Table Of Contents
- Decoding the Details of Defense Cybersecurity
- Assessing the Impacts of Assiduous Attacks
- SolarWinds Supply Chain Attack
- Defense in Depth
- Unveiling the Advantages of Defense Cybersecurity
- Redefining Cybersecurity in Defense with Integration of IoT and AI
- LAWS to Enhance Security
- Navigating the Challenges in Defense Cybersecurity

Onkar Sumant

Akshata Tiwarkhede
Defense Cybersecurity: Fortifying the Digital Fortress

In today's interconnected world, where digital technologies are penetrating in every sector, the security of cyberspace has become paramount. With the exponential growth of digital data and the proliferation of online transactions, safeguarding sensitive information from cyber threats has emerged as a critical concern for governments, businesses, and individuals. Thus, defense cybersecurity serves as the first line of defense to mitigate the risk of cybercrime.
Decoding the Details of Defense Cybersecurity
Defense cybersecurity encompasses a comprehensive set of strategies, technologies, and practices aimed at protecting digital systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, cyberattacks, and data breaches. Unlike traditional cybersecurity, which focuses on preventing, detecting, and responding to cyber threats within individual organizations or networks, defense cybersecurity takes a broader, more holistic approach. It involves collaboration between public and private sectors, information sharing, threat intelligence analysis, and the development of proactive defense measures.
One of the fundamental principles of defense cybersecurity is the concept of defense-in-depth. This strategy involves deploying multiple layers of security controls and measures, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, antivirus software, encryption, access controls, and security awareness training for personnel to create overlapping defenses, thereby increasing the resilience of digital systems and networks.
Assessing the Impacts of Assiduous Attacks
The consequences of a successful cyberattack can be catastrophic, ranging from financial losses and reputational damage to disruption of critical services and loss of life. The recent wave of high-profile cyber incidents, including the SolarWinds supply chain attack and the Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack, serve as the stark reminders of vulnerabilities inherent in the digital infrastructure.
SolarWinds Supply Chain Attack
