Table Of Contents

Lalit Janardhan Katare

Pooja Parvatkar
Space Tourism: Unveiling the Dynamics

Space tourism involves human space travel for leisure and recreational purposes, offering a spectrum of experiences, from suborbital jaunts to orbital odysseys and lunar escapades. In the multifaceted realm of space tourism, it is important to explore trends, dynamics, challenges, key players, costs, and the transformative experiences that it promises.
At its core, space tourism encompasses human space travel geared towards recreational pursuits. This commercial activity spans various experiences, including suborbital and orbital flights, lunar tourism, rocket launches, stargazing events, and visits to space-centric destinations.
The Advent of Space Tourism
The realization of space tourism is driven by technological strides and the entrepreneurial vision of leaders such as Elon Musk, Jeff Bezos, and Richard Branson. For instance, these billionaires are engaged in a fierce competition to pioneer the era of commercial space tourism. Their respective ventures, Virgin Galactic, Blue Origin, and SpaceX, represent cutting-edge investments, each vying to provide space journeys for affluent aspiring astronauts. The hefty price tags attached to these experiences, ranging from $250,000 to an auctioned $28 million, reflect the exclusivity of these ventures.
Branson's Virgin Galactic has secured over 600 reservations at $250,000 per ticket, with plans to commence regular commercial services in 2022, aiming to eventually reduce the ticket cost to around $40,000. Bezos' Blue Origin, while less specific about long-term pricing, recently auctioned a seat for $28 million for its suborbital mission on July 20. Meanwhile, Musk's SpaceX, having already achieved milestones like sending astronauts to the International Space Station, is set to launch an all-civilian crew into orbit in September, with ambitious plans for a lunar mission in 2023.
The design and itineraries of these spacefaring vehicles vary significantly. Virgin Galactic's SpaceShipTwo system involves a spaceplane that glides back to land on a runway after reaching 55 miles in altitude. Blue Origin's New Shepard rocket-and-capsule combo offers a 10-minute suborbital flight, featuring six observation windows—the most ever in a space vehicle. SpaceX's Crew Dragon capsule, perched atop a reusable Falcon 9 rocket, is designed for longer missions, with expectations of three to four days from launch to splashdown.
In terms of funding, Virgin Galactic operates as a publicly funded venture, with shares peaking at almost $60 following FAA approval in June 2021. Blue Origin, privately owned by Bezos, sees funding through his annual sale of around $1 billion in Amazon stock. SpaceX, also privately owned, has secured billions in funding from investors like Alphabet and Fidelity, with Musk directing charter flight fees toward missions to the moon and Mars. This dynamic competition among these visionary leaders is shaping the future of commercial space exploration.
This shift from traditional space exploration to a commercial venture is not just a scientific leap but also an economic one. Anticipated to bring about transformative economic impacts, space tourism is expected to create industries, jobs, and stimulate growth in spacecraft manufacturing, launch services, and space infrastructure. The economic prospects extend to innovations, commercialization, and revenue streams from ticket sales and luxury space experiences. While the full impact hinges on factors like regulations and risk management, space tourism represents a significant opportunity for economic expansion and human exploration.
Market Dynamics and Trends
The space tourism market is witnessing notable trends which are predicted to reshape the landscape of the market:
Diversification of Experiences: Beyond traditional suborbital flights, interest is growing in commercial flights, lunar exploration, and space hotels. Government Incentives: Increased support from governments worldwide, in the form of financial incentives, infrastructure development, and research funding, is propelling the industry forward. For instance, initiatives such as NASA Commercial Crew Program (United States), European Space Agency (ESA) Funding programs, and many more are notable aspects in the field.
Technological Advancements: Ongoing R&D efforts are focused on enhancing fuel efficiency, reducing costs, and expanding the duration of spaceflights. For instance, pioneering efforts, notably seen in companies like SpaceX, involve the development of reusable rocket technology. By enabling the recovery and reuse of certain rocket components, this innovation not only reduces manufacturing costs but also contributes to a more sustainable and economically viable space tourism industry. Ongoing research into alternative propulsion methods, such as ion propulsion, further underscores the industry's commitment to improving fuel efficiency and extending the duration of spaceflights.
