Table Of Contents

Onkar Sumant

Koyel Ghosh
Transforming Global Economies: The Future of the Remittance Market

Traditional ways of sending money, which often involved high fees, long waits, and lots of paperwork, are being replaced by more efficient, secure, and inclusive digital solutions. One of the biggest changes has come from digital payment platforms. Companies like Wise and Remitly are using mobile apps, internet banking, and digital wallets to make sending money internationally quicker and cheaper. These platforms offer lower fees and faster processing times than traditional banks and money transfer services.
Blockchain technology is also making a big impact. By enabling decentralized, peer-to-peer transactions, blockchain reduces the need for intermediaries, which lowers costs and speeds up transactions. For example, Ripple’s XRP can settle cross-border payments in seconds at a much lower cost than traditional methods. Cryptocurrencies, built on blockchain, are providing a real alternative to traditional banking, especially in places with limited financial services. In Kenya, for instance, sending $200 can cost over 8.7%. Using cryptocurrencies for remittances could reduce this cost to around 2%, saving millions of dollars each year.
Mobile wallets are another major advancement. These digital wallets allow people to send and receive money using their smartphones, eliminating the need for a bank account. In areas with limited banking access, services like M-Pesa in Kenya have significantly increased financial inclusion by enabling financial transactions through mobile phones. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are enhancing remittance platforms by making transactions more secure and efficient. AI and ML can detect and prevent fraud, ensuring transfers are safe. They also automate routine tasks and offer personalized customer support, improving the user experience.
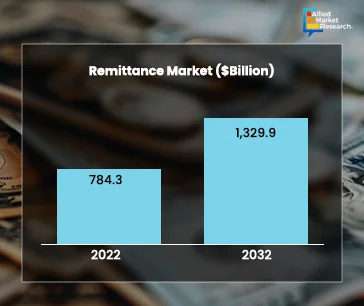
Technology is revolutionizing the remittance industry. Digital platforms, blockchain, and AI are making it easier and more affordable to send money across borders. As these technologies are evolving, the future of remittances has also become promising, with the potential to boost global financial inclusion and economic stability. The global remittance market was valued at $784.25 billion in 2022 and is estimated to reach $ 1,329.92 billion by 2032.
Economic Impact of Remittances on Developing Countries
Remittances, the funds transferred by migrants to their home countries, play a significant role in the economies of developing nations. These transfers not only provide financial support to millions of families but also contribute significantly to national economies by strengthening GDP, reducing poverty, and supporting overall economic stability.
In 2023, remittances to low- and middle-income countries were estimated to reach $669 billion, reflecting a growth of 3.8% from the previous year. This growth highlights the resilience of remittance flows, especially in times of economic uncertainty. For instance, in 2023, India received $125 billion and Mexico received $67 billion in remittances, making them important sources of foreign currency for both countries.
The economic impact of remittances is immense. On a macroeconomic level, remittances are more stable than other private capital flows, helping to mitigate the effects of economic shocks. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, remittances proved to be more resilient compared to foreign direct investment, which declined significantly. This stability is important for countries that owe a lot of money and can’t easily borrow from international markets.
On a microeconomic level, remittances directly enhance household income, reducing the incidence of poverty and enabling families to spend more on essential goods and services, such as food, healthcare, and education. In regions like Sub-Saharan Africa, remittances have been essential in combating the economic challenges posed by severe droughts and spikes in global energy and food prices. In 2022, remittances to this region grew by around 5%, despite a significant decline in growth rates from the previous year??.
Furthermore, remittances can have a profound impact on improving financial inclusion. For instance, the use of digital channels for remittance transfers has made it easier and cheaper for people to send money home, especially in rural and underserved areas. This has allowed more households to participate in the financial system, facilitating better access to savings, credit, and insurance products?.
The regional variations in the impact of remittances are also notable. In Latin America and the Caribbean, for example, remittances grew by 9.3% in 2022, significantly supporting economies like Guatemala and Colombia. Similarly, in countries like Tajikistan and Tonga, remittances account for more than 40% of GDP, highlighting their importance in maintaining economic stability and supporting development?.
