Electric Ships Market Insights, 2032
The global electric ships market size was valued at $4.6 billion in 2022, and is projected to reach $23.8 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 18% from 2023 to 2032.
Report Key Highlighters:
- The electric ship market studies more than 15 countries. The research includes a segment analysis of each country in terms of value ($ million) for the projected period 2022-2032.
- The study integrated high-quality data, professional opinions and analysis, and critical independent perspectives. The research approach is intended to provide a balanced view of global markets and to assist stakeholders in making educated decisions to achieve their most ambitious growth objectives.
- Over 3,700 product literature, annual reports, industry statements, and other comparable materials from major industry participants were reviewed to gain a better understanding of the market.
- The electric ship market share is moderately fragmented, with several players including Leclanché SA, Siemens, Wartsila, ECHANDIA AB, KONGSBERG, ABB, Corvus Energy, HOLLAND SHIPYARDS GROUP, Brodrene Aa, and Norwegian Electric Systems. Key strategies such as product development, expansion, agreement, contract, and other strategies of the players operating in the market are tracked and monitored.

An electric ship refers to a ship that primarily relies on an electric drive system for propulsion. Electric ships are maritime vessels that utilize electricity for propulsion and power generation, instead of conventional fossil fuel engines such as diesel or steam. They rely on electrical energy to drive their propulsion systems, auxiliary machinery, and onboard systems. The rise in awareness and concern about climate change and environmental pollution has led to a growing demand for cleaner and more sustainable transportation solutions. Electric-driven vessels have a positive environmental impact by reducing fuel consumption and minimizing oil emissions. Moreover, the compact nature of electrical propulsion systems requires less space, freeing up additional load capacity on the ship. In addition, electric ships offer reduced life cycle costs due to lower fuel consumption and maintenance expenses.
Factors such as environmental regulations, an increase in demand for high efficiency and less life cycle cost, and a surge in the retrofitting of hybrid systems in ships drive the growth of the electric ships market. However, limited infrastructure and charging facilities, and high initial investment costs hinder the growth of the market. Furthermore, the technological advancements and growing popularity of autonomous electric ships offer remarkable growth opportunities for the players operating in the electric ships industry.
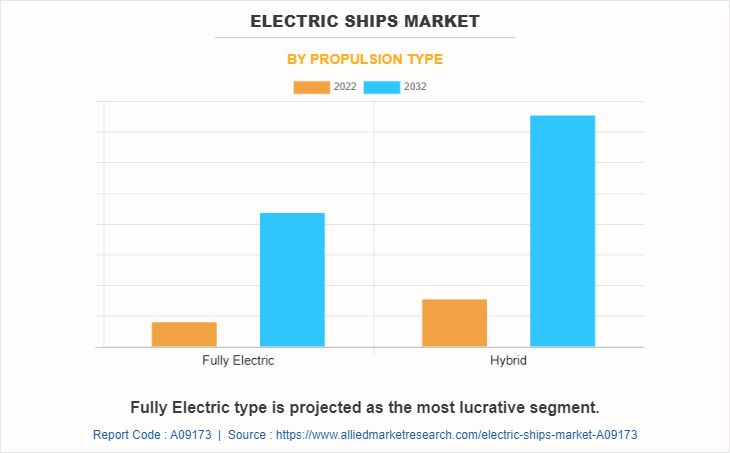
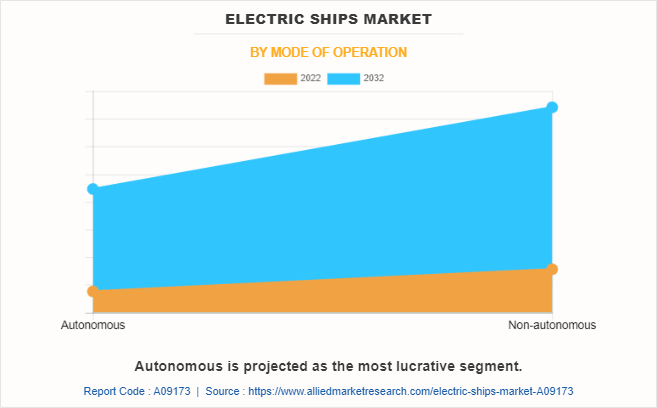
