Low Earth Orbit and Geostationary Satellite Market – 2031:
The global leo and geo satellite market was valued at $11.8 billion in 2021, and is projected to reach $43.9 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 14.3% from 2022 to 2031.

Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites are developed to orbit between 200 km to 2,000 km above the Earth’s surface. These satellites are required to travel at about 27,000 kph to complete a full circuit of the planet in 90 to 120 minutes. In addition, LEO satellite is used for various applications, such as data communication, remote sensing, and research.
Geostationary Earth Orbit (GEO) satellites are launched on a precise trajectory by launch systems to circle Earth above the equator from west to east at the same speed as the Earth. GEO is used by satellites that must remain above a certain point on Earth, such as telecommunication satellites. In addition, GEO satellite networks can provide very high broadband data throughput, with up to 50 Mbps downlink and 5 Mbps uplink. Moreover, weather-monitoring satellites can also use GEO since they can examine specific regions in real time to see how weather patterns develop.
The growth of the global LEO and GEO satellite market is propelling due to increase in adoption of small satellites and increase in demand for LEO-based services. However, rise in concerns over space debris is the factor that hampers the growth of the market. Furthermore, growth in investments by several governments in space technology is the factor expected to offer growth opportunities for the market during the forecast period.
LEO satellites are developed to orbit between 200 km to 2,000 km above the Earth’s surface. These satellites are required to travel at about 27,000 kph to complete a full circuit of the planet in 90 to 120 minutes. LEO orbit is used for various applications such as data communication, remote sensing, and research. Satellites operating in LEO often function as part of multiple satellites or constellations to provide constant coverage.
These constellations, usually arranged in more than about 18 satellites provide uninterrupted connectivity over a certain coverage area. Some known LEO communications satellite constellations include, ORBCOMM, LEO ONE, IRIDIUM, and GLOBALSTAR. The adoption of LEO satellites has increased over the years owing to its advantages, such as shorter orbital periods, higher orbital velocities, shorter trips, low cost, and reduced latency. Satellites in this orbit are often used for satellite imaging owing to its closeness to the Earth and ability to provide higher resolution imagery.
The surge in LEO satellites has resulted from a combination of technological advancements in higher resolution small cameras and greater attitude control along with superior demand for Earth observation, internet connectivity, and voice communications. Opportunities such as technological advancements, greater private funding, and growth in public sector funding has accelerated the growth of this segment. Evolution of Internet of Things (IOT), growth in commercial applications, and greater demand from the defense sector is expected to accelerate this growth.
As of April 2021, SpaceX launched 1,445 satellites as a part of its Starlink constellation in the LEO, and has begun testing its services in Europe, North America, and New Zealand. OneWeb has also launched 182 LEO satellites to enhance its satellite broadband services. Increase in adoption of wireless technologies, advanced motion & temperature sensors, high precision cameras, and others is expected to supplement the LEO and GEO satellite market growth.
