Microbial Cellulose Market Research, 2032
The global microbial cellulose market size was valued at $20.7 million in 2022, and is projected to reach $64.5 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 12.2% from 2023 to 2032.
Report Key Highlighters:
- The microbial cellulose market is consolidated, with few players including Ashland, Axcelon Biopolymers Corporation, BacPolyZyme, BIOESQUE, Borregaard AS, BOWIL Biotech Sp. z o.o., HBBE, HNB BIO CO., LTD, HYSSES, and Merck KGaA.
- More than 6,000 product literatures, annual reports, industry releases, and other such documents of key industry participants along with authentic industry journals, and government websites have been analyzed for generating high-value industry insights.
- The study covers nearly 20 countries. The segment analysis of each country in terms of value during the forecast period 2022-2032 is covered in the microbial cellulose market report.
Microbial cellulose, also called bacterial cellulose or biocellulose, is made by aerobic bacteria, such as acetic acid bacteria of the genus Gluconacetobacter xylinum. It is created as a polymer and nanomaterial by biotechnological assembly methods from low-molecular-weight carbon sources. Groups of microorganisms are responsible for the synthesis of microbial cellulose through static or agitated fermentation methods in the presence of competent media. Compared to static cultivation, agitated cultivation offers the maximum yield of microbial cellulose.
Microbial cellulose can positively interact with hydrophilic or hydrophobic biopolymers while being employed in the biomedical domain. In recent years, the reinforcement of biopolymer-based biocomposites and their applicability with microbial cellulose have grown in the research field. Also, the antibiofilm effectiveness of microbial cellulose biocomposites has unfurled a new dimension in the treatment of biofilm-mediated chronic wounds and infections.
Growing demand for microbial cellulose from the healthcare and food & beverage industries is expected to drive the microbial cellulose market
Microbial cellulose is utilized in the production of materials or devices for wound healing. Besides, microbial cellulose is used as a scaffold for skin engineering after seeded with epithelial cells. Further, microbial cellulose is usually nontoxic, and low cytotoxicity is observed. When modified, microbial cellulose has physical and chemical properties suitable for reconstructive surgery. The mechanical properties of microbial cellulose, including high tensile strength, elasticity and water retention rate, low inflammation induction, and a low level of cytotoxic effects make microbial cellulose an excellent material for surgical implants.
Further, microbial cellulose biosensors have undergone major advancements, due to the attractive intrinsic attributes of microbial cellulose, and have found applications in pollutant, humidity, food safety, gas, and biomedical applications. Microbial cellulose biosensors offer numerous advantages over traditional tests as microbial cellulose sensors are biodegradable, lightweight, and easily transported. These characteristics are favorably useful in producing novel biosensors as they allow them to be transported and used easily and quickly, delivering valuable accurate data in a short period of time.
Further, microbial cellulose is regarded as a GRAS (generally recognized as safe) food additive by FDA. It has possible applications in conventional desserts, vegetarian meat, food packaging, low cholesterol diet, food/beverage additives, and others.
Microbial cellulose made from static fermentation with a jelly-like pellicle is primarily employed as raw materials for food desserts and food ingredients. It is used in desserts owing to the crunchy texture, cool and smooth feeling, and juicy taste. It is also used as an additive to give the food a new flavor and texture.
Nowadays, it is used in nata de coco, which can be found in various foods including beverages, sausages, pies, yogurt, and salads. On the contrary, microbial cellulose produced from agitated fermentation with a hydrocolloid nature is used as suspension agent and thickener in beverages.
Moreover, microbial cellulose is used as a functional additive for the food & beverage sector. There are plenty of drinks and liquid foods that have particulate ingredients including milk beverages, porridge, coffee, and soybean milk, which need suspension. Typically, surfactant agents and thickeners such as soybean polysaccharide, xanthan gum, and pectin are added to the liquid products in order to suspend particulates.
