Nuclear Waste Management Market Overview
The global nuclear waste management market was valued at USD 4.8 billion in 2022, and is projected to reach USD 5.7 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 1.9% from 2023 to 2032.
Nuclear waste management refers to the handling, storage, and disposal of radioactive waste generated from nuclear power plants, nuclear research facilities, and other applications of nuclear technology. Effective management of nuclear waste is essential to protect human health and the environment from the potentially harmful effects of radiation. Nuclear waste is typically classified into different categories based on its radioactivity, half-life, and other characteristics. The most common classification systems include high-level waste (HLW), intermediate-level waste (ILW), and low-level waste (LLW). HLW contains highly radioactive materials and requires the most stringent containment measures.

Nuclear power plants and research facilities often store waste on-site in specially designed-storage facilities. These facilities may include pools or dry cask storage systems, depending on the type and level of radioactivity. On-site storage is usually an interim solution until a permanent disposal method is determined. When nuclear waste needs to be transported from one location to another, strict safety measures are followed. Specialized containers, such as robust casks, are used to ensure the safe transportation of radioactive materials. Transport routes and security protocols are carefully planned to minimize the risks associated with accidents or unauthorized access. The preferred long-term solution for high-level and some types of intermediate-level waste is geological disposal. This involves burying the waste deep underground in stable geological formations, such as deep rock formations or salt deposits. The idea is to isolate the waste from the biosphere and allow natural barriers, such as multiple layers of rock, to contain the radiation.
Before disposal, various techniques are employed to reduce the volume of nuclear waste. These methods include compaction, incineration, and vitrification. Vitrification involves transforming liquid waste into a solid glass form, which enhances its stability and reduces the risk of leaching. Ongoing R&D are crucial for improving nuclear waste management techniques. This includes developing advanced methods for waste treatment, exploring alternative disposal options, and studying the long-term behavior of waste materials in different environments.
Market Dynamics
Proper management of nuclear waste allows continued operation and expansion of nuclear power, contributing to a diversified energy mix and reduced greenhouse gas emissions. Effective nuclear waste management ensures the safe handling, storage, and disposal of radioactive materials, minimizing the risk of exposure to radiation for workers, the public, and the environment. Proper containment and isolation of waste help protect ecosystems and prevent contamination of soil, water, and air. Waste volume reduction techniques, such as compaction and vitrification, help reduce the overall volume of nuclear waste. This enables efficient use of storage space and reduces the need for additional disposal facilities. In addition, some components of nuclear waste, such as spent fuel, be reprocessed to extract valuable resources & reduce waste volume. Such factors drive the market growth for the nuclear waste management market.
Proper management of nuclear waste minimizes the potential risks associated with radiation exposure. By safely containing and isolating radioactive materials, nuclear waste management protects human health and the environment from the harmful effects of radiation. Nuclear waste management aims to prevent the release of radioactive materials into the environment, reducing the risk of contamination. Well-designed storage facilities and disposal methods ensure long-term containment and minimize the potential impact on ecosystems and natural resources.
Effective waste management techniques, such as solidification and vitrification, significantly reduce the volume of nuclear waste. This reduces the space required for storage and simplifies long-term disposal options. Nuclear waste management aims to establish long-term solutions for the safe and secure storage or disposal of radioactive waste. Technologies such as deep geological repositories provide a robust and reliable approach for isolating waste from the biosphere for extended periods, ensuring the protection of future generations. Nuclear waste management often involves reprocessing, a process that extracts valuable materials, such as plutonium and uranium, from spent nuclear fuel. These materials are recycled and reused as fuel in nuclear reactors, reducing the need for additional mining and preserving valuable resources. Reprocessing of nuclear waste contributes to the production of additional energy by utilizing the extracted plutonium and uranium in mixed oxide (MOX) fuel or advanced reactor technologies. This enhances energy sustainability and reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
Nuclear waste contains highly radioactive materials that pose hazards to human health and the environment if not effectively managed. Exposure to radiation lead to various health effects, including increased risk of cancer and genetic mutations. Strict safety measures are necessary throughout the waste management process to minimize the risk of radiation exposure. Public perception and acceptance of nuclear waste management practices is a challenge. Concerns over the potential risks associated with nuclear waste, including accidents during transportation and storage, lead to opposition and resistance from communities near waste facilities. Managing nuclear waste is expensive and the costs associated with it must be factored into the overall economics of nuclear power. The development and operation of storage and disposal facilities, transportation infrastructure, and long-term monitoring require significant financial resources. Such factors hamper the nuclear waste management market growth.