Challenges in Space tourism Industry
Infrastructure Development: Creating a robust infrastructure for space tourism, encompassing refueling stations and launch facilities, remains a critical challenge for several reasons. The substantial financial investment required, coupled with the technical intricacies of designing space-ready facilities, presents a formidable barrier. Meeting stringent safety standards and navigating complex international regulations further complicate the process. Additionally, the need for collaboration among nations and private entities adds to the challenge, emphasizing the multifaceted nature of establishing the essential infrastructure for a flourishing space tourism industry.
Regulatory Framework: Navigating complex regulatory frameworks for safety protocols and certifications is crucial for gaining widespread approval. A prominent example of a challenging certification is the Federal Aviation Administration's (FAA) Commercial Space Transportation Licensing in the United States. This certification process demands strict adherence to safety standards, risk mitigation measures, and environmental considerations. Achieving compliance involves intricate assessments of engineering and technical aspects, making it a complex and time-intensive endeavor. The dynamic nature of the space tourism industry adds an extra layer of complexity, requiring continuous adaptation of regulatory frameworks to keep pace with evolving technologies.
Pioneering Companies in Space Tourism
Six major players are currently leading the charge in making space tourism a reality:
- Virgin Galactic
- Blue Origin
- SpaceX
- Boeing
- Axiom Space
- Space Perspective
While Blue Origin and Virgin Galactic focus on suborbital flights (A suborbital flight is a spaceflight in which the spacecraft reaches outer space but does not complete one orbital revolution or reach escape velocity), Axiom and Boeing are actively working on orbital missions. SpaceX, under Elon Musk's leadership, is orienting towards lunar tourism. Notably, Space Perspective is charting a unique path with its balloon-based system, set to commence commercial flights in 2024.
