The global nuclear bombs and missiles market size was valued at $81.7 billion in 2022, and is projected to reach $137.3 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 5.4% from 2023 to 2032.
Report Key Highlighters:
- The nuclear bombs and missiles market studies more than 15 countries. The research includes a segment analysis of each country in terms of value ($ million) for the projected period 2022-2032.
- The study integrated high-quality data, professional opinions and analysis, and critical independent perspectives. The research approach is intended to provide a balanced view of global markets and to assist stakeholders in making educated decisions to achieve their most ambitious growth objectives.
- Over 3,700 product literature, annual reports, industry statements, and other comparable materials from major industry participants were reviewed to gain a better understanding of the market.
- The nuclear bombs and missiles market share is moderately fragmented, with several players including includes Airbus, Ariane group Sas, BAE Systems, Brahmos Aerospace, Lockheed Martin Corporation, MBDA, Northrop Grumman Corporation, Rafael Advanced Defense Systems Ltd, Raytheon Technologies Corporation, and Boeing. Key strategies such as contract, product upgrade/development, and other strategies of the players operating in the market are tracked and monitored.

Nuclear bombs and missiles function by rapidly releasing nuclear energy through a combination of fission or fission mechanisms. The historic "Trinity Test" marked the first nuclear weapons test on July 16, 1945. A month later, the U.S. dropped atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, and in 1949, the Soviet Union conducted its inaugural nuclear weapons test. During the 1960s, the U.S. possessed approximately 30,000 weapons, while in the 1980s, the Soviet Union had amassed over 40,000.
Presently, over 90% of the 19,000 existing nuclear weapons are attributed to the U.S. and Russia. The nine countries currently possessing nuclear weapons include North Korea, China, India, Pakistan, the U.S., Russia, the U.K., and France. Since 1970, the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty has garnered 189 signatories. This treaty actively encourages recognized nuclear-weapon states to engage in disarmament efforts and acknowledges the right of non-nuclear-weapon states to pursue peaceful nuclear technology. The NPT has three pillars: nonproliferation, the right to peaceful nuclear technology, and disarmament.
Factors such as increase in investments by government bodies and corporate giants, increase in cross border conflicts, and rise in nuclear testing and technology transfers drive the growth of the nuclear bombs and missiles market. However, international treaties and consortiums discouraging nuclear testing, and high initial investment and maintenance cost hinder the growth of the market. Furthermore, collaboration with government bodies and defense organizations, and technological advancements offer remarkable growth opportunities for the players operating in the nuclear bombs and missiles industry.
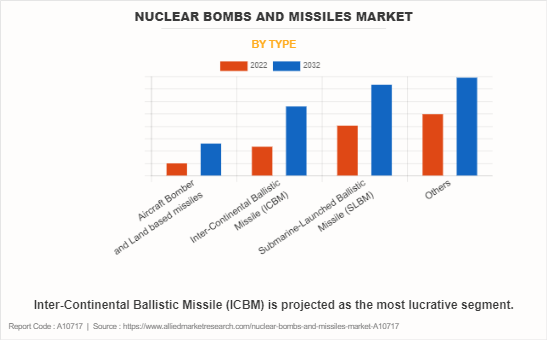
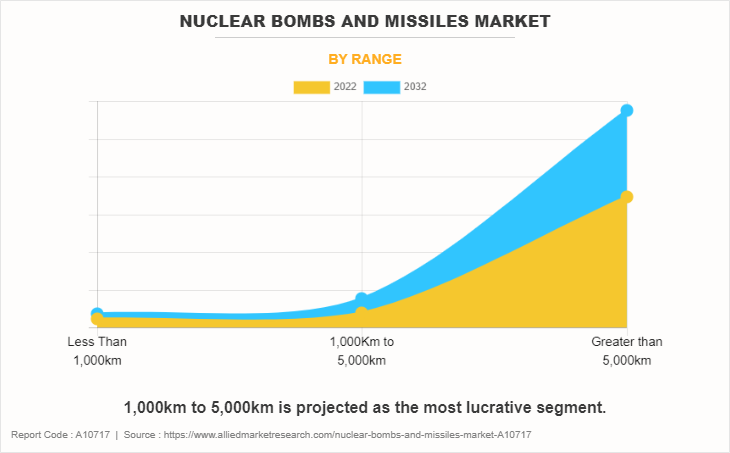
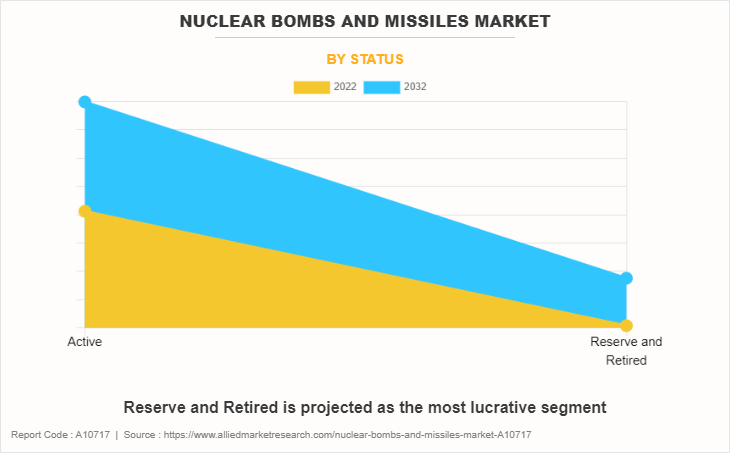
The nuclear bombs and missiles market report is segmented based on type, range, status, and region. In terms of type, the segmentation encompasses aircraft bombers and land-based missiles, including intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBM), submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBM), and other specialized categories. By range, the market is categorized into less than 1,000km, 1,000km to 5,000km, and greater than 5,000km. By status segment, it is further fragmented into active, reserve, and retired. By region, the market analysis is studied across North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and LAMEA.
