Bunker Fuel Market Research, 2034
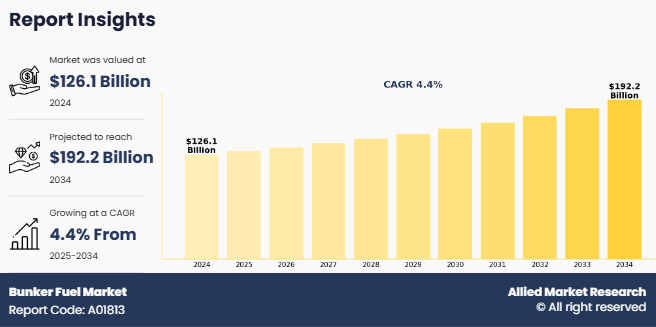
The global bunker fuel market size was valued at $126.1 billion in 2024, and is projected to reach $192.2 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 4.41% from 2025 to 2034.
 Introduction
Introduction
Bunker fuel, known as marine fuel, refers to the heavy oil or diesel-type fuel used by ships to power their engines. The term "bunker" historically refers to a container or storage tank on ships where fuel was stored; over time, it came to refer to the fuel itself. This fuel is a crucial component in maritime transport, which carries over 80% of global trade by volume. Bunker fuel can range from the highly viscous residual fuels (like heavy fuel oil, or HFO) to lighter distillate fuels like marine gas oil (MGO) and marine diesel oil (MDO). More recently, cleaner alternatives such as liquefied natural gas (LNG), biofuels, methanol, ammonia, and hydrogen are being considered or adopted to comply with increasingly stringent environmental regulations. The bunkering market refers to the global trade and supply of marine fuels for ships. It plays a crucial role in supporting international shipping and maritime logistics.
Bunker fuels, essential for powering marine vessels, can be broadly categorized into three primary groups: residual fuels, distillate fuels, and alternative fuels. Each category differs in terms of chemical composition, environmental impact, cost, and usage, depending on vessel type, engine configuration, and regulatory requirements. Residual fuel is the most traditional and widely used category in the maritime industry. It is by-product of the crude oil refining process, primarily composed of what remains after lighter fractions like gasoline and diesel are extracted. The most common form of residual fuel is heavy fuel oil (HFO), a thick, viscous, tar-like substance.
Key Takeaways
- The bunker fuel market study covers 20 countries. The research includes a segment analysis of each country in terms of value for the projected period.
- The study integrated high-quality data, professional opinions and analysis, and critical independent perspectives. The research approach is intended to provide a balanced view of global bunker fuel markets and to assist stakeholders in making educated decisions in order to achieve their most ambitious growth objectives.
- Over 3,700 product literature, annual reports, industry statements, and other comparable materials from major industry participants were reviewed to gain a better understanding of the bunker fuel market share.
- The bunker fuel market forecast highlights expected trends in demand, pricing, and adoption of low-sulfur fuels over the coming years.
- The key players in the bunker fuel market are Petroliam Nasional Berhad (PETRONAS), BP p.l.c., Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Limited, Indian Oil Corporation Ltd, LUKOIL, Shell plc, Neste, Exxon Mobil Corporation, TotalEnergies, Chevron Corporation, BUNKER HOLDING, Vitol Bunkers, and others. They have adopted strategies such as acquisition, product launch, merger, and expansion to gain an edge in the market.
Market Dynamics
Increase in demand for commercial shipping vessels is expected to drive bunker fuel market growth. The global expansion of the commercial shipping fleet is a key driver of rising bunker fuel demand, fueled by growing international trade and the need for more vessels such as oil tankers, container ships, bulk carriers, and cruise liners. This trend is especially evident in emerging economies with increasing import-export activity. In a notable development in June 2023, Hyundai Heavy Industries delivered the world's first methanol-fueled container ships to A.P. Moller-Maersk. These dual-fuel vessels, capable of operating on both traditional fuel and green methanol, reflect Maersk's commitment to achieving a carbon-neutral fleet by 2040 and represent a major advancement in maritime decarbonization.
