Table Of Contents

Lalit Janardhan Katare

Pooja Parvatkar
Evolving Trends in Logistics: Challenges, Innovations, and Growth Opportunities

The logistics industry plays a critical role in the global economy by managing the movement of goods and services across various supply chain networks. This sector encompasses a wide range of activities, including transportation, warehousing, distribution, and inventory management. Logistics involves the process of coordinating and moving resources, such as equipment, food, liquids, inventory, materials, and people, from one location to the storage at the desired destination. It is the management of the flow of goods from one point of origin to the point of consumption, to meet the requirements of customers. Logistics management focuses on the efficiency and effective management of daily activities concerning the production of the company’s finished goods and services.
Logistics in the Past Decade
The logistics industry has undergone significant transformations in the past decades, shaped by technological advancements, globalization, and changing consumer expectations. Historically, logistics primarily involved the physical movement of goods from suppliers to manufacturers, and then to distributors and retailers. However, with the advent of information technology, particularly the internet, logistics evolved into a more sophisticated and interconnected system. The 20th century saw the introduction of containerization, revolutionizing maritime transport and enabling faster and more cost-effective global trade. Additionally, innovations such as barcode scanning, GPS tracking, and RFID technology improved inventory management, shipment tracking, and supply chain visibility. Furthermore, the rise of e-commerce platforms like Amazon and Alibaba has led to a paradigm shift in logistics, with a growing emphasis on last-mile delivery efficiency and customer experience.
Today, the logistics landscape is characterized by automation, robotics, and artificial intelligence, promising further optimization of processes and the emergence of concepts like drone delivery and autonomous vehicles. Amidst these changes, sustainability concerns have also come to the forefront, driving efforts towards greener practices and eco-friendly solutions in the logistics sector. Overall, the past landscape of the logistics industry reflects a continuous evolution driven by innovation, globalization, and the relentless pursuit of efficiency and customer satisfaction.

Current Face of Logistics
The logistics industry market comprises Third-Party Logistics (3PL),Fourth-Party Logistics (4PL), inbound logistics, outbound logistics, reverse logistics, green logistics, military logistics, and other logistics services. The logistic process provides efficient and effective transportation & storage of goods and services. At present, logistics services are widely being used in various applications, including warehousing, procurement, supply chain, material handling, inbound & outbound transportation, packaging, and inventory.
As per AMR analysis the global logistics market size was valued at $9,833.8 billion in 2022, and is projected to reach $16,794.7 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 5.6% from 2023 to 2032. Whereas the global fourth party logistics market was valued at $57.9 billion in 2021, and is projected to reach $111.7 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 6.7% from 2022 to 2031. Additionally, the global fifth party logistics market is expected to be valued at $9.21 billion in 2025, and is projected to reach $17.30 billion in 2035, registering a CAGR of 6.5%.
Tech-driven Logistics to be a Game Changer
Factors such as the growing e-commerce industry coupled with a rise in reverse logistics operations and surge in trade-related agreements fuel market growth. In addition, the rise of tech-driven logistics services and an upsurge in adoption of IoT-enabled connected devices are expected to drive the market growth. However, lack of control of manufacturers on logistics service, poor infrastructure, and higher logistics costs hinder the market growth. Further, the emergence of last mile deliveries, logistics automation, and cost cutting & lead time reduction due to adoption of multi-modal system are some of the factors that are expected to foster market growth.