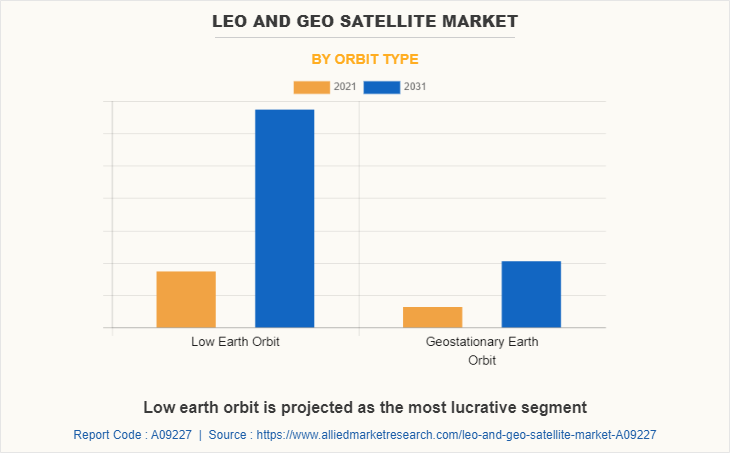
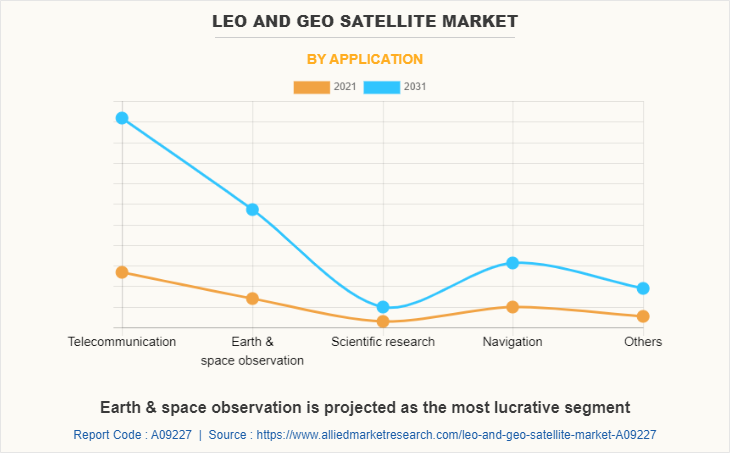
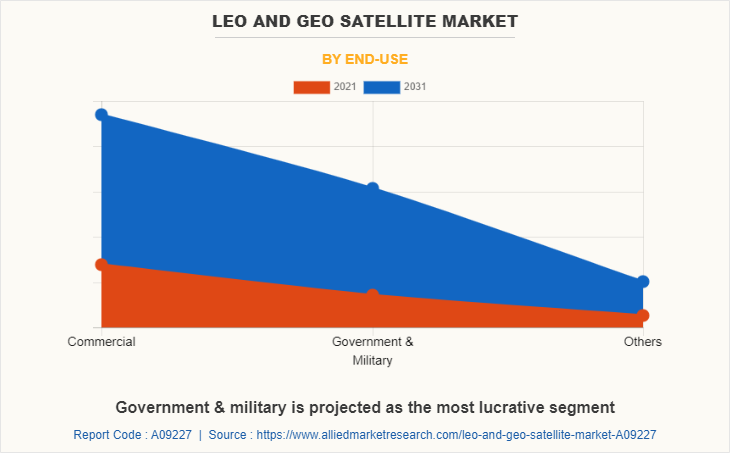
The LEO and GEO satellite market is segmented on the basis of orbit type, application, end-use, and region. By orbit type, it is segmented into Low Earth Orbit (LEO) and Geostationary Earth Orbit (GEO). By application, it is fragmented into telecommunication, earth & space observation, scientific research, navigation, and others. By end-use, it is categorized into commercial, government & military, and others. By region, the report is analyzed across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA.
Some leading companies profiled in the LEO and GEO satellite market report comprise Airbus, Furuno Electric Co., Ltd., Inmarsat Global Limited, Intelsat S.A., Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI), L3Harris Technologies, Inc., Lockheed Martin Corporation, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Qualcomm Technologies, Inc., Texas Instruments Incorporated, Thales Group, and The Boeing Company.
Increase in adoption of small satellites
Small satellites are primarily used in civil, government, defense, and commercial sectors for earth observation and telecommunication applications. Small satellites are increasingly being used for high speed space-based internet services. Organizations are increasingly using small satellites for technology demonstration and scientific research and experimentation. The growing commercial sector along with launch of affordable small satellites drive the LEO and GEO satellite industry. Increasing use of small satellites among small and medium enterprises and startups is further expected to supplement the growth of this market during the forecast period.
Nanosatellites are increasingly being adopted for developing the Internet of Things (IoT) on a global scale. They provide global connectivity, even in remote areas without land communication cover. Small satellites that were earlier used by research institutes and universities, are now being developed by the private sector to provide commercial services.
Satellites are being miniaturized by using concepts such as advanced technology memory devices, System on Chip, MEMs/NEMS, SMD based systems, nano electrons devices, and solid state switches. Innovative manufacturing processes such as 3D printing are being implemented in satellite manufacturing to offer benefits, such as short development time, reduced wastage of material, and lesser environmental impact.
Increase in demand for LEO based services
A LEO satellite, is typically placed between 500 and 2,000 km. Unlike GEO satellite, LEO satellite, at altitudes of 1,000 km, can maintain an orbital velocity of 7.3 km/s. In addition, the low altitude of LEO satellite reduces the time it take for data travel between two points, referred as Latency, from approximately 477 milliseconds inherent to GEO service, to less than 27 milliseconds, which implies that LEO satellites can be utilized for applications, which rely on low latency, such as video conferencing, processing of sensitive financial transactions or remote operations of machines. Moreover, LEO-based telecommunication systems cost less as compared to medium earth orbit (MEO), which take longer to orbit the Earth. Owing to such factors, there has been an increase in the demand for LEO-based services, which in turn is driving the growth of the LEO and GEO satellite industry during the forecast period.
