Zero Emission Building Market Research, 2033
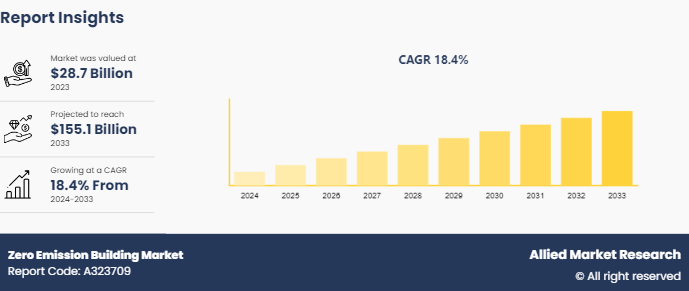
The global zero emission building market size was valued at $28.7 billion in 2023, and is projected to reach $155.1 Billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 18.4% from 2024 to 2033.
Market Introduction and Definition
Zero emission buildings are structures that are made to emit no net greenhouse gases during operation. These buildings make use of cutting-edge building materials, sustainable practices, and innovative technology to reduce energy usage. High-performance insulation, HVAC systems, energy-efficient windows, and on-site renewable energy sources such as solar and wind turbines are majorly included in these buildings.
Zero emission buildings are important for lowering greenhouse gas emissions and battling climate change. They are designed to be highly insulated, which helps prevent outdoor pollutants from entering the building. Besides, they lessen dependence on fossil fuels and other non-renewable energy sources by producing their renewable energy on-site. Also, they usually include advanced ventilation systems that deliver a constant supply of fresh air, enhancing indoor air quality and occupant health. Zero emission buildings are primarily employed by the institutional, residential, and commercial industries. They offer better internal environments and lower operating costs for institutional buildings including hospitals and schools.
Key Takeaways
The zero emission building market study covers 20 countries. The research includes a segment analysis of each country in terms of value for the projected period.
More than 1, 500 product literatures, industry releases, annual reports, and other such documents of major zero emission buildings industry participants along with authentic industry journals, trade associations' releases, and government websites have been reviewed for generating high-value industry insights.
The zero emission building market is highly fragmented, with several players including Skanska AB, Bouygues Construction, Turner Construction Company, Siemens AG, Johnson Controls International plc, Schneider Electric, Tesla, Inc., SunPower Corporation, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, and GreenTree Global.
Zero emission building market news and key industry trends are also included in the report.
Key market dynamics
The zero emission buildings industry is driven by a strengthening demand for sustainable and environment-friendly construction processes. The global focus on reducing carbon emissions and mitigating climate change is a significant driver. According to the Global Status Report for Buildings and Construction, the building and construction industry accounted for 34% of total energy demand and 37% of energy-related CO2 emissions in 2021. The sector's operational CO2 emissions from energy use exceeded 2020 levels by 5% and the pre-pandemic peak of 2019 by 2%. Furthermore, in 2021, the operating energy demand for heating, cooling, lighting, and equipment in buildings increased by roughly 4% compared to 2020.
The buildings sector accounts for a considerable portion of Europe's energy demand, encompassing 40% of the total demand. Alarmingly, 80% of this energy consumption is produced from fossil fuels. This highlights the urgent need for action, investment, and policy initiatives aimed at promoting both short-term and long-term energy security. Achieving the decarbonization of the buildings sector by 2050 is imperative for achieving significant reductions in carbon emissions and advancing sustainability goals. However, the zero emission building market growth is hindered by high initial costs, technological complexity, and regulatory barriers, which can hinder widespread adoption. Nonetheless, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation, cost reductions, and policy reforms. As the zero emission building market continues to evolve, opportunities abound for industry players to develop scalable and cost-effective solutions, leverage emerging technologies, and collaborate across sectors to accelerate the transition towards a more sustainable built environment.