Key companies highlighted in the nuclear bombs and missiles market research report include Airbus, Ariane Group SaaS, BAE Systems, BrahMos Aerospace, Lockheed Martin Corporation, MBDA, Northrop Grumman Corporation, Rafale Advanced Defense Systems Limited, Raytheon Technologies Corporation, and Boeing. These companies play pivotal roles in shaping the dynamics of the market, contributing to advancements and innovations within the industry.
North America nuclear bomb and missile market including U.S is expected to be affected by increases in national defense budgets for overall nuclear weapons production. The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) forecasts that the U.S. nuclear forces plan to spend $756 billion on nuclear weapons between 2023 and 2032. The study projects an increase of $122 billion compared to the Congressional Budget Office’s (CBO) previous forecast for that period in 2021–2030. In July 1945, the United States conducted its first atomic bomb test, followed by the use of atomic bombs in August 1945 on Hiroshima and Nagasaki in Japan Currently, the United States possesses 1,419 strategic warheads distributed among various bombers and missiles, with continuous initiatives underway to modernize its nuclear delivery systems. The first hydrogen bomb, detonated at Enewetak Atoll in the Marshall Islands, surpasses the Nagasaki bomb in power by 500 times.
The expansion of the nuclear bombs and missiles market is linked to the allocation of defense budgets. The fiscal year 2023 budget proposal unveiled by the Biden administration outlines a distinct allocation of $50.9 billion earmarked for nuclear weapons. Within this financial framework, a significant allocation of $16.5 billion is specifically designated for the Department of Energy's semi-autonomous National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA). The NNSA holds crucial responsibilities for the development and maintenance of the nation's nuclear weapons arsenal. This targeted allocation underscores the administration's dedication to preserving and enhancing the capabilities of the country's nuclear deterrent, signifying a strategic commitment to national security. The remaining $34.4 billion is allocated to the Pentagon, where it intricately supports the development of nuclear delivery systems.
Notably, this financial commitment constitutes 6.5% of the nation's overall defense budget, signifying an 18% increase compared to the expenditures in the preceding fiscal year. Increased financing for R&D for nuclear capabilities, is expected to stimulate the nuclear bombs and missiles market. Moreover, the country carries out testing of nuclear weapons such as missiles to maintain their reliability and functionality. In September 2023, the Air Force routinely test-fired an unarmed Minuteman III intercontinental ballistic missile over the Pacific Ocean This test launch plays a key role in confirming the accuracy and reliability of the ICBM weapon system, and provides valuable information to support the safety, security and effectiveness of ongoing nuclear deterrence. In addition, the escalated geopolitical tensions, both on a regional and global scale, are expected to drive an augmented demand for nuclear capabilities. In response to perceived threats, the U.S. government may opt to invest in reinforcing its nuclear deterrent, potentially influencing market growth.