Despite safety measures, accidents or failures in waste storage or disposal facilities lead to environmental contamination. Contaminated land, water, or air could have severe consequences for ecosystems, biodiversity, and public health. The potential for leaks or breaches in containment barriers necessitates ongoing monitoring and maintenance. Nuclear waste remains radioactive for extended periods, often spanning thousands of years. Managing such long-lived waste poses challenges in terms of ensuring containment and isolation to prevent radiation exposure over prolonged timeframes. The potential hazards associated with radiation necessitate strict safety measures and long-term monitoring.
The disposal of high-level waste, which contains highly radioactive materials, presents significant challenges. Finding suitable disposal sites and implementing robust containment measures requires careful consideration of geological, environmental, and societal factors. The long-term safety and security of high-level waste is technically and socially complex to address. Nuclear waste management often faces public concerns and opposition due to fears of radiation hazards and the long-term implications of waste disposal. Public acceptance of waste management facilities, transportation routes, and disposal sites is a significant challenge, requiring open communication, transparency, and community engagement. The management of nuclear waste involves substantial financial investments for the construction, operation, and maintenance of storage and disposal facilities. Developing and implementing waste treatment technologies, transportation infrastructure, and long-term monitoring systems require significant resources. Ensuring compliance with stringent safety regulations and regulatory frameworks adds complexity to nuclear waste management. Meeting regulatory requirements and obtaining necessary permits and approvals are time-consuming and costly.
The development of advanced reactor technologies, such as small modular reactors (SMRs) and Generation IV reactors, holds promise for more efficient and sustainable nuclear power generation. These technologies often have improved waste characteristics, reduced waste production, and aid in on-site waste treatment, enhancing the overall management of nuclear waste. This is expected to offer lucrative opportunities for the nuclear waste management industry growth.
Segment Overview
The nuclear waste management market is studied on the basis of waste type, reactor type, disposal method, and region.
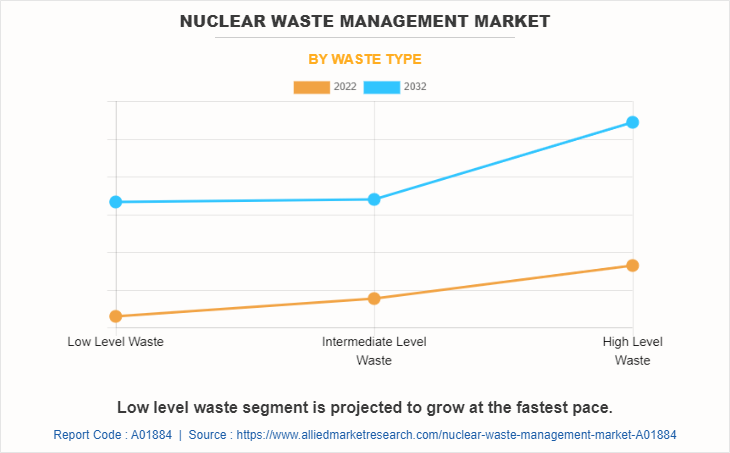
By waste type, the nuclear waste management market is divided into low-level waste, intermediate-level waste, and high-level waste. High level waste segment dominated the nuclear waste management market share for 2022. It is expected to grow at the fastest pace during the nuclear waste management market forecast period. Low-level nuclear waste (LLW) refers to radioactive materials that have relatively low levels of radioactivity and pose a lower risk compared to high-level waste (HLW) or intermediate-level waste (ILW). LLW typically includes items that have been in contact with radiation, such as protective clothing, tools, filters, and other equipment used in nuclear facilities. It includes materials from the decontamination of nuclear facilities or medical facilities that use radioactive materials for diagnostic or treatment purposes.