However, high operational cost and scrubber installation are expected to hamper the growth of bunker fuel market. For shipping companies, bunker fuel often represents up to 60% of a vessel's total operational expenditures, making it the largest cost component of maritime transport. The volatility and rising prices of bunker fuel driven by factors such as fluctuating global oil prices, geopolitical instability, and supply chain disruptions have put increasing pressure on profit margins of shipping companies, especially those operating older, less fuel-efficient fleets. Smaller shipping operators are particularly vulnerable, as they may lack the financial resources to absorb price increases or invest in alternative fuel technologies and modern, efficient vessels. As bunker costs rise, many operators are forced to pass these costs onto customers through higher freight rates, a strategy that is increasingly difficult to sustain in a competitive market.
Segments Analysis
The bunker fuel market is segmented into type, commercial distributor, application and region. On the basis of type, the market is divided into high sulfur fuel oil (HSFO), low sulfur fuel oil (LSFO), marine gas oil, bio-LNG, methanol, ammonia, hydrogen, and others. On the basis of commercial distributor, the market is categorized into oil majors, large independent, and small independent. On the basis of application, the market is fragmented into bulk carrier, oil tanker, general cargo, container lines, chemical tanker, fishing vessels, gas tankers, and others. Based on region, the market is analyzed across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East and Africa.
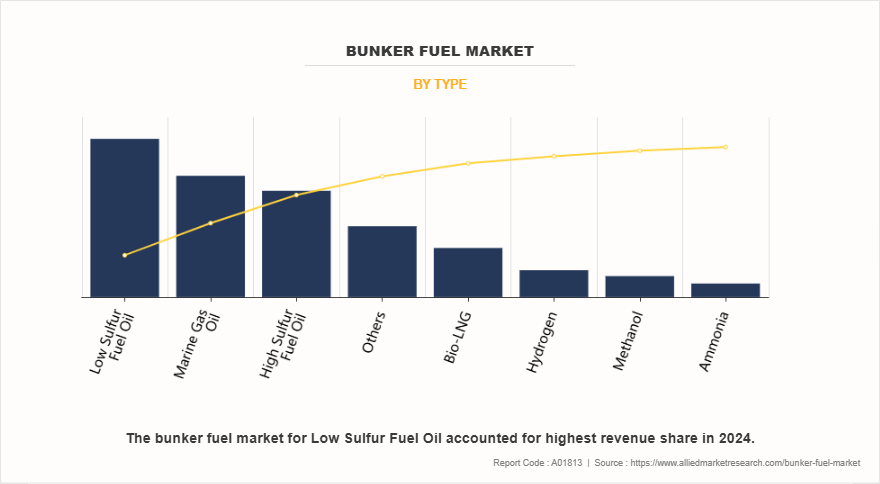
On the basis of type, the low sulfur fuel oil segment dominated the bunker fuel market. The demand for LSFO has surged in major bunkering hubs such as Singapore, Rotterdam (ARA region), Fujairah, and Shanghai. Shipping companies have opted for LSFO due to its immediate compatibility with existing engines, lower upfront investment, and global availability. Moreover, LSFO blends are developed to meet ISO 8217 standards, ensuring adequate lubricity, viscosity, and combustion properties suitable for modern marine engines. Many refiners and suppliers have ramped up LSFO production using a blend of desulfurized heavy fuel oil and distillates to meet the growing global need.
