Table Of Contents

Sonia Mutreja

Koyel Ghosh
The SEMI Industry in Q4 2024: Key Developments, Investments, and Technological Progress
In Q4 2024, the semiconductor industry experienced significant developments driven by rising global demand and ongoing geopolitical tensions. Many leading businesses in the domain focused on modern technologies such as AI, chip manufacturing, and sustainability. Furthermore, regional markets such as the US, Europe, and Asia-Pacific experienced robust growth, driven by investments in domestic production and cutting-edge technologies. In this newsletter, Allied Market Research highlights all key advancements, initiatives of leading players, regional insights, and solutions to supply chain hurdles that helped the sector achieve new heights during the period.
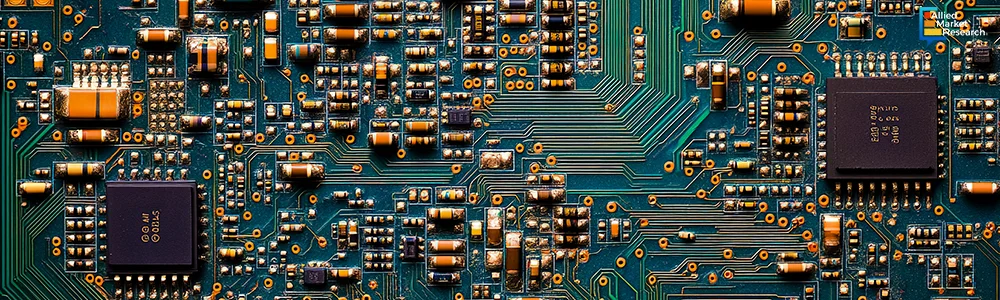
Investments made by key players in the SEMI sector in Q4 2024
In December 2024, Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co. (TSMC) led the SEMI sector with its advanced chip manufacturing technology. The company joined hands with Nvidia Corp to manufacture its Blackwell AI chips at TSMC's new Arizona facility. Preparations for production of these chips are expected to begin early next year. Previously, these chips were produced at TSMC's facilities in Taiwan, driven by high demand from clients in generative AI and accelerated computing, as they offer speeds 30 times faster for tasks like chatbot responses. This agreement would add another significant customer to TSMC's Arizona plant, which is expected to start volume production in 2025.
In Q4 2024, Samsung Electronics announced significant expansions in memory chip production to address rising demand from data centers and smartphones. The company planned to increase high-bandwidth memory (HBM) supply by at least 2.5 times compared to the previous year, driven by the growing need for AI workloads and advanced computing applications. This strategic move showcased the dominance of Samsung in the memory market.
Similarly, Intel Corporation gained momentum in the U.S. semiconductor market by opening its new fabrication facility, Fab 9, in Rio Rancho, New Mexico. This $3.5 billion investment enhanced Intel's manufacturing capabilities and enabled it to better compete with Asian manufacturers, particularly in advanced packaging technologies essential for modern computing demands.
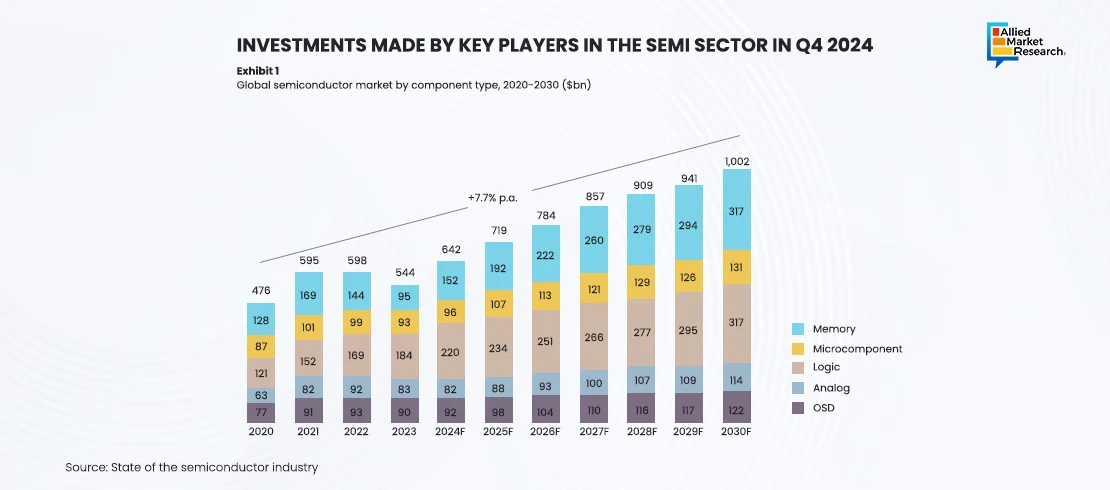
Regional highlights impacting the growth of the SEMI domain in Q4 2024
The SEMI industry experienced significant growth in different geographical areas across the globe. The U.S. semiconductor market is experiencing significant growth, influenced by robust government support through initiatives like the CHIPS Act, which promotes domestic manufacturing. Major companies such as Intel and GlobalFoundries are investing in new facilities to enhance production capabilities. Meanwhile, NVIDIA led the AI chip sector, achieving record sales fueled by the increasing adoption of AI technologies across various industries. This trend highlights the key role semiconductors play in modern electronics, driving advancements across computing, telecommunications, and automotive industries.