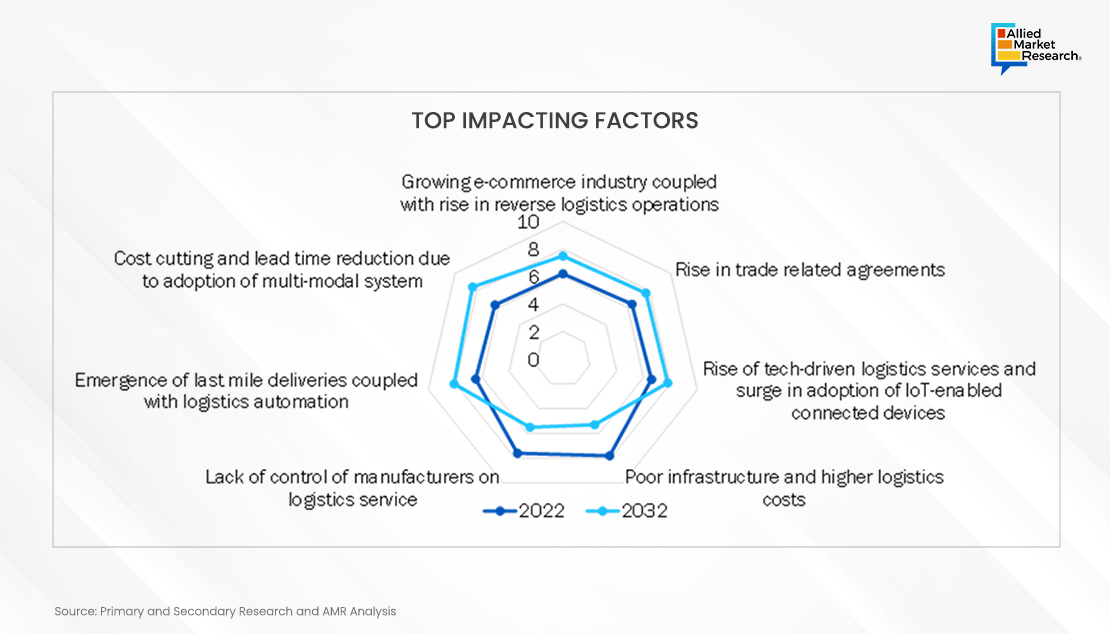
Adoption of IoT-Enabled Connected Devices
Increase in penetration of Internet of things (IoT) in the logistics sector enables freight companies and consumers direct access to the company network via the internet. The logistics infrastructure is constantly upgraded to meet the need. Surge in use of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, radio-frequency identification (RFID), and Bluetooth coupled with other newly introduced technologies, such as drone delivery and driverless vehicles, is being witnessed in logistics services. These growing technological advancements function as the catalyst to the growth of the logistics market size. In addition, some of the logistics companies across the globe have increased their spending and are using technologically advanced systems for logistics enhancement, which are further expected to propel the growth of the logistics market. For instance, SimpliRoute, an urban logistics solution, raised the $3 million funding to improve its AI-powered logistics platform.
The new funding is expected to help the startup to grow its logistics intelligence platform and expand to other countries besides Mexico, Chile, Peru, and Uruguay. In addition, AT&T provides Internet of Things (IoT) solutions for Honeywell’s transport and logistics offerings internationally in countries across Europe, North America, Latin America, Asia, Africa, and Australia.
Growing E-commerce Industry Coupled with Rise in Reverse Logistics Operations
E-commerce refers to the buying and selling of goods by using internet. Third-party logistics service providers encompass shipping of products to consumers. In addition, the e-commerce industry utilizes logistics service to manage and oversee the supply chain of e-commerce companies, which allows these companies to focus on marketing and executing other business operations. Thus, due to numerous benefits provided by logistics to the e-commerce industry, adoption of logistics service is rising at a significant rate, which is driving the growth of the logistics market.
For instance, according to the report published by the UN’s trade and development body (UNCTAD) released on April 2020, e-commerce sales hit $25.6 trillion globally in 2018, which was equivalent to 30% of the global gross domestic product (GDP). The value of global B2B e-commerce in 2018 was $21 trillion, representing 83% of all e-commerce, whereas B2C e-commerce was valued at $4.4 trillion. The growth is attributed to fast growth in consumers and cross-border purchases. According to the report, more than 1.4 billion people shopped online in 2018 while the U.S., China, and Japan dominated in e-commerce sales.
Challenges and Roadblocks to Overcome
Logistics demands good infrastructure, supply chain, and trade facilitation. Without these, firms have to build up more stock reserves and working capital, which can strongly affect national and regional competitiveness due to high financial costs. In addition, lack of infrastructure hinders the logistics market as it increases costs and reduces supply chain reliability.
These include significant inefficiencies in transport, poor condition of storage infrastructure, complex tax structure, low rate of technology adoption, and poor skills of logistics professionals. For instance, according to a report by the Economist, an international newspaper, Latin America lacks adequate infrastructure. More than 60% of the region’s roads are unpaved. Further, inconsistency in the address and postal system is the other challenge for parcel delivery in Latin American countries. As many countries lack postal codes and rely on local landmarks for addresses, shipping companies often have trouble delivering parcels successfully. Moreover, logistics costs are heavily determined by the availability and quality of infrastructure. Infrastructure directly influences transport costs and indirectly affects the level of inventories, and consequently financial costs.
Thus, owing to poor transport infrastructure, firms need to have high levels of inventories to account for contingencies, which can result in higher overall logistics costs. Therefore, poor infrastructure along with high inventory prices and insufficient warehousing space are expected to hamper the logistics market growth.
