Table Of Contents

Lalit Janardhan Katare

Pooja Parvatkar
Aerostructures Market: Building the Future of Aviation Industry

Aerostructures, integral in the aviation industry, are the foundational pillars of aerospace engineering, embodying a pivotal role in the construction of an aircraft. Essentially, these components constitute the structural framework, including key elements such as wings, fuselage, tail, and their associated counterparts. Aerostructures are more than just physical parts of an aircraft. They represent the careful balance between form and function, going through detailed design processes to ensure the aircraft's overall performance and safety.
Essentially, these components carry the responsibility of maintaining the aircraft's structure, optimizing its aerodynamics, and ensuring its safety. Every aspect of their design, from shape to material choice, is carefully considered to achieve the right balance between durability and lightweight design. In simple terms, aerostructures are a blend of precise engineering and artistic design, working together to keep the aircraft flying smoothly and safely through the skies.
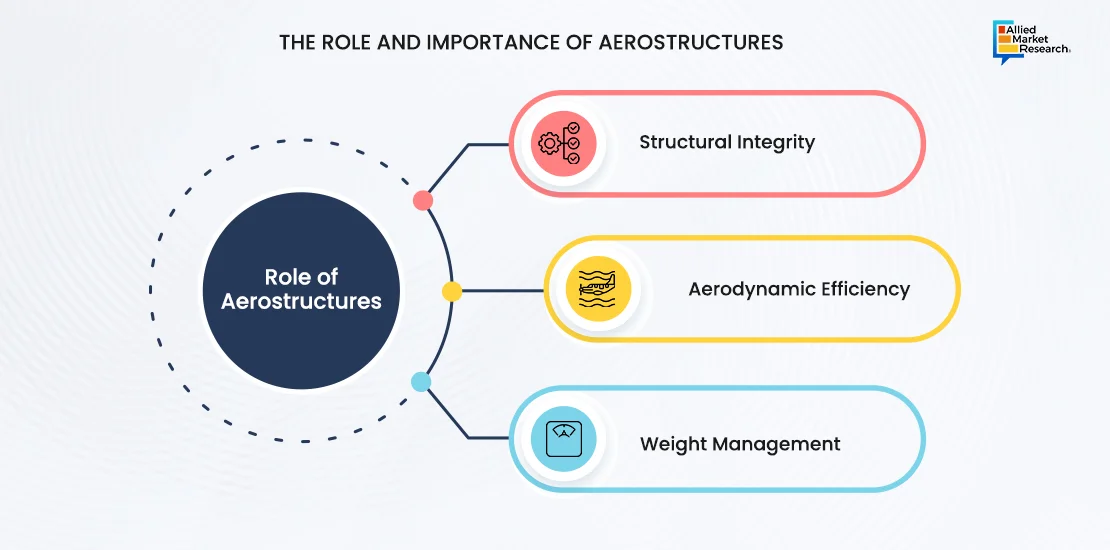
Addressing crucial user needs, aerostructures play a pivotal role in the following aspects
Structural Integrity: Structural integrity in aerostructures refers to the ability of the aircraft's framework to withstand various stresses and loads experienced during flight, ensuring a high level of robustness. This is paramount for safe and reliable flight operations. Aerostructures, such as wings, fuselage, and tail components, are designed and manufactured to endure forces such as turbulence, take-off and landing stresses, and in-flight dynamics. Aerostructures ensure safe flight by enduring turbulence and in-flight stresses. Cutting-edge materials and techniques maintain robustness, increasing the aircraft's lifespan by 10-15%.
Aerodynamic Efficiency: Aerodynamic efficiency involves optimizing the design of aerostructures to minimize air resistance (drag) and improve the overall aerodynamic performance of the aircraft. Efficient aerodynamics contribute directly to enhanced fuel efficiency by reducing the power required to propel the aircraft through the air. Optimized designs reduce air resistance, improving fuel efficiency by 15-20%. Enhanced aerodynamics also boost range and speed, aligning with sustainability goals.
Weight Management: Weight management in aerostructures involves finding an optimal balance between the need for durability and the imperative to keep the aircraft as lightweight as possible. The materials used in aerostructure construction significantly impact the overall weight of the aircraft. Use of lightweight materials decreases aircraft weight by 10-15%, directly impacting fuel consumption. This balance between durability and weight enhances payload capacity and operational performance of the aircrafts.
Currently, aerostructures technology is in an established stage of development, with continuous advancements aimed at improving performance, safety, and environmental sustainability. The global aerostructures market is characterized by sophistication in design, materials, and manufacturing processes. Recent breakthroughs in the market have been contributing to the growth of the industry.
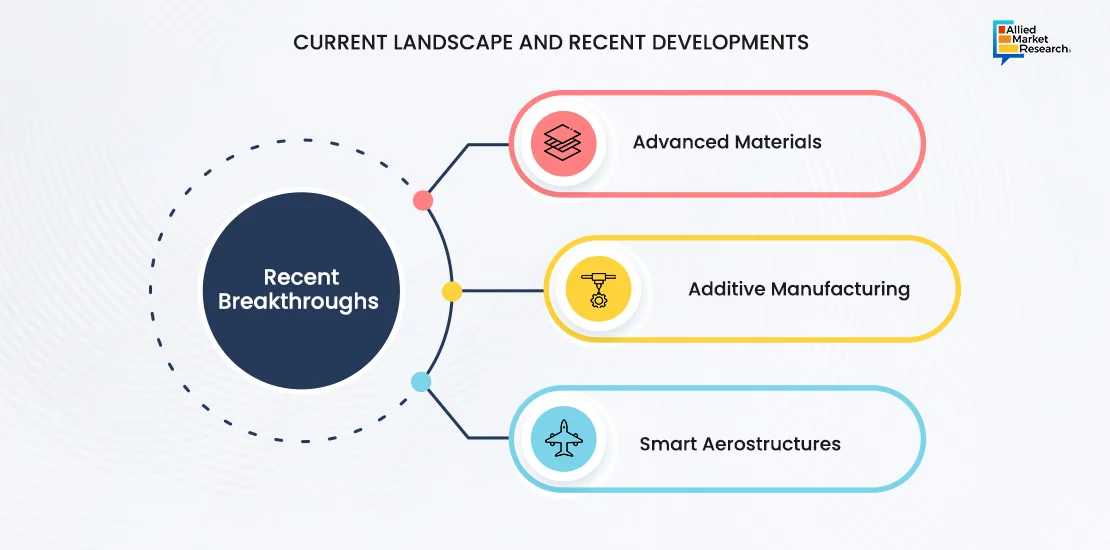
Advanced Materials: The integration of advanced materials is a pivotal aspect of modern aerostructure design, aiming to enhance structural efficiency. Lightweight and high-strength materials, such as carbon composites and titanium alloys, are strategically employed in aerostructures to achieve a favorable balance between durability and weight. Incorporating materials like carbon composites and titanium alloys improves structural efficiency. Carbon composites offer exceptional strength-to-weight ratios, reducing component mass by up to 20%. Titanium alloys enhance strength and corrosion resistance, extending aircraft lifespan by 15%.