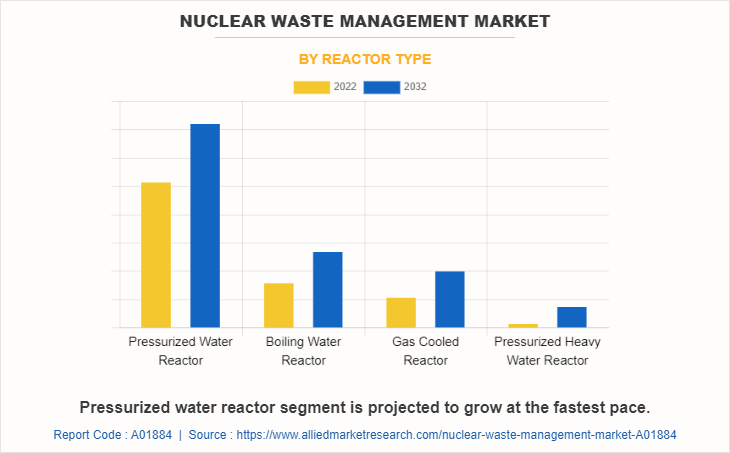
By reactor type, the market is categorized into pressurized water reactors, boiling water reactors, gas-cooled reactors, and pressurized heavy water reactors. Pressurized water reactor significantly contributed and holds the largest nuclear waste management market size. Pressurized Water Reactors (PWRs) are a common type of nuclear reactor used in commercial nuclear power plants. The management of nuclear waste generated from PWRs involves several key steps and considerations. The primary waste generated in PWRs is spent fuel, which consists of fuel assemblies that no longer sustain a chain reaction. Spent fuel is highly radioactive and requires careful handling and storage. Initially, it is stored in on-site spent fuel pools, where it is kept underwater to provide cooling and radiation shielding. The spent fuel is stored in the pools for several years to allow heat and radioactivity to decrease. The water in the pools provides radiation shielding and helps to dissipate heat generated by the spent fuel.
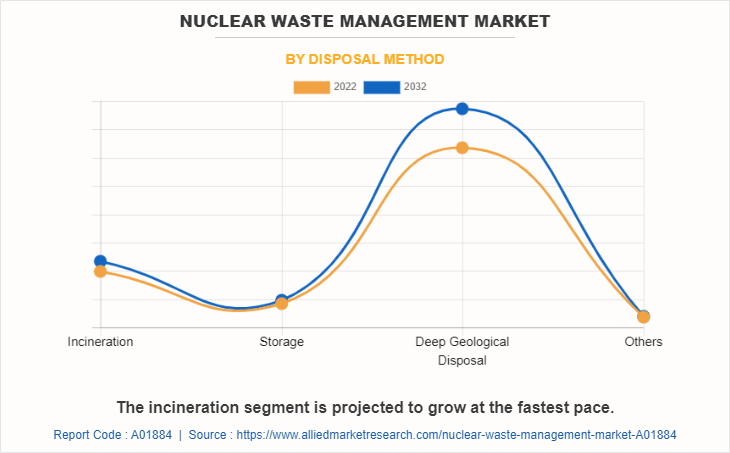
Depending on the disposal method, the market is classified into incineration, storage, deep geological disposal, and others. Deep geological disposal dominated the nuclear waste management market. Deep geological disposal is a method used for the long-term management and disposal of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) and some types of intermediate-level waste (ILW). It involves placing the waste deep underground in specially designed repositories located in stable geological formations. The process begins with site selection, which involves identifying suitable geological formations that provide long-term stability, isolation, and containment of the waste. Suitable formations may include deep rock formations, salt deposits, or clay formations. Once a suitable site is identified, the repository is designed to ensure the safe and secure containment of the waste.
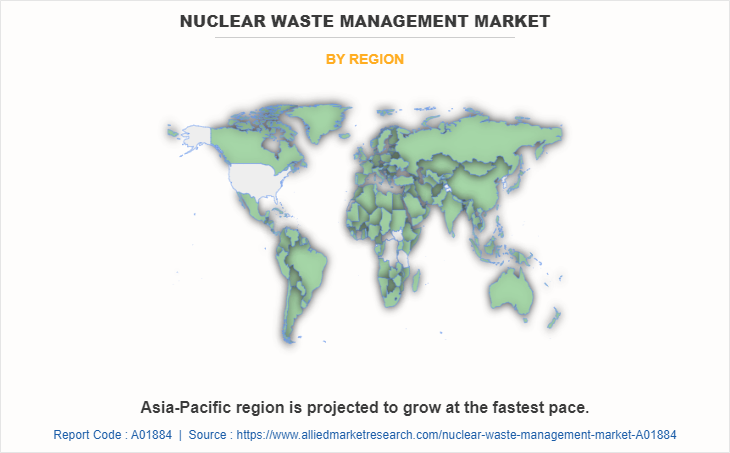
By region, the nuclear waste management market analysis is done across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA (Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa). Nuclear waste management in the Asia-Pacific region involves the handling, storage, treatment, and disposal of radioactive waste generated from nuclear power plants, research facilities, medical institutions, and other sources of nuclear technology. Reprocessing of nuclear waste has been practiced in some countries in the Asia-Pacific region, including Japan and China. Reprocessing involves the separation and extraction of valuable materials, such as plutonium and uranium, for reuse in nuclear fuel production. The remaining waste, known as high-level waste, undergoes further treatment and disposal.