However, these formulations usually depict poor suspension stability and are often troubled with phase separation and transparency interferences. Also, the high viscosity renders an unpleasant taste to customers. Thus, new suspension agents such as microbial cellulose with superior dispersion stability and low viscosity can fulfill the function to suspend particulates.
Furthermore, microbial cellulose is consumed as food stuff as a pure source of dietary fiber. In Asian countries, microbial cellulose is consumed as a dessert called “Nata de Coco”. Also, it is used to make a fermented drink called Kombucha by utilizing a bacterial cellulose pellicle colonised with yeasts and bacteria, known as “SCOBY”—Symbiotic Culture of Bacteria and Yeast. The SCOBY then ferments a tea solution that results in a drink high in probiotics. Moreover, microbial cellulose is employed as a meat-free option for vegetarians, owing to its structure and is also utilized as a high fiber dietary supplement. Also, microbial cellulose is used for stabilization of peanut butter.
However, higher cost associated with microbial cellulose production is expected to hinder the growth of the microbial cellulose industry.The production of microbial cellulose is a relatively expensive process compared to plant cellulose production, owing to the low productivity of known strains and the usage of expensive culture media. During the production of microbial cellulose, the culture medium represents about 30% of the total cost. Consequently, higher cost associated with microbial cellulose production is expected to hinder the market growth.
Nevertheless, in order to lower the cost of microbial cellulose biosynthesis, various researchers are suggesting the usage of media that include myriad waste products such as wheat straw, wood hot water extracts, spruce hydrolysate, rotten fruit, pineapple agro-industrial residues, molasses, fruit juices, cotton-based waste textiles, waste from the dairy industry, wine fermentation waste broth, wastewater of candied jujube-processing industry, waste and by-product streams from biodiesel and confectionery industries, and acetone-butanol-ethanol fermentation wastewater.
The microbial cellulose market is segmented into growth medium, application, and region. On the basis of growth medium, the market is categorized into synthetic and natural. As per application, the market is divided into food & beverage, medical, cosmetics & personal care, paper, textile, and others. Region-wise, the microbial cellulose market share is studied across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA.
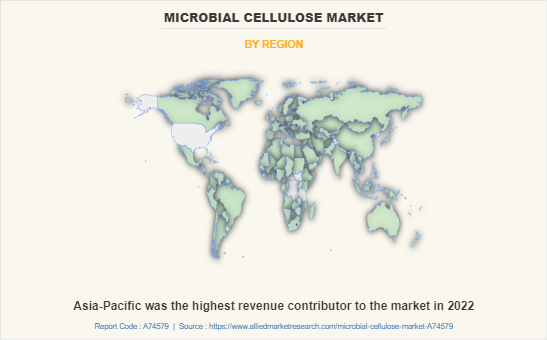
Asia-Pacific was the highest revenue contributor to the market in 2022. In recent years, there has been an upsurge in environmental pollution caused by cosmetics & personal care products made from raw materials with toxic properties. As per Frontiers Media S.A., personal care and cosmetic products containing microbeads are widely available for sale in Asia-Pacific, with over 70% of personal care and cosmetic products possessing at least one type of microbeads as an ingredient, with polyethylene being the most common one.
Hence, microbial cellulose is considered an ecofriendly biomaterial for use in cosmetics & personal care products since it is biodegradable and does not cause environmental pollution. Microbial cellulose is exceptionally promising with multiple dermo-pharmacological applications owing to its biological properties, such as high-water absorption; purity; morphology; high mechanical strength; no toxic characteristics; and high biocompatibility. Moreover, it can replace synthetic, petroleum-derived, and toxic-ecological personal care ingredients.
Further, the cosmetics sector in Southeast Asia is rising rapidly due to the growing middle-class population and the increasing purchasing power of the populace. Thus, the above-mentioned factors are expected to boost the growth of the microbial cellulose market during the forecast period.