Increase in Investments by Government Bodies and Corporate Giants
Increased financial commitments imply a dedication to update and potentially expand nuclear capabilities. Governments and prominent corporations are allocating resources to nuclear weapons initiatives to improve the efficiency, reliability, and technological sophistication of their arsenals. The increase in investments from diverse nations may indicate changes in the broader global strategic scenario, hinting at a reassessment of geopolitical threats and a motivation to exert influence globally through strengthened nuclear capabilities. Russia and the U.S. jointly possess nearly 90% of the world's nuclear weapons. The sizes of their usable nuclear arsenals appear to have remained relatively consistent in 2022, despite a decrease in transparency following Russia's invasion of Ukraine in February 2022. In addition to their operational nuclear weapons, both countries maintain over 1000 retired warheads, gradually undergoing dismantlement.
The Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) reported that China's nuclear warheads grew from 350 in January 2022 to 410 in January 2023. They predict even more growth. By the decade's end, China could hold as many intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) as the U.S or Russia. It depends on what moves they make strategically. Hans M. Kristensen, from SIPRI's Weapons of Mass Destruction Programme and the Nuclear Information Project at the Federation of American Scientists (FAS), stated 'China kicked off a significant growth of its nuclear stockpile. This raises questions regarding China's stated objective of maintaining the minimum nuclear forces necessary for national security. France proceeded with the development of a new air-launched cruise missile and a third-generation nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarine (SSBN) in 2022. In addition, programs to refurbish and upgrade existing systems are increasingly conducted in some countries.
Increase in Cross Border Conflicts
Escalation in conflicts across borders often raises security concerns among nations. Amid escalating geopolitical tensions, nations may find it crucial to boost their defense capabilities, involving the acquisition and modernization of nuclear weapons and missile systems as a deterrent against potential adversaries. Owing to cross-border conflicts, countries may perceive nuclear weapons as a strategic deterrence tool, capable of dissuading adversaries from engaging in aggressive actions due to the potentially catastrophic consequences.
This perception is expected to lead to a rise in the investments or expansions in their respective nuclear arsenals, and increase in development of nuclear weapon by nuclear bombs and missiles market producers. Moreover, the increase in cross-border conflicts is anticipated to elicit concerns about the initiation of a new nuclear arms race. As tensions intensify, multiple nations may concurrently pursue upgrades to their nuclear arsenals, creating a competitive atmosphere reminiscent of the Cold War era, thereby contributing to the growth of the market for nuclear bombs and missiles.
International Treaties and Consortiums Discouraging Nuclear Testing
Agreements and accords discouraging nuclear testing place constraints on the technological progress that nations can pursue. This hinders the advancement of more intricate and potent nuclear weapons, as testing plays a pivotal role in refining designs and enhancing efficiency. International treaties prioritize non-proliferation objectives, striving to prevent the dissemination of nuclear weapons. Consequently, nations are incentivized to curtail their nuclear testing endeavors to align with these agreements, thereby limiting the expansion of nuclear arsenals and, consequently, impeding the growth of the market for nuclear bombs and missiles. Treaties advocating against nuclear testing often underscore disarmament initiatives, encouraging nations to diminish their existing nuclear arsenals. This emphasis on disarmament redirects priorities away from the acquisition and innovation of new nuclear weapons and missiles, thereby hampering the potential growth of the market.
High Initial Investment and Maintenance Cost
The considerable initial investment necessary for the development, production, and acquisition of nuclear bombs and missiles erects a financial barrier, limiting the participation of numerous nations and consequently, impeding the overall expansion of the market. The substantial financial dedication to nuclear weapons directs funds away from crucial sectors such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure. Nations encounter difficulties in rationalizing the allocation of substantial financial resources to the nuclear bombs and missiles market, particularly when faced with urgent domestic needs.
Operating within budgetary constraints, many countries may experience financial strain by allocation of a significant portion of their budget for nuclear weapons development and maintenance. This strain can impose restrictions on the scope and pace of nuclear arsenal expansion, thereby affecting the overall growth of the market.