Key Market Players
The major players operating in the nuclear waste management industry are Augean, Perma-Fix Environmental Services, Inc., Swedish Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Company, Stericycle, Inc., US Ecology, Inc., Veolia, Bechtel Corporation, Waste Control Specialists LLC, JGC Holdings Corporation, and Energy Solutions, Inc. These players have been adopting various strategies to gain a higher share or to retain leading positions in the market. Augean completed the acquisition of Future Industrial Services Limited (FIS). This development enhances and expands range of Augean services. EnergySolutions announced additional capabilities in support of U.S. Nuclear Plant Life Extension and New Plant Construction, and in support of the energy industry's 2050 Net Zero goals.
Key Benefits For Stakeholders
This report provides a quantitative analysis of the market segments, current trends, estimations, and dynamics of the nuclear waste management market analysis from 2022 to 2032 to identify the prevailing nuclear waste management market opportunities.
The market research is offered along with information related to key drivers, restraints, and opportunities.
Porter's five forces analysis highlights the potency of buyers and suppliers to enable stakeholders make profit-oriented business decisions and strengthen their supplier-buyer network.
In-depth analysis of the nuclear waste management market segmentation assists to determine the prevailing market opportunities.
Major countries in each region are mapped according to their revenue contribution to the global market.
Market player positioning facilitates benchmarking and provides a clear understanding of the present position of the market players.
The report includes the analysis of the regional as well as global nuclear waste management market trends, key players, market segments, application areas, and market growth strategies.
Nuclear Waste Management Market Report Highlights
| Aspects | Details |
| Market Size By 2032 | USD 5.7 billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 1.9% |
| Forecast period | 2022 - 2032 |
| Report Pages | 300 |
| By Waste Type |
|
| By Reactor Type |
|
| By Disposal Method |
|
| By Region |
|
| Key Market Players | Svensk Karnbranslehantering AB, Veolia Environnement SA., Bechtel Corporation, EnergySolutions, US Ecology, Inc., Augean, Stericycle, Inc., JGC HOLDINGS CORPORATION, Waste Control Specialists LLC (WCS), Perma-Fix Environmental Services, Inc. |
| | Others |
Analyst Review
According to the insights from the CXO’s, the nuclear waste management market has grown at a higher pace owing to a surge in dependency on nuclear energy in the primary energy mix. This was attributed to the impact of the pandemic, which led the countries to switch to nuclear sources of energy for meeting the energy demand. Post-pandemic, the nuclear energy demand was driven by the Russo-Ukrainian war, which compelled economies to divert their energy need fulfilment and become self-dependent. This led to an increase in the nuclear waste management market growth. The market faces challenges from high radioactivity of the waste, which raises several environmental and health concerns. Moreover, the risks involved in the transportation and storage of the waste hampers the nuclear waste management market growth. However, technological advancements aimed at reducing the risk during transport, storage, and advancements in waste processing offer lucrative opportunities for industry growth.
Deep geological disposal method is the leading disposal methods of Nuclear Waste Management Market.
Radioactive hazard mitigation and environment protection, volume reduction and long-term solutions, and resource conservation & energy generation are the upcoming trends of Nuclear Waste Management Market in the world.
$5.7 billion is the estimated industry size of Nuclear Waste Management by 2032.
Asia-Pacific is the largest regional market for Nuclear Waste Management.
The top companies to hold the market share in Nuclear Waste Management are Augean, Perma-Fix Environmental Services, Inc., Swedish Nuclear Fuel and Waste Management Company, Stericycle, Inc., US Ecology, Inc., Veolia, Bechtel Corporation, Waste Control Specialists LLC, JGC Holdings Corporation, and Energy Solutions, Inc.
Loading Table Of Content...
Loading Research Methodology...