One of the major cybersecurity breaches of the 21st century was the SolarWinds hack. This was one of the epoch-making events not only because a single company was involved but also because a large supply chain was impacted, affecting a myriad of organizations, including the U.S. Government. SolarWinds—a major software-based company—has access to IT systems to obtain system performance data, as it is a key provider of an IT performance monitoring system, Orion. Orion network management system is used by more than 30,000 public and private organizations to manage their IT resources. In was December 2020, a malware called SUNBURST was inserted into a software update by unknown actors. This act granted access to data and network of its customers and partners, including government agencies across the globe and the U.S. military. The malicious updates were installed by more than 18,000 customers of SolarWinds.
Microsoft also reported that it has found the malware in its systems. To cut off hackers from the customers’ systems, Microsoft collaborated with GoDaddy and FireEye to block Orion, which was known to contain the malware.
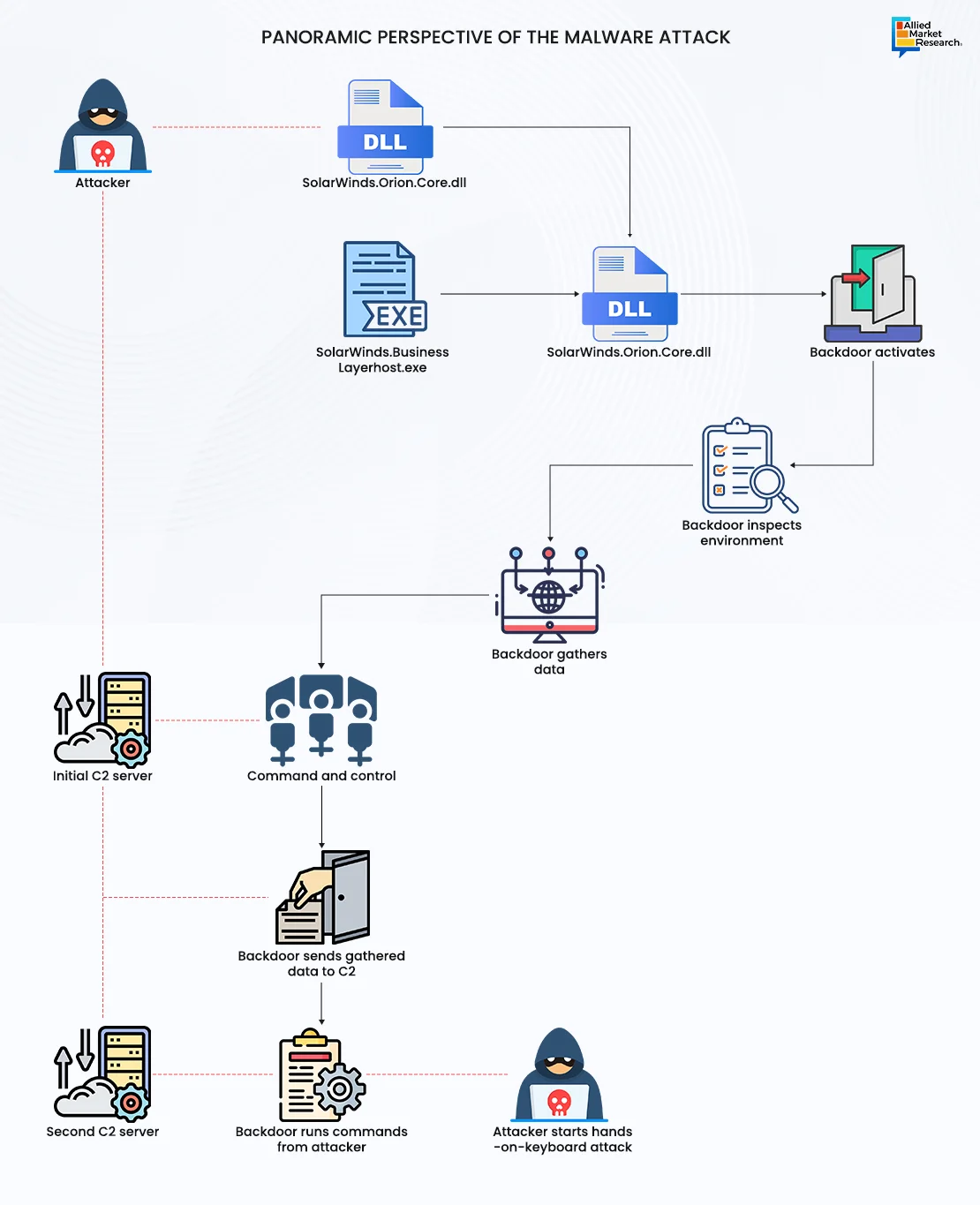
Thus, the interconnected nature of the modern world means that a cyberattack against one organization or sector can have far-reaching consequences. In addition to the immediate impact of cyberattacks, there are broader geopolitical implications to consider. As cyberspace is becoming increasingly vulnerable, governments around the world are heavily investing in offensive cyber capabilities, cyber deterrence strategies, and international norms of behavior in cyberspace. Defense cybersecurity plays a crucial role in this context, as it enables nations to protect their critical infrastructure, defend against cyber threats, and deter potential adversaries from launching attacks.
Defense in Depth
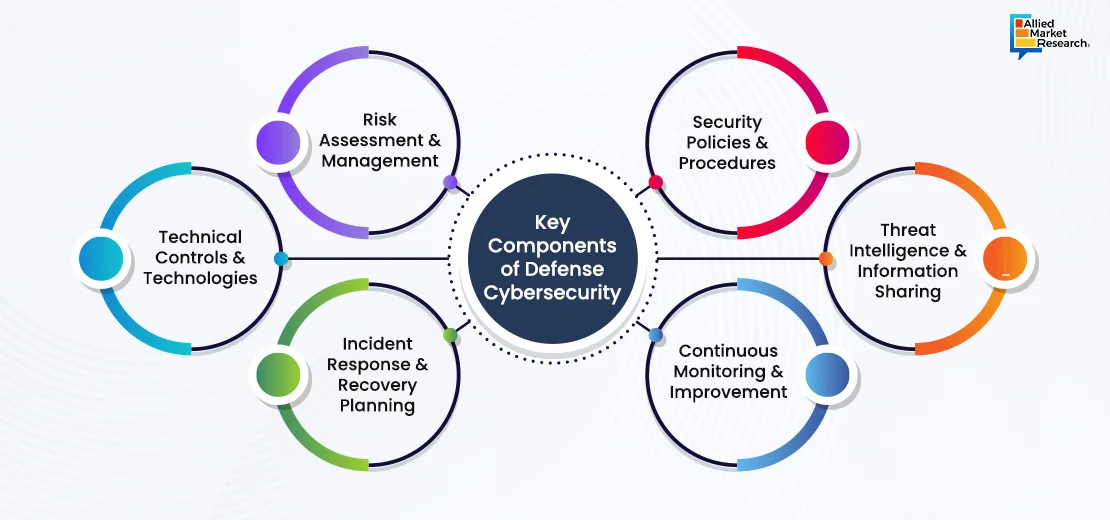
The key parameter of defense cybersecurity includes risk assessment & management wherein the system identifies, evaluates, and prioritizes cybersecurity threats & vulnerabilities to determine the potential impact on the organization. The other components such as technical controls & technologies, incident response & recovery planning, security policies & procedures, threat intelligence & information sharing, and continuous system monitoring & improvement facilitate smooth operations and simultaneously ensure system safety from external threats.