Collaboration with Government Bodies and Defense Organizations
Collaborative efforts enable joint research and development endeavors involving government bodies, defense organizations, and private entities. This collaborative synergy drives progress in nuclear technology, materials, and delivery systems, fostering the creation of advanced and more potent nuclear bombs and missiles. In addition, engaging in collaboration with government bodies ensures adherence to regulatory frameworks and compliance with international treaties and agreements. This backing assists in navigating legal and regulatory challenges, streamlining the pathway for the development and deployment of nuclear bombs and missiles. Overall, partnering with government bodies and defense organizations stands as a pivotal catalyst for the growth of the nuclear bombs and missiles market.

Recent Developments in the Nuclear Bombs and Missiles Industry
- In February 2022, Northrop Grumman Corporation entered into an agreement with HDT Global to supply engineering and manufacturing experience to the Air Force's Ground-Based Strategic Deterrent initiative. This will comprise weapon systems engineering, development, testing, and evaluation as well as nuclear certification.
- In January 2021, France conducted the first test launch of a modified MBDA ASMPA nuclear missile from a Dassault Rafale fighter jet. The missile's penetrating and range performance has been greatly improved, according to MBDA, because of the incorporation of a different medium energy thermonuclear component.
- In September 2021, The Boeing Company retained its contract with the U.S. Air Force for maintaining the guidance system for the Minuteman III intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM). Boeing built an ICBM (intercontinental ballistic missile) weapon system that served as the reliable and lasting ground-based leg of the U.S. nuclear triad.
- In July 2021, Raytheon Technologies Corporation received $2 billion contract from the United States U.S. Air Force to create the Pentagon's next air-launched nuclear cruise missile. Raytheon Corporation is delivering advancement for the (LRSO) long-range standoff weapon, which would be replacing the AGM-86B Air Launched Cruise Missile, often called as ALCM, which provided air-launched capabilities as an element of the nuclear triad in the 1980s.
- In June 2021, Raytheon Technologies Corporation signed a $2 billion contract with the U.S. Air Force to develop a long-range standoff nuclear cruise missile that carries B-52 & B-21 bombers.
- In September 2020, Northrop Grumman Corporation signed a contract to update the United States U.S. Air Force's aging intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) system. According to the Air Force Nuclear Weapons Center, the project will last 8.5 years and will comprise weapon systems integration, qualifying, testing and evaluation, and nuclear certifications.
Key Benefits For Stakeholders
- This report provides a quantitative analysis of the market segments, current trends, estimations, and dynamics of the nuclear bombs and missiles market analysis from 2022 to 2032 to identify the prevailing market opportunities.
- The market research is offered along with information related to key drivers, restraints, and opportunities.
- Porter's five forces analysis highlights the potency of buyers and suppliers to enable stakeholders make profit-oriented business decisions and strengthen their supplier-buyer network.
- In-depth analysis of the market segmentation assists to determine the prevailing market opportunities.
- Major countries in each region are mapped according to their revenue contribution to the global market.
- Market player positioning facilitates benchmarking and provides a clear understanding of the present position of the market players.
- The report includes the analysis of the regional as well as global nuclear bombs and missiles trends, key players, market segments, application areas, and market growth strategies.
Nuclear Bombs and Missiles Market Report Highlights
| Aspects | Details |
| Market Size By 2032 | USD 137.3 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 5.4% |
| Forecast period | 2022 - 2032 |
| Report Pages | 260 |
| By Type |
|
| By Range |
|
| By Status |
|
| By Region |
|
| Key Market Players | MBDA, Rafael Advanced Defense Systems Ltd., Raytheon Technologies Corporation, BrahMos Aerospace, Boeing, Northrop Grumman Corporation, Lockheed Martin Corporation, BAE Systems, Airbus, ArianeGroup SAS |
The global nuclear bombs and missiles market was valued at $81,694.2 million in 2022, and is projected to reach $137,261.5 million by 2032, registering a CAGR of 5.4% from 2023 to 2032
The leading companies profiled in the report include Airbus, ArianeGroup SAS, BAE Systems, Brahmos Aerospace, Lockheed Martin Corporation, MBDA, Northrop Grumman Corporation, Rafael Advanced Defense Systems Ltd, Raytheon Technologies Corporation, and Boeing.
The largest regional market for nuclear bombs and missiles is North America.
The leading range of nuclear bombs and missiles market is greater than 5,000km
The upcoming trends of nuclear bombs and missiles market in the world are collaboration with government bodies and defense organizations, and technological advancements
Loading Table Of Content...
Loading Research Methodology...