Hence, remittances are essential for developing countries because they provide steady income, help with household expenses, improve access to financial services, and support overall economic stability.
Challenges and Innovations in the Remittance Industry
The remittance industry is navigating a landscape filled with both significant challenges and groundbreaking innovations. As the demand for more efficient and cost-effective money transfer solutions grows, several key obstacles and technological advancements are reshaping the sector.
The remittance industry faces several significant challenges, including high transaction costs, stringent regulatory compliance, and difficulties in maintaining banking relationships. Traditional banks often charge high fees, sometimes over 7%, for international transfers, which is burdensome for low-income migrants. Despite efforts to lower these fees, sending $200 still costs a lot. Compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) and combating the financing of terrorism (CFT) regulations adds to the operational costs and complexity for service providers. Many remittance companies also face difficulties maintaining banking relationships due to de-risking by correspondent banks, especially in high-risk areas.
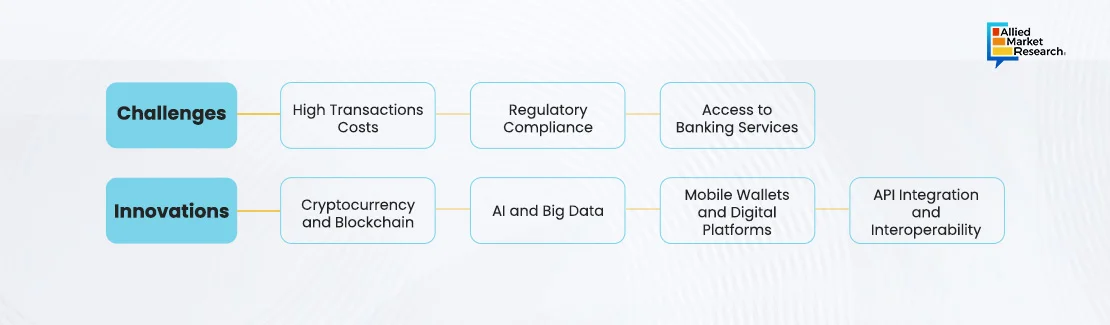
To address these challenges, the industry is embracing several innovations. The use of cryptocurrency and blockchain technology is reducing transaction costs and enabling faster transfers by facilitating direct peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries. Artificial intelligence and big data analytics enhance fraud detection, improve compliance, and offer personalized services, thereby streamlining operations. Mobile wallets and digital platforms are increasing financial inclusion by allowing users to send and receive money conveniently via smartphones, without needing traditional banks. Furthermore, API integration enables seamless transactions across various financial service providers, enhancing user experience and reducing friction in cross-border transfers. These innovations are paving the way for a more efficient and inclusive future in the remittance industry.
The Social and Cultural Influence of Remittances
Remittances are not just economic transactions; they carry significant social and cultural significance, transforming both individual lives and communities in profound ways. These transfers of money from migrants to their families back home foster social stability and promote cultural exchange, which can reshape societal norms and expectations.
Enhancing Social Welfare and Stability

Remittances often serve as a lifeline for households in developing countries, providing financial support for essential needs such as food, healthcare, and education. This influx of funds can improve living standards and reduce poverty, leading to more stable and resilient communities. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, remittances played a crucial role in helping families withstand economic shocks by acting as a form of social insurance, mitigating the impact of job losses and economic downturns?.
Promoting Education and Health
Investments in education and health are among the most significant benefits of remittances. Families use remittance money to pay for school fees, books, and other educational materials, which can increase literacy rates and educational attainment in migrant-sending countries. Similarly, funds are often allocated for medical expenses, improving overall health outcomes and life expectancy. This prioritization of education and health helps build human capital, which is essential for long-term economic development?.
Cultural Exchange and Social Remittances
Beyond financial support, remittances include the transfer of ideas, values, and practices—known as social remittances. These can influence social norms, behaviors, and identities in the migrants' home countries. Migrants often bring back new perspectives on gender roles, democratic practices, and work ethics, which can lead to cultural shifts and societal development. For instance, migrants from countries with strong democratic institutions may introduce new political ideas and practices, fostering greater civic engagement and political participation at home?.