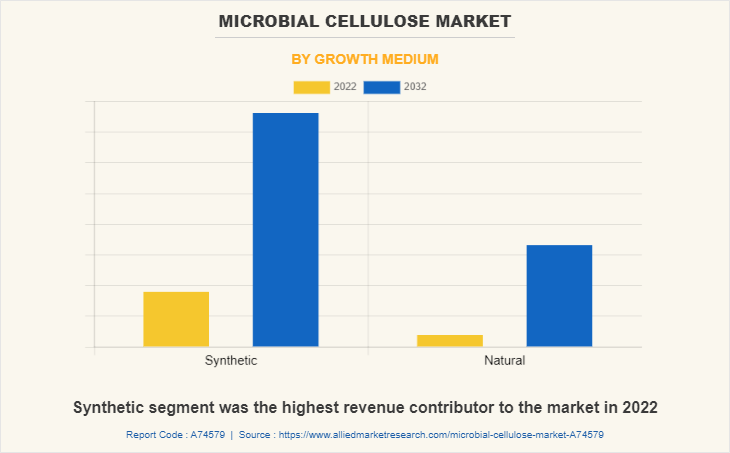
Synthetic segment was the highest revenue contributor to the market in 2022. Corn steep liquor (CSL) is found to be the most suitable for microbial cellulose production byAcetobacter xylinumsubsp.sucrofermentans. The lactate, which is present in CSL, promotes cell growth during the early stage of culture and functions by linking with the respiratory chain and generating energy for growth.A xylinum is the most commonly studied source of bacterial cellulose owing to its ability to make relatively high levels of polymer from an expansive range of carbon and nitrogen sources.
The most popular synthetic medium for producing microbial cellulose is Hestrin–Schramm medium (HS), composed of 2% glucose, 0.5% yeast extract, 0.5% peptone, 0.27% Na2HPO4, and 1.15 g/L citric acid. During the production of microbial cellulose, other by-products, such as gluconic and other acids are formed, which can reduce the microbial cellulose yield. The HS medium composition can be further optimized for the highest microbial cellulose yield by replacing glucose with other carbon sources, including sucrose, maltose, cellobiose, fructose, mannitol, xylose, galactose, and others.
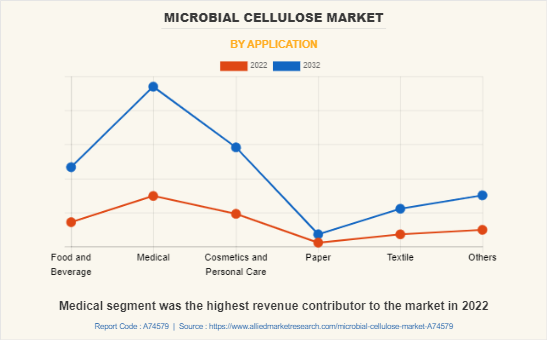
Medical segment was the highest revenue contributor to the market in 2022. Microbial cellulose is a biomaterial and used in various applied scientific areas, such as biomedical devices. In recent years, the biomedical materials have been gaining popularity due to the grown interest in tissue engineering materials for wound care and regenerative medicine.
Microbial cellulose membrane is utilized as a wound-healing device for damaged skin. It also functions as a scaffold for producing numerous tissue-engineered constructs. Besides, microbial cellulose membranes, having a distinctive nanostructure, have multiple other applications in wound healing and regenerative medicine, such as periodontal treatments, guided tissue regeneration, or a replacement for dura mater (a membrane which surrounds brain tissue).
Further, microbial cellulose is widely used in numerous surgical fields. Microbial nanocellulose patches are remarkable biological dressings functioning as temporary skin substitute when applied to exudative and bleeding tissues. This is crucial in wounds with a substantial loss of tissue, such as ulcers or burns. Furthermore, it is an incredible scaffold for type I collagen synthesis by mesenchymal stem cells.