Unveiling the Advantages of Defense Cybersecurity
Defense cybersecurity plays a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive information, critical infrastructure, and national security against cyber threats. Below mentioned are some of the advantages that enable efficient operations
- Threat Detection and Prevention: Defense cybersecurity systems are equipped with advanced threat detection mechanisms that continuously monitor network traffic, system behavior, and potential vulnerabilities. By analyzing patterns and anomalies in real time, these systems can identify and neutralize cyber threats before they cause significant harm. This proactive approach helps in preventing data breaches, malware infections, and other cyberattacks.
- Data Protection and Privacy: In today's digital age, data is a valuable asset that needs to be protected from unauthorized access, theft, or manipulation. Defense cybersecurity employs encryption techniques, access controls, and data loss prevention mechanisms to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive information. By implementing robust data protection measures, organizations can mitigate the risk of data breaches and maintain the privacy of their users and stakeholders.
- Resilience and Continuity: Cyberattacks can disrupt operations & services and cause financial losses for organizations. Defense cybersecurity focuses on building resilience and continuity by implementing redundant systems, backup solutions, and disaster recovery plans. In the event of a cyber incident, these measures help in restoring services quickly, minimizing downtime, and mitigating the impact on business operations. By maintaining resilience, organizations can effectively withstand cyber threats and ensure the continuity of critical services.
- Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with cybersecurity regulations and standards is essential for organizations operating in various industries, such as finance, healthcare, and government. Defense cybersecurity helps organizations adhere to regulatory requirements by implementing controls, policies, and procedures that align with industry standards and best practices. By demonstrating compliance, organizations can avoid legal penalties, reputational damage, and loss of trust from customers and stakeholders.
- Strategic Advantage and Competitive Edge: In today's competitive landscape, organizations that prioritize cybersecurity gain a strategic advantage over their counterparts. Defense cybersecurity not only protects against cyber threats but also enhances the organization's reputation, trustworthiness, and credibility in the marketplace. Customers, partners, and investors are more likely to engage with organizations that demonstrate a commitment to cybersecurity, thereby providing a competitive edge in the industry.
- National Security and Critical Infrastructure Protection: Defense cybersecurity plays a vital role in safeguarding national security and protecting critical infrastructure, such as power grids, transportation systems, and communication networks. Cyberattacks targeting critical infrastructure can have severe consequences, including disruption of essential services, economic damage, and even loss of life. Defense cybersecurity initiatives collaborate with government agencies, law enforcement, and private sector partners to strengthen the resilience of critical infrastructure and defend against cyber threats posed by hostile actors, both domestic and foreign.
Redefining Cybersecurity in Defense with Integration of IoT and AI
Several countries use IoT in military and defense applications to resolve difficulties during conflict and combat. Internet of Military Things (IoMT) or Internet of Battlefield Things (IoBT) is used in current warfare and information warfare. IoMT helps in building a small ecosystem of smart technologies that can process sensory data and handle many tasks at once. Its main objective is to solve difficulties that come up during modern conflicts.
A nation’s major strength is its robust armed force. To sustain the technology-driven warfare, many countries invest in AI-powered military devices. In July 2022, the Government of India (GoI) launched 75 newly developed AI products or technologies. For instance, around 140 AI-based surveillance systems were installed by the Indian Army to get live feed of the activities taking place at the borders of China and Pakistan. Moreover, the government has already set up the Defense Artificial Intelligence Council (DAIC) and targets to give the defense the correct structure to implement IoT applications. Furthermore, in March 2022, Northrop Grumman Corporation announced that it has established the 100th U.S. Air Force training site on the company's distributed mission operations network (DMON), enabling combat air force (CAF) crews around the world to securely connect with other sites in virtual training and exercises. The DMON connects dissimilar aircraft simulator platforms, allowing CAF crews to seamlessly interoperate and train together in a high-fidelity, realistic virtual environment.
LAWS to Enhance Security
Deploying lethal autonomous weapon systems (LAWS)—a class of advanced military weapon—will strengthen the military & defense sector of a nation. This is attributed to the fact that LAWS are integrated with sensor suites and computer algorithms, which help to independently identify a target and employ an onboard weapon system to engage and destroy the target without human intervention.
Such technologies will further enhance the needs and importance of IoT and AI in current problems and challenges and meet the gaps in existing methods and ideas for improving surveillance & reconnaissance in cyber security in the Indian defense ecosystem and operations. Thus, increasing adoption of IoT and AI in cybersecurity will further help in creating potential opportunities for the market in the coming future.
