in the space logistics market report comprises ArianeGroup, ATOMOS SPACE, Deutsche Post DHL Group, D-Orbit SpA, EXOLAUNCH GmbH, Exotrail, Impulse Space, Inc., Launcher Inc., Momentus Space, Northrop Grumman, Space Machines Company Pty Ltd., and Yusen Logistics Co., Ltd
Space situational awareness is leading application of Space Logistics Market
North America is the largest regional market for Space Logistics
Increase in space exploration missions and rise in space stations and growing investment by private companies are the upcoming trends of space logistics market
Loading Table Of Content...