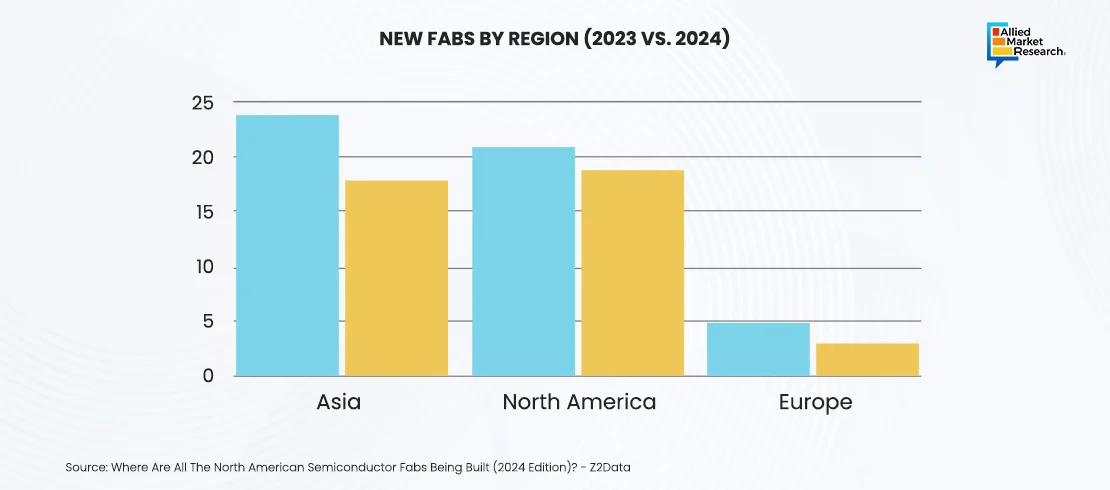
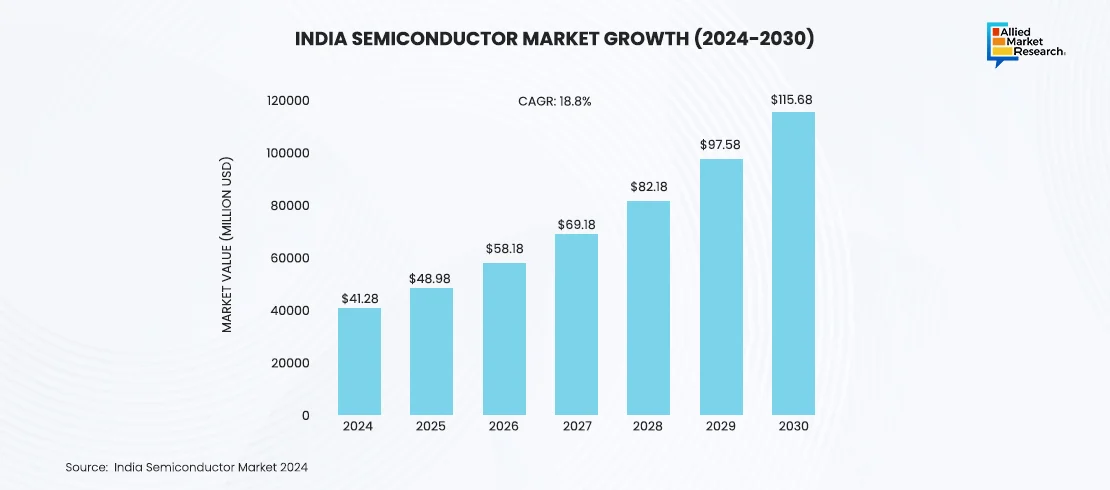
Moreover, the Asia-Pacific region also remained a strong player in Q4 2024. Taiwan and South Korea remained the leading semiconductor producers in this region, with TSMC and Samsung invested in advanced technologies like 3nm chips to sustain their market dominance. However, China’s semiconductor sector faced challenges due to trade restrictions. Also, companies such as SMIC expanded their capacity for less advanced chips. Meanwhile, the Indian semiconductor market, valued at approximately USD 41.2 billion in 2024, is projected to grow significantly in the coming years. The industry is expected to reach around USD 115.6 billion by 2030, reflecting a CAGR of 18.8% during this period. This growth strengthens the increasing importance of semiconductors in the region's economy.