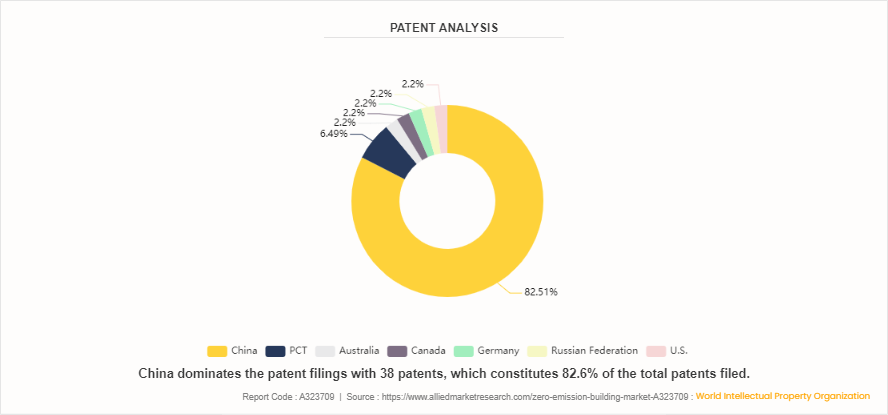
Patent Analysis of Global Zero emission building market
Market Segmentation
The zero emission building market is segmented into element type, building type, and region. On the basis of element type, the market is divided into lighting, walls & roofs, Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems, and others. As per building type, the market is segregated into residential and commercial. Region wise, the zero emission building market share is analyzed across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and LAMEA.
Competitive Landscape
The major players operating in the zero emission building market include Skanska AB, Bouygues Construction, Honeywell International Inc, Siemens AG, Johnson Controls International plc, Schneider Electric, Tesla, Inc., SunPower Corporation, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, and GreenTree Global.
Recent Key Strategies and Developments
Honeywell International Inc., formed a partnership with Nexii Building Solutions, a pioneer in green building materials and construction technology, in February 2023. The collaboration aims to bring together the experience of both companies to provide energy-saving solutions for small to medium-sized commercial buildings.
Siemens introduced the Masterguard E-Hybrid system in July 2023, with the goal of reaching net zero energy consumption. This innovative technology is made up of three primary components: energy storage, solar panels, and intelligent building controls. By integrating these components, the technology allows buildings to generate, store, and manage their own energy rather than relying heavily on the existing power system. This independence from the grid not only helps to reach the goal of zero energy use, but also contributes significantly to environmental efforts. The Masterguard E-Hybrid system decreases dependency on external energy sources, lowering greenhouse gas emissions and hence the environmental impact.
Regional/Country Industry Outlook
Governments around Asia-Pacific, including China, are initiating major initiatives to combat climate change and improve energy efficiency. They are setting ambitious objectives for lowering greenhouse gas emissions. These objectives often include incentives and restrictions to stimulate the construction of zero-emission buildings. Subsidies, tax benefits, and building codes are used to encourage sustainable construction techniques. Furthermore, these governments are synchronizing their efforts with international accords such as the Paris Agreement. This global initiative aims to keep global warming below 2 degrees Celsius. Asia-Pacific countries actively support global climate change mitigation efforts by establishing specific emission reduction targets and enhancing energy efficiency.
Furthermore, China has made significant investments in green building technology research and development, which includes renewable energy systems, energy-efficient building materials, and intelligent building controls. These developments make it easier and more cost-effective to construct zero-emission buildings in China. China has actively taken part in international efforts and collaborations to promote sustainable development and combat climate change. This includes collaborating with other nations, organizations, and projects to promote zero-emission buildings and share best practices in green building design and construction.
China, a major Asia-Pacific country, has lately taken great strides to promote energy-efficient construction standards. The T/CABEE003-2019 "Near-zero Energy Building Evaluation Standard, " issued in 2019, includes technical requirements and assessment procedures for near-zero energy building demonstration projects. This guideline evaluates the safety performance of near-zero energy buildings across the country and recommends corrective actions for projects that do not meet the standards.