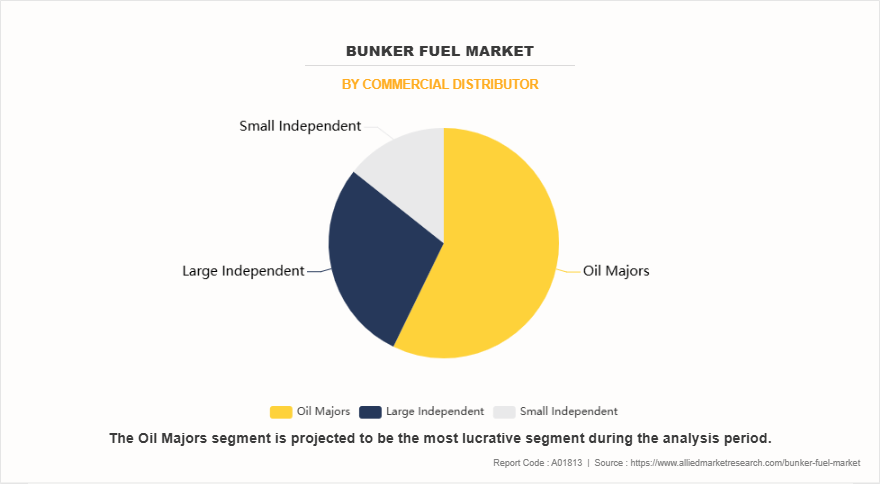
On the basis of commercial distributor, the oil majors segment dominated the bunker fuel market. ExxonMobil and Chevron have also adapted their product offerings by supplying very low sulfur fuel oil (VLSFO) blends tailored to various marine engine requirements while maintaining a robust HSFO supply for vessels equipped with scrubbers. These companies have also started investing in future-ready fuels such as methanol and ammonia, collaborating with shipbuilders and shipping companies to develop dual-fuel engines. TotalEnergies, leveraging its refining and trading operations, has expanded its bunkering operations in the Middle East, Africa, and Europe, and is actively promoting LNG and biofuels as part of its low-carbon marine strategy.
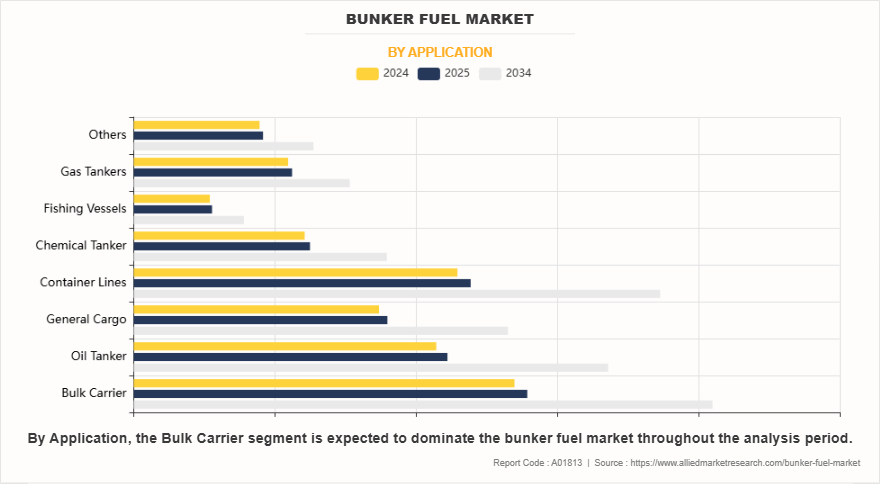
On the basis of application, the bulk carrier segment dominated the bunker fuel market. Bulk carriers, which are specialized vessels designed to transport unpackaged bulk cargo such as coal, grain, ore, and cement, are among the largest consumers of bunker fuel in the global maritime industry. These ships rely heavily on marine fuels to power their massive engines and auxiliary systems during long-haul voyages across oceans. Bunker fuel usage in bulk carriers is directly influenced by factors such as the vessel size (Handysize, Supramax, Panamax, Capesize, and Very Large Ore Carriers), the distance of trade routes, cargo weight, and operational efficiency.