In 2024, Europe mainly emphasized reducing its reliance on semiconductor imports by investing in domestic manufacturing capabilities. For instance, Bosch's semiconductor plant in Dresden, Germany, commenced a production unit to enhance the region's technological infrastructure. Additionally, TSMC established its first European fabrication facility in Dresden, with a significant investment aimed at producing automotive and industrial chips. Similarly, STMicroelectronics also ramped up production of automotive chips to support the burgeoning electric vehicle industry. These initiatives aligned with the EU's goal to increase its share of global semiconductor production from 10% to 20% by 2030, representing the region’s resolution toward achieving technological sovereignty and resilience in the semiconductor sector.
In Q4 2024, the Middle East region significantly focused on chip design rather than manufacturing, with Israeli companies leading advancements in AI and IoT chip development. This transition is driven by a growing demand for semiconductors associated with the expansion of consumer electronics and renewable energy projects. The region's semiconductor market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 9% from 2024 to 2032, reflecting strong investments in technology. With the increased demand for high-performance chips, the Middle East region stood out as a significant player in the global semiconductor landscape, capitalizing on its innovative capabilities and emerging market needs.
Notable SEMI supply chain challenges and solutions in Q4 2024
In Q4 2024, the semiconductor supply chain faced significant challenges, primarily driven by geopolitical tensions between the U.S. and China, which disrupted global trade and created uncertainty. Although the global semiconductor market showed signs of recovery, with projected sales reaching USD 588 billion, excess inventory remained a key issue, particularly in the automotive and electronics sectors. High inventory levels hindered the sales of the market in 2024 as companies worked to balance supply and demand. Additionally, manufacturing capacity utilization was below optimal levels which further restrained the profitability of many firms.
To overcome such problems, companies like TSMC and Intel took pioneering initiatives during the period. For instance, in November 2024, TSMC announced plans to establish new CoWoS advanced packaging plants in the U.S. and Japan, driven by strong demand for AI chips, particularly from NVIDIA. This strategic move aimed to diversify TSMC's supply chain amid increasing global competition and geopolitical tensions. The company envisioned doubling its production capacity in Q4 2024 and throughout 2025 to meet the rising needs of the semiconductor market. With the increased expansion of TSMC’s footprint internationally, these new facilities are expected to enhance its ability to deliver cutting-edge technology while reducing reliance on its Taiwan operations. Traditionally, Taiwan operations used to be the hub of its manufacturing capabilities.
Similarly, in Q4 2024, Intel's $20 billion investment in Ohio is expected to build two state-of-the-art chip factories, enhancing domestic semiconductor production. This initiative was taken to reduce reliance on foreign supply chains and create thousands of jobs across the US. Additionally, through this initiative Ohio became a key player in the U.S. semiconductor industry, addressing the growing demand for chips.
Simultaneously, Samsung significantly expanded its production facilities in Texas with a $45 billion investment, aiming to lessen its dependence on manufacturing operations in South Korea. This initiative included the construction of two new semiconductor fabrication plants and a dedicated research facility, boosting local job creation and boosting the U.S. semiconductor supply chain amid global shortages.
Technological advances driving sustainability in the SEMI sector in Q4 2024
In the fourth quarter of 2024, the semiconductor industry emphasized advancing smaller and faster chips, with the active involvement of companies like TSMC and Samsung in 3nm and 2nm chip production technologies. These chips utilized innovative gate-all-around (GAA) transistor architectures, enhancing performance by up to 15% while significantly reducing power consumption by 30%. These advances in chip production led to improved efficiency and increased transistor density, addressing the growing demand for high-performance computing in various applications. The mass production of 2nm chips is expected to begin in 2025.
Moreover, the increased adoption of AI-optimized chips by industry leaders like NVIDIA, AMD, and Qualcomm significantly fueled the semiconductor sector during Q4 2024. These companies focused on advanced chip designs tailored for cloud computing and autonomous systems, optimizing performance and energy efficiency. During this period, NVIDIA's dominance in AI accelerators remained strong. However, AMD's new MI325X and Ryzen AI chipsets intensified the competition prominently. Also, Qualcomm's Snapdragon X series contributed to this trend, boosting innovation and expanding market opportunities in the rapidly evolving AI landscape.
Furthermore, during the quarter, many leading manufacturers increasingly prioritized energy-efficient chip designs to meet sustainability goals, particularly for data centers and EVs. This trend was driven by the need to reduce power consumption and carbon footprints while enhancing performance. In addition, rapid innovations in low-power techniques and advanced materials enabled the development of chips that deliver high efficiency without sacrificing functionality during the period. This sustainable advancement further supported a greener future in technology and transportation and reshaped the semiconductor sector significantly.
In a nutshell
In Q4 2024, the SEMI industry demonstrated remarkable advancements in technology, regional growth, and sustainable developments by key players. With prominent geopolitical tensions and supply chain hurdles, many leading companies focused on bringing innovations and expanding globally. They emphasized adopting AI, advanced chip technologies, and sustainable practices. These moves created new opportunities and avenues across the sector during the period.
To attain more insights into the upcoming trends in the SEMI industry, feel free to reach out to our industry analysts today!