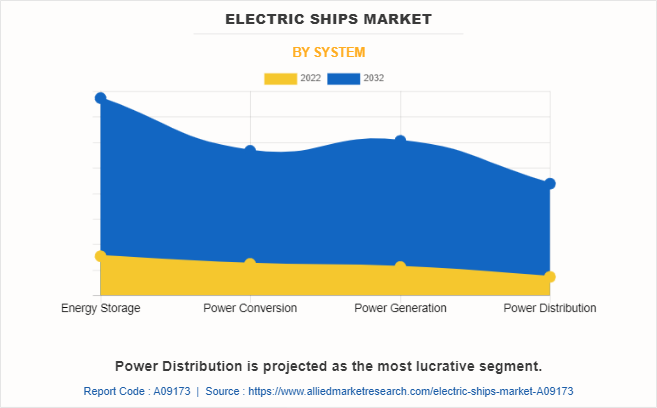
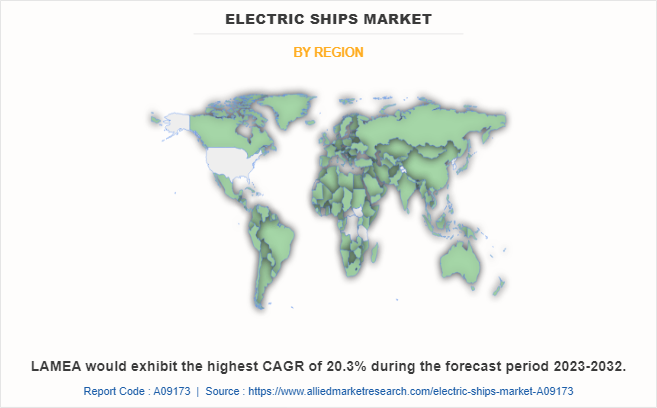
The electric ships market is segmented on the basis of propulsion type, mode of operation, system, and region. By propulsion type, it is bifurcated into fully electric, and hybrid. By mode of operation, it is fragmented into autonomous, and non-autonomous. By system, it is categorized into energy storage, power conversion, power generation, and power distribution. By region, the market is analyzed across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA.
The leading companies profiled in the electric ships market report include Leclanché SA, Siemens, Wartsila, ECHANDIA AB, KONGSBERG, ABB, Corvus Energy, HOLLAND SHIPYARDS GROUP, Brodrene Aa, and Norwegian Electric Systems. To strengthen their market standing, the corporations have implemented strategies including product development, expansion, agreement, contract, and others. China, India, Japan, South Korea, and the rest of Asia-Pacific are included in the region known as Asia-Pacific. The promotion of electric ferries, are fueled by the implementation of renewable energy and emissions reduction targets developed by government. Through initiatives such as incentives, subsidies, and regulatory frameworks, ship operators are encouraged to invest in electric technology. The development of the electric ship sector is fueled by government policies that make it easier to use electric ferries and support the switch to clean, low-emission transportation.
A sustainable and emission-free alternative to conventional diesel-powered ships is provided by electric ships. With the use of electric ships, many nations in the region intend to drastically cut air pollution and fight climate change. Additionally, public transportation organizations in various nations want to invest in low-emission ferries to lessen the environmental impact of their fleet and its carbon footprint. For instance, Auckland Transport, Auckland, New Zealand's public transport provider, ordered a fourth low-emission boat in July 2023. The low-emission ferry is expected to be built by Q-West; a boatbuilding company based in New Zealand. The vessel is expected to be designed to operate with reduced emissions compared to conventional ferries, contributing to improved air quality, and reduced environmental impact.
Europe comprises the UK, Germany, France, Russia, and the rest of Europe. The surge in the public demand for sustainable and eco-friendly transportation options is expected to accelerate the growth of the electric ships market in the region. Passengers actively seek greener alternatives, and electric ferries have emerged as a popular choice. To meet the expectations of customers, ferry operators, and authorities make huge investments in electric ferries, recognizing the need to provide environmentally friendly modes of transportation.