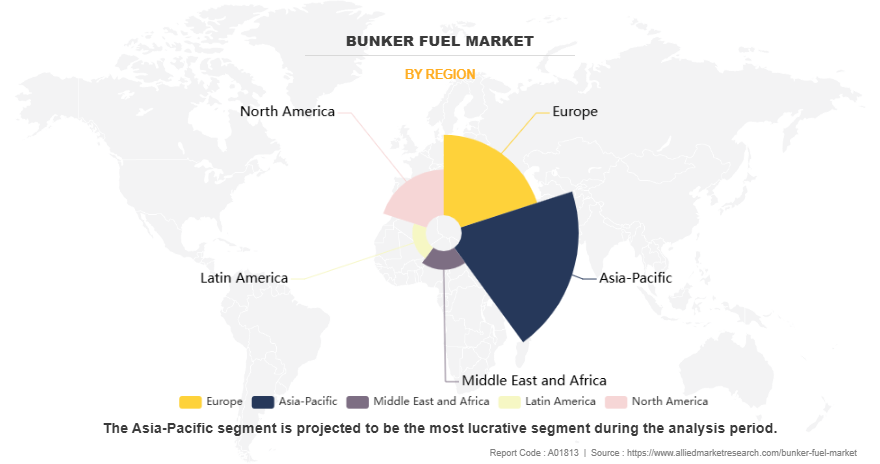
Based on region, Asia-Pacific was the highest revenue contributor in the bunker fuel market. The Asia-Pacific region plays a pivotal role in the global bunker fuel market due to its extensive maritime trade routes, dense shipping traffic, and the presence of major port hubs. Countries such as Singapore, China, South Korea, and Japan are among the top consumers of bunker fuel, primarily driven by their strategic geographic positions, strong export economies, and well-developed port infrastructure. Singapore remains the world's largest bunkering hub, with its high throughput and efficient refueling infrastructure. The country's Maritime and Port Authority (MPA) has actively promoted the use of compliant fuels post-IMO 2020, leading to a significant rise in demand for VLSFO.
Competitive Analysis
The major prominent players operating in the bunker fuel market include Petroliam Nasional Berhad (PETRONAS), BP p.l.c., Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Limited, Indian Oil Corporation Ltd, LUKOIL, Shell plc, Neste, Exxon Mobil Corporation, TotalEnergies, Chevron Corporation, BUNKER HOLDING, Vitol Bunkers, and others.
Recent Key Developments in Bunker fuel in the Market
- In April 2024, Singapore unveiled its Methanol and Low-Carbon Fuels Strategy, aiming to supply over 1 million metric tons of low-carbon methanol annually by 2030. As part of the plan, a regulatory framework and national standards for methanol as a marine fuel implemented in 2025.
- In October 2024, Singapore introduced a technical reference standard for methanol as a marine fuel, followed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) issuing the global standard ISO 6583:2024 in November.
- In February 2024, TotalEnergies announced the launch of a new bunker barge equipped to supply VLSFO and LNG bunkers at the Port of Rotterdam, strengthening its foothold in Europe's busiest marine fuel hub.
- In March 2024, Neste expanded its bio-based marine fuel supply chain in Northern Europe by collaborating with major shipping lines to reduce carbon emissions, aligning with the rising demand for sustainable bunker solutions.
Trump's Tarriff Impact on Bunker fuel Industry
In December 2024, after re-election, then-President-elect Trump announced plans to impose 25% tariffs on imports from Canada and Mexico, explicitly including residual fuel oil used for bunkering. This raised concerns that U.S. Gulf and East Coast refiners and ship operators might either face substantially higher costs or reroute bunkering to alternative ports such as Singapore, Rotterdam, Fujairah, or Panama. The EIA data indicated that Mexico supplied approximately 74% of residual fuel oil to the Gulf coast and 29% to the East coast, while Canada contributed around 7% and 16%, respectively
In February 2025, Ship & Bunker reported that with the tariffs on the verge of going into effect (after a brief postponement), U.S. bunker prices were expected to rise. Refineries reliant on Mexican and Canadian heavy crude would be forced to either absorb the tariff or replace it with lighter and less efficient alternatives, both scenarios likely pushing up the price of bunker fuel.
Argus Media reported that due to uncertainties surrounding tariffs, very low-sulfur fuel oil (VLSFO) prices at several U.S. ports hit their lowest levels since early 2021 with monthly averages in Houston around $470/ton and New Orleans around $491/ton. Traders exhibited mixed behavior: some rushed to purchase for future delivery to lock in prices, while others delayed purchases, anticipating further volatility
The application of tariffs directly impacted bunker fuel prices and trade flows. For example, tariffs placed on Mexican and Canadian residual fuel oils which comprise substantial volumes of US bunker fuel imports were expected to raise prices at US Gulf and East Coast ports. As a result, ship owners began shifting bunker purchases away from the US and towards more price-competitive hubs like Singapore and Rotterdam, thereby altering established shipping patterns and port demand. Global bunker fuel prices responded with significant volatility: benchmark prices reached 20-month lows in early 2025 ($523.5/mt) due to sliding trade volumes and anticipation of wider tariff implementation. Nevertheless, the Americas maintained higher price points than Asia-Pacific (APAC) and EMEA, reflecting intensified demand and constrained supply lines post-tariff.