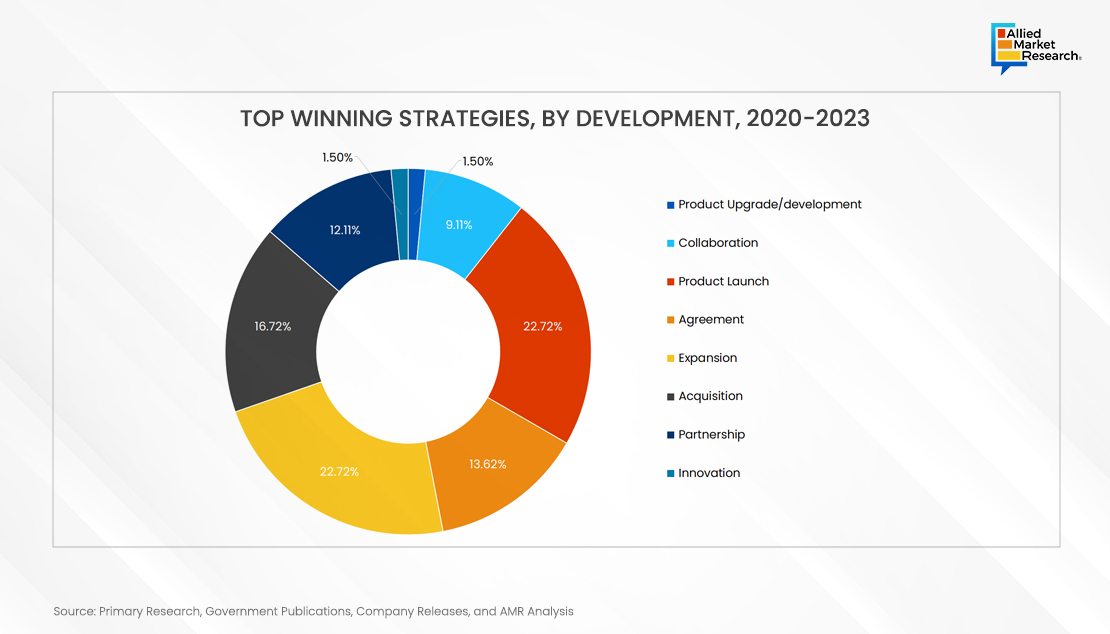
Developments by Key Players in the Market to Offer Monetary Prospects
The key players operating in the logistics industry are A.P. Moller - Maersk, C.H. Robinson Worldwide Inc., DB Schenker, Deutsche Post AG, DSV, FedEx Corporation, GEODIS, Kuehne+Nagel Inc., Nippon Express Co., Ltd., United Parcel Service of America, Inc. Post Covid-19, major of the players have adopted product launch and expansion as their key strategy to sustain in trying times.
In January 2024, CEVA Logistics signed an agreement to provide all logistics services for Scuderia Ferrari's cars and equipment during Grand Prix events as well as for GT races and Ferrari Challenge events. This strategy strengthens the relationship and mutual trust between two renowned brands in the world of motorsport and logistics.
In November 2023, DHL Group planned to open four more automated warehouses in a move to further digitize its global warehousing operations. Currently, it operates nine automated warehouses around the world, including four U.S. sites in Memphis, Tennessee; Fort Worth, Texas; Indianapolis; and Atlanta. The warehouses use automated storage and retrieval systems from AutoStore, a warehouse technology company.
In October 2023, DB Schenker signed a contract to provide third-party logistics (3PL) at an electronics spare parts warehouse in New South Wales. The logistics provider will manage the 12,800 square meter warehouses, which have four recessed docks and three on-grade docks and the capacity to handle 30,000 SKUs.
As per AMR analysis the global warehousing and distribution logistics market is projected to reach $25,788.7 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 7.7% from 2022 to 2031. The global warehousing and distribution logistics market has undergone a revolutionary transformation due to changing technological trends and the integration of advanced technologies across various industries such as FMCG and pharmaceuticals.
The Future Outlook
The widespread adoption of Internet of Things (IoT) solutions in logistics operations has further facilitated direct access to company networks for both customers and freight companies through the internet. Moreover, the logistics industry is experiencing the evolution of cutting-edge technologies, including artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, radio-frequency identification (RFID), Bluetooth, and other emerging technologies. In February 2021, Sensitech introduced IoT supply chain monitoring devices, which are real-time, multi-modal solutions designed for tracking shipments during air travel. The digital transformation of supply chains on a global scale is leading to increased efficiency and reduced waste, thereby driving the utilization of IoT-enabled devices in warehousing and logistics services. For deeper insights on the market, get in touch with AMR analysts.