The growth in the global emphasis on reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and climate change concerns has generated greater interest in sustainable transportation options. Electric ferries, which produce no direct emissions, play a significant role in improving air quality and minimizing the environmental effects associated with conventional fossil fuel-powered vessels. This trend is further fueled by a rise in the demand for autonomous and electric transportation solutions, particularly within the maritime sector.
For instance, in October 2022, Holland Shipyards, a shipbuilding company based in the Netherlands received a contract to build four ferries that are autonomous and powered by electricity. The contract was reportedly awarded by GVB, the public transport operator in Amsterdam, Netherlands. The four ferries are expected to be delivered by Holland Shipyards to GVB for operational use by 2023. Therefore, such developments shift towards cleaner and more efficient modes of maritime transportation are expected to drive the growth of the market in the region during the forecast period.
Stringent environment regulations
Approximately 90% of the world's trade relies on around 90,000 marine vessels that traverse the oceans. Around 1,000 metric tonnes of CO2 are emitted annually by the maritime sector, making up about 3% of all CO2 emissions worldwide. The International Maritime Organisation estimates that by 2050, shipping emissions are expected to increase by up to 50% if severe emission reduction measures are not implemented.
Growing public concern over environmental issues, particularly air pollution and climate change, has increased pressure on the shipping sector to cut back on harmful emissions and carbon emissions. As a result, many countries and international organizations have implemented stricter regulations and emission standards for ships. Electric ships emit no direct emissions, making them a suitable alternative for businesses looking to adhere to environmental standards and strengthen their sustainability credentials. By switching to electric ships, the shipping industry may significantly reduce its emissions of carbon dioxide and other hazardous pollutants, assisting global efforts to combat climate change and improve air quality. The usage of electric ships is anticipated to rise as governments and international organizations continue to advocate for environmentally friendly shipping practices, fueling the expansion of the industry.
Increase in demand for high efficiency and less life cycle cost
As environmental concerns and regulatory pressures continue to grow, the shipping industry is seeking more efficient and sustainable solutions. Electric ships offer higher energy efficiency compared to conventional vessels using internal combustion engines. Electric propulsion systems can convert a larger percentage of energy from the power source into useful work, resulting in reduced energy waste and lower operating costs. The higher efficiency of electric ships makes them an attractive choice for companies aiming to optimize their operations and reduce fuel consumption. Electric ships can provide cost savings over their lifetime due to reduced fuel consumption and lower maintenance requirements. While the initial investment in electric ship technology may be higher than traditional vessels, the lower operating costs and fewer maintenance needs can lead to significant savings over time.
Limited infrastructure and charging facilities
One of the significant challenges for electric ships is the need for adequate charging infrastructure. Unlike conventional fueling stations, charging points for electric ships require substantial investment and specialized facilities. The establishment of efficient charging infrastructure in ports and along shipping routes may take time and considerable financial resources. The absence of a robust charging network can limit the range and flexibility of electric ships, making them less appealing for certain long-haul or remote routes.
High initial investment cost
While electric ships can lead to long-term cost savings, the initial investment required to adopt electric propulsion technology can be significant. Electric vessels typically have higher upfront costs compared to conventional ships with internal combustion engines. The cost of advanced battery systems and electric propulsion equipment can be a barrier for some shipowners and operators, particularly for smaller companies or those with tight budget constraints. The higher upfront investment may deter some stakeholders from transitioning to electric ships, at least in the short term
Growing popularity of autonomous electric ships
There is a rise in research and development to develop autonomous ships that can leverage advanced sensors, artificial intelligence, and machine learning to navigate more efficiently and safely. Removing the human factor from ship operations reduces the risk of human errors and accidents, leading to improved safety records and enhanced operational efficiency. Autonomous electric ships offer a double advantage in terms of environmental impact. Electric propulsion reduces emissions and air pollution, while autonomy optimizes navigation and route planning, further reducing fuel consumption and environmental impact.