Key Benefits For Stakeholders
- This report provides a quantitative analysis of the market segments, current trends, estimations, and dynamics of the bunker fuel market analysis from 2024 to 2034 to identify the prevailing bunker fuel market opportunities.
- The market research is offered along with information related to key drivers, restraints, and opportunities.
- Porter's five forces analysis highlights the potency of buyers and suppliers to enable stakeholders make profit-oriented business decisions and strengthen their supplier-buyer network.
- In-depth analysis of the bunker fuel market segmentation assists to determine the prevailing market opportunities.
- Major countries in each region are mapped according to their revenue contribution to the global market.
- Market player positioning facilitates benchmarking and provides a clear understanding of the present position of the market players.
- The report includes the analysis of the regional as well as global bunker fuel market trends, key players, market segments, application areas, and market growth strategies.
Bunker Fuel Market Report Highlights
| Aspects | Details |
| Market Size By 2034 | USD 192.2 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 4.4% |
| Forecast period | 2024 - 2034 |
| Report Pages | 499 |
| By Type |
|
| By Commercial Distributor |
|
| By Application |
|
| By Region |
|
| Key Market Players | LUKOIL, Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Limited, Exxon Mobil Corporation, Shell plc, Chevron Corporation, TotalEnergies, Petroliam Nasional Berhad (PETRONAS), Indian Oil Corporation Ltd., Neste, Vitol Bunkers, Bunker Holding A/S, BP p.l.c. |
Analyst Review
According to the opinions of various CXOs of leading companies, growth in international maritime trade is expected to drive the growth of the bunker fuel market. The rise in e-commerce, industrial manufacturing, and bulk commodity trade including crude oil, LNG, iron ore, and agricultural products has driven higher activity among container ships, tankers, and bulk carriers. Emerging economies in Asia, Africa, and Latin America are witnessing rapid infrastructure development and trade growth, further amplifying the need for marine transportation. As these regions integrate more deeply into global trade routes, demand for bunker fuel increases proportionally, since it remains the primary source of energy for most ocean-going vessels.
Additionally, international trade agreements, free trade zones, and global logistics hubs (e.g., Singapore, Rotterdam, Shanghai, Gibraltar, and Fujairah) have reinforced the necessity for frequent and efficient maritime transport. This surge in seaborne trade directly translates to increased voyage frequency, longer shipping distances, and greater fuel consumption. As a result, the global bunker fuel market continues to expand, closely linked to the sustained momentum in international maritime trade.
Emerging bunker hubs in Africa and Southeast Asia are expected to offer lucrative opportunities in the bunker fuel market. The rise of new strategic bunker hubs in Africa and Southeast Asia presents a significant opportunity for the growth of the global bunker fuel market. As regional trade expands and shipping routes diversify, countries such as Djibouti, South Africa, and Indonesia are investing heavily in port infrastructure, positioning themselves as key maritime refueling and logistics centers. These emerging hubs are strategically located along major shipping lanes, such as the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait, Cape of Good Hope, and the Strait of Malacca, which are vital transit points for global trade between Asia, Europe, and Africa.
Asia-Pacific is the largest regional market for bunker fuel in the world.
Asia-Pacific is the largest regional market for Bunker Fuel.
The major prominent players operating in the bunker fuel market include Petroliam Nasional Berhad (PETRONAS), BP p.l.c., Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Limited, Indian Oil Corporation Ltd, LUKOIL, Shell plc, Neste, Exxon Mobil Corporation, TotalEnergies, Chevron Corporation, BUNKER HOLDING, Vitol Bunkers, and others.
Bulk Carrier is the leading application of bunker fuel market.
Investments in green shipping are the upcoming trends of bunker fuel market
Loading Table Of Content...
Loading Research Methodology...