Strengthening Family and Community Ties
Remittances reinforce family bonds and community solidarity. Regular financial support helps maintain close relationships between migrants and their families, despite physical distances. This financial and emotional connection contributes to a sense of community and shared responsibility, promoting social unity and shared well-being??.
For example, in the Philippines, remittances have played a key role in economic and social change. The country received over $38 billion in remittances in 2022, which has been used to fund education, health, and small businesses. This financial support has not only improved living standards but also enabled families to invest in local economies, thereby enhancing community development and resilience?.
Remittances are a powerful tool for social and cultural transformation. They provide critical financial support, foster cultural exchange, and strengthen family and community ties, contributing to the overall development and stability of migrant-sending countries. The evolving remittance market is expected to significantly impact global development socially and culturally.
Case Study: Transforming Remittance Processing through People, Process, and Technology
Introduction
In a competitive financial landscape, one of North America's top 10 banks faced significant challenges in its remittance processing operations. The bank was losing business to competitors and struggling to retain key sales executives. To address these issues, the bank sought to overhaul its remittance processing capabilities, aiming to enhance efficiency, service quality, and customer satisfaction.
The Challenges
Competitive Pressures: The bank was losing market share to key competitors.
Operational Efficiency: Existing systems and processes were outdated, leading to inefficiencies.
Customer Service: The bank's demanding corporate clients required high levels of service and quick access to funds.
Investment Constraints: Securing funding for necessary upgrades in an environment of selective project funding was difficult.
The Solution
The bank partnered with Conduent Financial Industry Solutions to implement a comprehensive solution focusing on people, process, and technology.
People:
Re-badging Staff: Conduent took over 300 bank staff in key locations, preserving jobs and essential knowledge while enhancing performance oversight.
Nearshore Operations: Utilizing a banking center in Guatemala City provided a cost-effective solution for keying data.
Process:
Flagship Facility: A new, advanced lockbox processing facility was opened in Chicago to demonstrate the bank's capabilities.
National Network: Conduent set up a network of capture sites in Dallas, Los Angeles, Atlanta, and Secaucus, NJ, operating 24/7 to meet the needs of corporate customers.
Technology:
Advanced Scanning Technology: New scanning equipment was installed across all sites to speed up processing and reduce errors.
Processing Software: Implemented new software to allow sites to manage volumes efficiently and provide backup during outages.
Results
The collaboration with Conduent resulted in numerous benefits:
Increased Funds Availability: The national network expedited deposit processing, enhancing fund availability for corporate customers.
Improved Service: Streamlined processes and advanced technology reduced errors and ensured consistent SLA adherence, boosting customer confidence.
Lower Costs: By moving to variable cost transaction pricing and utilizing nearshore staff, the bank significantly reduced operational costs.
Conclusion
The partnership between the bank and Conduent exemplifies how strategic investments in people, processes, and technology can transform remittance processing operations. By addressing competitive pressures, improving operational efficiency, and enhancing customer service, the bank successfully retained key customers and achieved substantial cost savings, processing $5 billion in deposits per month. This case study highlights the importance of innovation and collaboration in the financial industry, ensuring long-term success and customer satisfaction.
Future Predictions for the Remittance Market
With new technologies on board, the remittance market is changing rapidly. Blockchain and cryptocurrency are cutting costs and boosting security, while AI and machine learning are helping detect fraud and tailor services. Mobile wallets are making it easier for more people to access financial services. Plus, new regulations are driving down costs and improving transparency. Overall, these innovations are making sending money faster, cheaper, and more accessible around the world.
Allied Market Research provides detailed reports on the global remittance market, covering new technologies, market trends, and regulations. These insights help businesses find opportunities, drive innovation, and adopt better financial practices to improve efficiency and engagement.
For an in-depth analysis of the growth drivers and investment opportunities in the remittance industry, feel free to contact our experts!