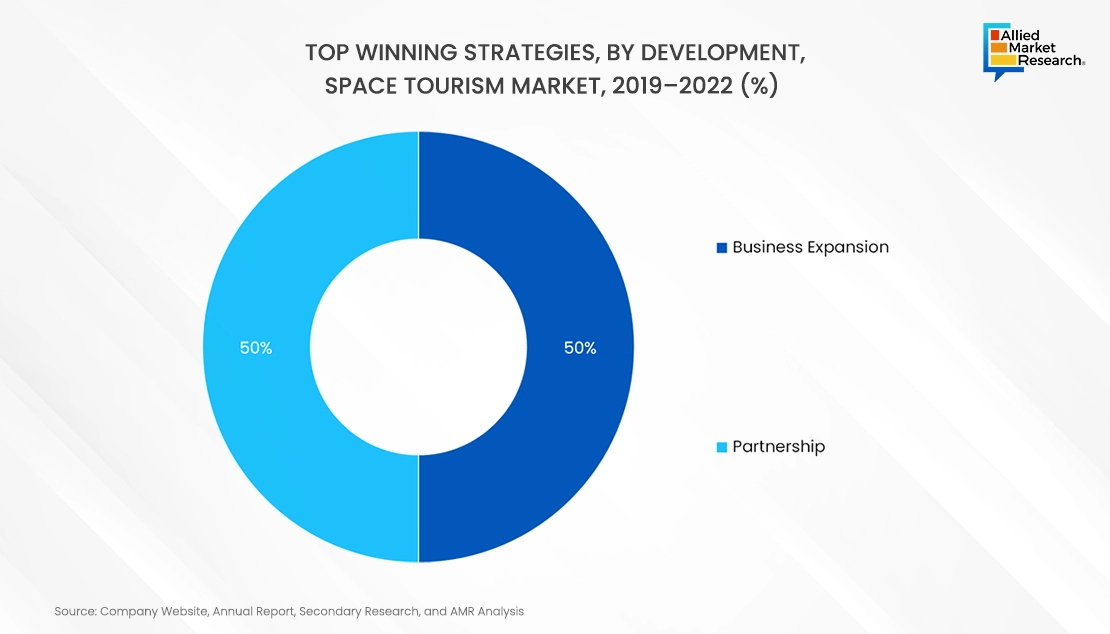
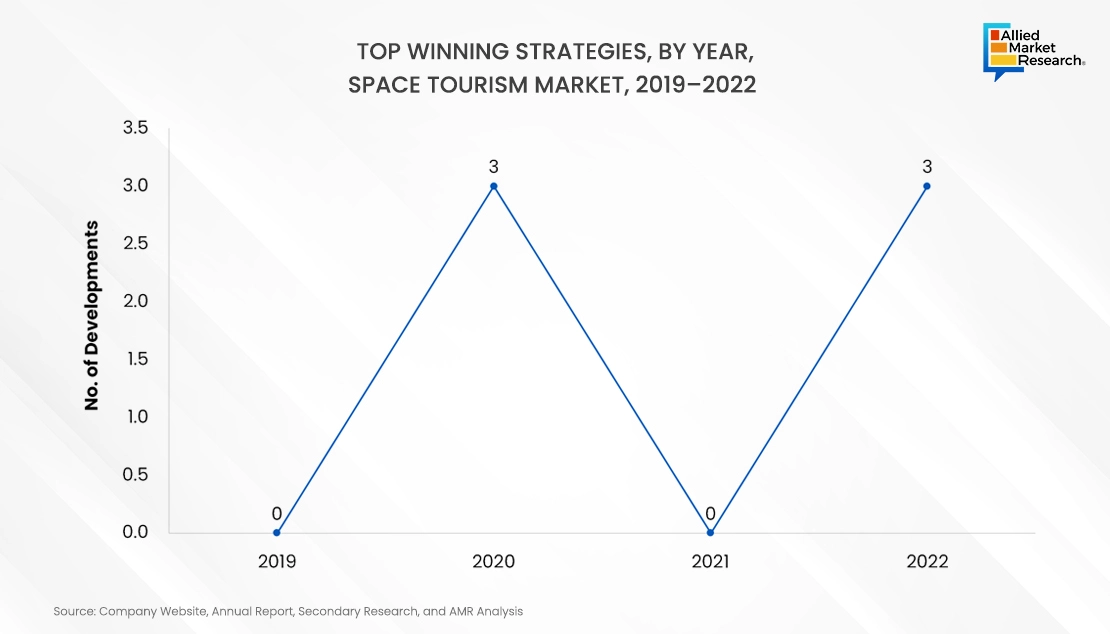
There are several strategies that these companies adopt and innovate with to stronghold their position in the market. Collaboration, product innovation, acquisitions, and innovation are few such strategies.
Affordability and Accessibility in Space Tourism
Embarking on a celestial journey comes at a price, and the costs vary depending on the type of experience:
- Virgin Galactic: $250,000 for a 2-hour suborbital flight at 80 km altitude.
- Blue Origin: Approximately $300,000 for a 12-minute suborbital flight at 100 km altitude.
- Axiom Space: $55 million for a 10-day orbital flight.
- Space Perspective: $125,000 for a 6-hour flight to the edge of space (32 km above Earth).
It's worth noting that suborbital space flights are generally more budget friendly.
Is Space Tourism Worth it?
The allure of space tourism lies in the unique experiences it offers:
- Weightlessness: A brief but captivating encounter with weightlessness during suborbital flights.
- Space Sickness: An unpredictable companion, affecting even seasoned astronauts with symptoms like nausea, fatigue, and cold sweating.
- G-force: The acceleration experienced during rocket launches, providing a firsthand encounter with the force of gravity.
Conclusion
The space tourism market size was around half million in 2021 and is expected to reach around 13 billion by 2031, registering a CAGR of 35% to 40% from 2022 to 2031. As the space tourism industry continues to rocket ahead, it marks a significant shift in how humans approach exploration. With leaps in technology, backing from governments, and a growing fascination with all things extraterrestrial, space tourism is poised for extraordinary expansion. For eager adventurers yearning for an otherworldly experience, these heavenly adventures offer a captivating peek into the potential of recreational space travel, promoting a cleaner, more environmentally friendly, and sustainable means of exploring the vast unknown. Get in touch with AMR analysts for deeper understanding of the market.