Rise in concerns over space debris
According to NASA, more than 100 million pieces of orbital debris of about 1 mm or larger are tracked by the Department of Defense’s global Space Surveillance Network (SSN) sensors. The presence of debris in space poses a threat to human spaceflight and robotic missions. Presence of millimeter-sized orbital debris poses risks to robotic spacecraft operating in low-Earth orbit. With around 3,000 active satellites in space, the amount of space debris is expected to increase in the coming years. Reusable rockets and miniaturized satellites have resulted in greater debris formation.
The Space Safety Coalition (SSC) was formed in 2019 with forty-eight organizations and other government and industry stakeholders, including D-Orbit, to implement best practices for the long-term sustainability of space operations. Several guidelines have been established for avoiding launch and on-orbit collisions, reducing human casualties from spacecraft, and debris reentry and minimizing the impact of radio frequency interference (RFI) events.

The leo and geo satellite market is segmented into Orbit Type, Application and End-Use.
Key Benefits For Stakeholders
- This report provides a quantitative analysis of the market segments, current trends, estimations, and dynamics of the leo and geo satellite market analysis from 2021 to 2031 to identify the prevailing leo and geo satellite market opportunities.
- The market research is offered along with information related to key drivers, restraints, and opportunities.
- Porter's five forces analysis highlights the potency of buyers and suppliers to enable stakeholders make profit-oriented business decisions and strengthen their supplier-buyer network.
- In-depth analysis of the leo and geo satellite market segmentation assists to determine the prevailing market opportunities.
- Major countries in each region are mapped according to their revenue contribution to the global market.
- Market player positioning facilitates benchmarking and provides a clear understanding of the present position of the market players.
- The report includes the analysis of the regional as well as global leo and geo satellite market trends, key players, market segments, application areas, and market growth strategies.
LEO and GEO Satellite Market Report Highlights
| Aspects | Details |
| By Orbit Type |
|
| By Application |
|
| By End-Use |
|
| By Region |
|
| Key Market Players | L3 Harris Corporation, Texas Instruments, Thales Group, Israel Aerospace Industries Ltd., Furuno Electric, Qualcomm Inc, INTELSAT S.A., Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Inmarsat plc., Lockheed Martin Corporation, The Boeing Company, Airbus S.A.S., Topcon Corporation |
Analyst Review
The global LEO and GEO satellite market is expected to witness significant growth due to increase in adoption of small satellites and increase in demand for LEO-based services.
The overall space economy consists of revenue-generating commercial space activities and government investments in space. The government investments shaped the space industry in the 20th century, whereas commercial activities are now setting the pace. The private spaceflight industry is evolving at a fast pace with new entrants and private funding creating opportunities for innovations in products, services, and processes.
Increasing investments by governments across the globe for improvement of infrastructure and rising need to deliver high quality telecommunication services to consumers provides growth opportunities for this market. High demand for satellite imagery in the government sector including federal agencies, local, and state governments for various purposes such as urban planning, border mapping, infrastructure security, homeland security are contributing significantly to the growth of the market. One of the major factors positively affecting the growth of the market is the large number of satellites that have been launched by various agencies, such as NASA, European Space Imaging, and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency.
The European public funding landscape includes programs, such as Horizon Europe, InvestEU, and European Fund for Strategic Investments (EFSI), for product development, research, and innovation. The European Space Agency (ESA) Business Incubator and Acceleration Centers and the Copernicus Start-Up Program encourage early-stage investments.
In order to gain a fair share of the market, major players adopted different strategies, for instance, partnership, product launch, and product development. Among these, product launch is the leading strategy used by prominent players, such as Airbus S.A.S., Boeing Defense, Furuno Electric, and Israel Aerospace Industries Ltd.
The global LEO and GEO satellite market was valued at $11,780 million in 2021 and is projected to reach $43,913.9 million in 2031, registering a CAGR of 14.3%.
The leading application is telecommunication.
The largest region is North America.
Some leading companies include Airbus, Furuno Electric Co., Ltd., Inmarsat Global Limited, Intelsat S.A., Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI), L3Harris Technologies, Inc., Lockheed Martin Corporation, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Qualcomm Technologies, Inc., Texas Instruments Incorporated, Thales Group, and The Boeing Company.
The upcoming trends include greater adoption by government & military sectors and growing demand from emerging nations.
Loading Table Of Content...