Additive Manufacturing: The growing utilization of additive manufacturing, particularly 3D printing technologies, is transforming the production of aerostructure components. This innovative approach allows for the creation of complex and customized parts with greater precision and efficiency. Additive manufacturing cuts production time and costs by 30%, enabling complex part fabrication with 50% fewer components. This technology enhances agility, allowing quick adaptation to changing performance requirements.
Smart Aerostructures: Smart aerostructures refer to the integration of sensor technologies for real-time monitoring of the structural health of aircraft components. Integrating sensors for real-time monitoring reduces maintenance costs by 25% through predictive maintenance. Early detection of structural issues decreases downtime by 20%, optimizing aircraft operation.
Risk Factors and Hindrances
Challenges persist, including the need for further advancements in materials science, increased automation, and sustainable manufacturing practices. Also, while adoption is strong within the aerospace sector, hindrances such as high initial costs, regulatory compliance challenges, and the need for skilled labor restrict the market. Integration with emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and robotics is critical for overcoming these challenges.
Adoption of Technology
The adoption of aerostructures technology is widespread within the aerospace industry, including commercial and military aviation. There are various factors driving interest and adoption, such as
- Fuel Efficiency Demands: Amid global concerns about environmental sustainability, aerostructures innovations contribute to lighter aircraft, reducing fuel consumption and emissions.
- Advancements in Air Travel: The surge in demand for air travel, coupled with the development of more fuel-efficient aircraft, propels the adoption of advanced aerostructures.
- Military Modernization: Defense agencies globally are investing in aerostructures to enhance the performance and capabilities of military aircraft.
Early adopters are primarily within the aerospace and defense industries, but broader adoption is expected as technology matures and costs decrease.
Future Outlook
The future of the global aerostructures market holds several exciting possibilities.
- Innovative Design Architectures: Future aerostructures may explore unconventional design architectures, leveraging biomimicry, and novel structural configurations for enhanced aerodynamics and efficiency.
- Advanced Manufacturing Technologies: Continued advancements in additive manufacturing and automation will streamline production processes, reducing costs and lead times.
- Sustainability Integration: Increasing focus on sustainable practices is expected to drive the development of eco-friendly materials and manufacturing methods within the aerostructures sector.
Experts forecast a roadmap that includes increased integration with digital technologies, further automation, and a push towards sustainable aviation. Realizing the full potential of aerostructures technology requires ongoing innovations, collaboration across industries, and a commitment to addressing environmental concerns.
On an Upward Trajectory
In conclusion, the global aerostructures market is on a trajectory of sustained expansion and continual innovation. As aviation evolves, aerostructures will persist as a cornerstone element, guiding the development of the next generation of aircraft characterized by enhanced safety, efficiency, and sustainability. However, innovations in materials, manufacturing processes, and design methodologies contribute to the evolution of aerostructures, allowing for the creation of lightweight yet robust components. These advancements not only improve fuel efficiency but also address environmental concerns by reducing emissions.
Moreover, the integration of advanced technologies, such as composite materials and additive manufacturing, into aerostructures enhances the overall performance and durability of aircraft. These innovations play a crucial role in ensuring that future aviation solutions align with both economic and environmental sustainability goals.
For further insights, get in touch with AMR analysts.