Major players operating in the global microbial cellulose market includes Ashland, Axcelon Biopolymers Corporation, BacPolyZyme, BIOESQUE, Borregaard AS, BOWIL Biotech Sp. z o.o., HBBE, HNB BIO CO., LTD, HYSSES, and Merck KGaA. These players adopted several growth strategies such as product launch and collaboration to strengthen their position in the market.
Key Benefits For Stakeholders
- This report provides a quantitative analysis of the market segments, current trends, estimations, and dynamics of the microbial cellulose market analysis from 2022 to 2032 to identify the prevailing microbial cellulose market opportunities.
- The market research is offered along with information related to key drivers, restraints, and opportunities.
- Porter's five forces analysis highlights the potency of buyers and suppliers to enable stakeholders make profit-oriented business decisions and strengthen their supplier-buyer network.
- In-depth analysis of the microbial cellulose market segmentation assists to determine the prevailing market opportunities.
- Major countries in each region are mapped according to their revenue contribution to the global market.
- Market player positioning facilitates benchmarking and provides a clear understanding of the present position of the market players.
- The report includes the analysis of the regional as well as global microbial cellulose market trends, key players, market segments, application areas, and market growth strategies.
Microbial cellulose Market Report Highlights
| Aspects | Details |
| Market Size By 2032 | USD 64.5 million |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 12.2% |
| Forecast period | 2022 - 2032 |
| Report Pages | 204 |
| By Growth Medium |
|
| By Application |
|
| By Region |
|
| Key Market Players | BacPolyZyme, HBBE, Ashland, BOWIL Biotech Sp. z o.o., Merck KGaA, HYSSES, BIOESQUE, Axcelon Biopolymers Corporation, Borregaard AS, HNB BIO CO., LTD. |
Analyst Review
According to the opinions of various CXOs of leading companies, microbial cellulose market is driven by rise in demand from medical industry. Microbial cellulose is extensively used as a wound?dressing, particularly in burn cases. It is considered that burns treated with microbial cellulose coverings heal faster than conventional treatments. The microbial cellulose topical applications are useful owing to the water vapor permeability of microbial cellulose and water-holding capacity. The high water-holding ability offers a moist atmosphere at the injury site, which is crucial in healing. Furthermore, the microbial cellulose molds remarkably well to the surface of the skin,delivering a conformal covering even in challenging places to dress wounds, such as areas on the face. Moreover, microbial cellulose is used to treat wounds from venous ulcers. Conventional gauze dressings are treated with a microbial cellulose biopolymer in order to improve the properties of the gauze.???
Further, microbial cellulose also has broad applications in commercial industries. In papermaking, microbial cellulose is employed as an ultra-strength paper and as a reticulated fine fiber network with coating, thickening, binding, and suspending properties. Owing to its low dynamic loss and high sonic velocity,?microbial cellulose has been utilized as an acoustic or filter membrane in high-fidelity loudspeakers and headphones. Also, microbial cellulose is employed as an additive in the? cosmetics & personal care industry. It is also being tested in the textile sector for producing cellulose-based clothing.?
The global microbial cellulose market was valued at $20.7 million in 2022, and is projected to reach $64.5 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 12.2% from 2023 to 2032.
The growth of the global microbial cellulose market is majorly attributable to its wide applications such as personal care products, biomedicine, household chemicals, textile, composite materials, and others. Moreover, growth in demand for microbial cellulose from the food & beverage industry is expected to drive the market growth during the forecast period.
Medical is the leading application of microbial cellulose Market
Asia-Pacific is the largest regional market for microbial cellulose.
The report covers profiles of key industry participants such as Ashland, Axcelon Biopolymers Corporation, BacPolyZyme, BIOESQUE, Borregaard AS, BOWIL Biotech Sp. z o.o., HBBE, HNB BIO CO., LTD, HYSSES, and Merck KGaA.?
Loading Table Of Content...
Loading Research Methodology...