The combination of these two technologies aligns with the industry's sustainability goals and enhances the reputation of shipping companies as environmentally responsible. Autonomous ships generate vast amounts of data through sensors and onboard systems. This data can be analyzed and utilized to optimize vessel performance, maintenance scheduling, and route planning. The insights derived from this data can lead to continuous improvements in operational efficiency and overall fleet management. Therefore, the widespread adoption of fully autonomous electric ships is expected to offer lucrative opportunities for the growth of the market.
Recent Developments
- In April 2023, ABB signed an agreement with Sembcorp Marine Ltd. to deliver the complete electrical system automation for a floating production storage and offloading (FPSO) facility for the Petrobras vessel. ABB is supplying both the topside and hullside electrical systems for P-82, providing seamless project integration.
- In June 2023, Corvus Energy developed a containerized solution – the Corvus BOB (Battery-On-Board) and received approval from DNV. The Corvus BOB system is based on use with the marine battery system with the highest installation count across globally such as the Corvus Orca Energy.
- In March 2023, Brodrene Aa signed a contract with Norled for the construction of a new hybrid electric vessel named MS Bre. The hybrid vessel has dual sustainable functions i.e., it is used both as a reserved vessel on connection and as an electric sightseeing boat.
- In March 2022, KONGSBERG, through its subsidiary Kongsberg Maritime, developed and supplied a complete propulsion and control system package for a Scandlines zero-emissions vessel. The ferry was designed by LMG Marin AS in Norway and constructed at Cemre Shipyard in Turkey, in cooperation with Scandline’s vessel-newbuild experts.
- In February 2021, Corvus Energy entered into an agreement with Seaspan Ferries Corporation for the first delivery of Corvus’ Blue Whale ESS, to be installed onboard one of the cargo ferries. ESS is a groundbreaking battery system designed for large ships with high zero-emission energy demand, such as cruise ships, large Ro-Pax and Ro-Ro ferries, and cargo ships.
- In December 2020, ECHANDIA AB signed an agreement with Siemens to provide E-LTO battery systems for 23 modern electric ferries for the South Indian city of Kochi’s public transport. The project comprises a total of 78 zero-emission vessels. It is the one of the largest fleets of electric ferries.
Key Benefits For Stakeholders
- This report provides a quantitative analysis of the market segments, current trends, estimations, and dynamics of the electric ships market analysis from 2022 to 2032 to identify the prevailing electric ships market opportunities.
- The market research is offered along with information related to key drivers, restraints, and opportunities.
- Porter's five forces analysis highlights the potency of buyers and suppliers to enable stakeholders make profit-oriented business decisions and strengthen their supplier-buyer network.
- In-depth analysis of the electric ships market segmentation assists to determine the prevailing market opportunities.
- Major countries in each region are mapped according to their revenue contribution to the global market.
- Market player positioning facilitates benchmarking and provides a clear understanding of the present position of the market players.
- The report includes the analysis of the regional as well as global electric ships market trends, key players, market segments, application areas, and market growth strategies.
Electric Ships Market Report Highlights
| Aspects | Details |
| Market Size By 2032 | USD 23.8 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 18% |
| Forecast period | 2022 - 2032 |
| Report Pages | 231 |
| By Propulsion Type |
|
| By Mode of Operation |
|
| By System |
|
| By Region |
|
| Key Market Players | ECHANDIA AB, Siemens, Brodrene Aa, Wartsila, Corvus Energy, Norwegian Electric Systems, HOLLAND SHIPYARDS GROUP, Leclanché SA, KONGSBERG, ABB |
The global electric ships market was valued at $4,631.7 million in 2022, and is projected to reach $23,794.8 million by 2032, registering a CAGR of 18.0% from 2023 to 2032.
The top companies to hold the market share in electric ships are Leclanché SA, Siemens, Wartsila, ECHANDIA AB, KONGSBERG, ABB, Corvus Energy, HOLLAND SHIPYARDS GROUP, Brodrene Aa, and Norwegian Electric Systems
The largest regional market for electric ships is Asia-Pacific.
The leading propulsion type of electric ships market is hybrid.
The upcoming trends of electric ships market in the world are technological advancements, and growing popularity of autonomous electric ships.
Loading Table Of Content...
Loading Research Methodology...