The assessment method is broken down into three stages such as engineering design evaluation, construction evaluation, and operational evaluation. Energy conservation reviews involve evaluating the energy efficiency of each phase of a building's life cycle in order to detect any discrepancies between actual performance and planned outcomes. China has built about 5 million square metres of near-zero energy buildings. By the end of 2019, 18 demonstration projects around the country have reached ultra-low or near-zero energy usage levels. These buildings, which follow the "Technical Standard for Near-zero Energy Buildings, " were methodically planned and built to satisfy technical criteria while using local natural circumstances to reach their energy efficiency goals. This collaborative effort has sped up China's healthy transition to near-zero energy habits.
???Public Policies
Building guidelines and standards in several nations mandate minimum energy performance criteria for new construction and renovations. These standards frequently contain requirements for generation-efficient building envelopes, HVAC systems, lighting, and renewable energy integration. Zero emission buildings criteria may be incorporated in building regulations to promote or require zero-emission development.?
Green building certification programmes, like Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) , Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method (BREEAM) , and Green Star, offer voluntary frameworks for evaluating and recognizing?sustainable building practices. zero emission buildings can be certified by attaining specific requirements for energy efficiency, renewable energy utilization, interior environmental quality, and resource conservation.
Some jurisdictions have implemented mandates or targets for achieving net-zero energy or carbon emissions in new construction by a certain date. These mandates typically require zero emission buildings to offset all or a significant portion of their energy consumption with on-site renewable energy generation or other measures. Compliance with these mandates may be enforced through building permits, inspections, or performance reporting requirements.
Governments may offer financial incentives, grants, or rebates to encourage the development of zero emission buildings. These incentives can include tax credits for energy-efficient building technologies, subsidies for renewable energy systems, and low-interest loans for green building projects. Financial incentives help offset the higher upfront costs associated with zero emission buildings construction and incentivize developers to invest in sustainable building practices.
Key Sources Referred
World Green Building Council
European Union
Department of Energy
JRC Publications Repository
Federal Register
U.S. Green Building Council
Whole Building Design Guide
Building Energy Exchange
Key Benefits For Stakeholders
- This zero emission building market report provides a quantitative analysis of the market segments, current trends, estimations, and dynamics of the zero emission building market analysis from 2023 to 2033 to identify the prevailing zero emission building market opportunities.
- The market research is offered along with information related to key drivers, restraints, and opportunities.
- Porter's five forces analysis highlights the potency of buyers and suppliers to enable stakeholders make profit-oriented business decisions and strengthen their supplier-buyer network.
- In-depth analysis of the zero emission building market forecast assists to determine the prevailing market opportunities.
- Major countries in each region are mapped according to their revenue contribution to the global market.
- Market player positioning facilitates benchmarking and provides a clear understanding of the present position of the market players.
- The report includes the analysis of the regional as well as global zero emission building market trends, zero emission building market statistics, key players, market segments, application areas, and zero emission building market growth strategies.???????
Zero Emission Building Market Report Highlights
| Aspects | Details |
| Market Size By 2033 | USD 155.1 Billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 18.4% |
| Forecast period | 2024 - 2033 |
| Report Pages | 280 |
| By Element Type |
|
| By Building Type |
|
| By Region |
|
| Key Market Players | Johnson Controls International plc, Schneider Electric, SunPower Corporation, Tesla, Inc., Turner Construction Company, Skanska AB, Bouygues Construction, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Siemens AG, GreenTree Global. |
Analyst Review
According to CXOs, zero-emission buildings (ZEBs) are increasingly gaining attention as a crucial component in combating climate change and achieving sustainability goals. The primary drivers behind the adoption of ZEBs include stringent environmental regulations, heightened public awareness of climate issues, and the economic benefits associated with energy efficiency. Governments worldwide are implementing policies and incentives to promote ZEBs, such as tax rebates, grants, and certifications like LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method). Additionally, there is a growing market demand for green buildings, driven by both corporate sustainability initiatives and individual consumer preferences. Businesses are recognizing that sustainable buildings can enhance their brand image, attract environmentally conscious customers, and improve employee satisfaction and productivity. Furthermore, the long-term cost savings from reduced energy consumption and maintenance are compelling financial motivators for both residential and commercial property owners to invest in zero-emission buildings.
Loading Table Of Content...