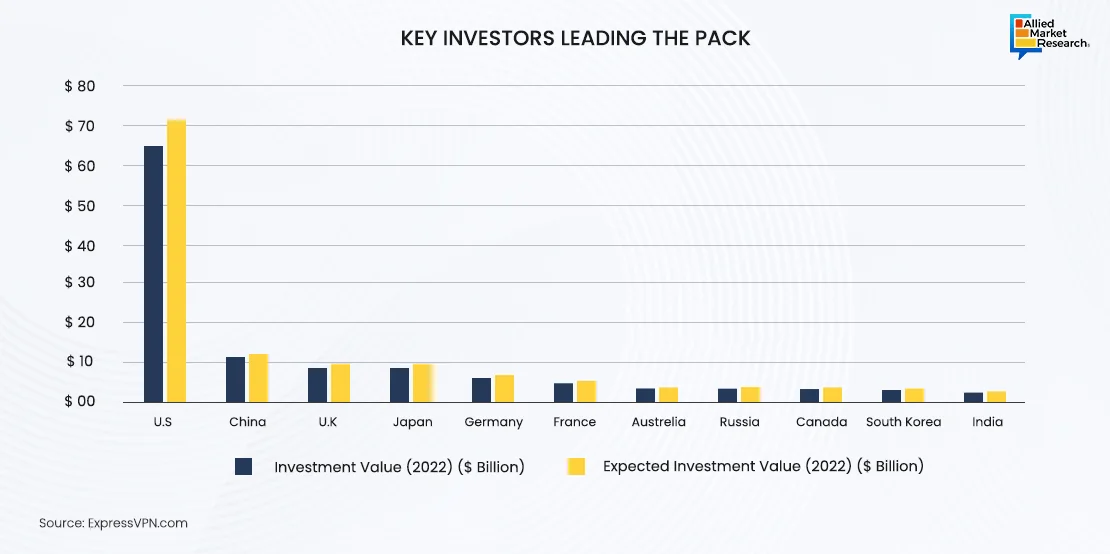
Leading nations are heavily investing in fortifying their defense against cyber threats by heavily investing in strengthening their cyber security infrastructure. Foremost among these nations is the U.S., which invested $63 billion in 2022, showcasing its commitment to bolster national resilience against evolving cyber challenges. Projections indicate that the U.S. leads the league, with an investment exceeding $70 billion in 2023 to safeguard digital assets and critical infrastructure.
Moreover, China, the UK, Japan, and Germany are actively investing in cyber security to ensure a safer digital environment. These investments signify that these nations aim to build a robust cyber ecosystem that fosters innovation, protects sensitive data, and preserves national security interests.
In 2022, the global cyber security sector stood as remarkable economic entity, substantiating market value of $150.4 billion. Within this vast domain, defense cyber security showcased its prominence by garnering $22.3 billion of the total global market. This indicates the growing importance of fortified cyber defenses within military and governmental entities. As cyber threats continue to escalate, investment in defense cyber security emerges as a strategic imperative for nations aiming to strengthen their national security against cyber incursions and attacks, thereby highlighting the need for robust protective measures to safeguard critical assets and infrastructure within the defense sector.
Navigating the Challenges in Defense Cybersecurity
- The defense cybersecurity sector faces an array of challenges, stemming from the evolving nature of cyber threats and the complexities of modern military operations.
- Sophisticated Adversaries: Nation-states, terrorist organizations, and cybercriminal syndicates deploy advanced techniques such as malware, ransomware, and phishing attacks to breach defense networks and steal sensitive information.
- Insider Threats: Malicious insiders or unwitting personnel with access to sensitive systems pose a significant risk, as they can intentionally or inadvertently compromise security protocols.
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: The interconnected nature of defense ecosystems introduces vulnerabilities through third-party suppliers and contractors, increasing the risk of supply chain attacks.
- Rapid Technological Advancements: The adoption of emerging technologies such as AI, IoT, and quantum computing introduces new attack vectors that outpace traditional defense mechanisms.
- Legal and Ethical Dilemmas: Balancing the imperatives of national security with individual privacy rights and international laws presents complex legal and ethical challenges in the realm of defense cybersecurity.
Thus, implementing adequate cybersecurity measures in this high-tech digital environment holds immense importance. To navigate the complexities of defense cybersecurity, organizations must remain active against sophisticated adversaries, insider threats, and supply chain vulnerabilities. Furthermore, initiatives taken by government to mitigate cybersecurity risks and will help to maintain a cyber-secure environment. For instance, the Government of India has set up a National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Center (NCIIPC)—a central government establishment—to safeguard critical information about national security, economic growth, and public healthcare of the country. This initiative emphasizes the need for robust risk management strategies and proactive security measures to safeguard critical assets and maintain resilience.
A Promising Future
In an era of rapid technological innovation and digital connectivity, defense cybersecurity emerges as a prerequisite in safeguarding national security interests and preserving military readiness. By adopting a proactive and holistic approach encompassing technological innovation, policy frameworks, and collaborative partnerships, defense organizations can fortify their cyber defenses against evolving threats and ensure the resilience of critical infrastructure and operations. As the digital world continues to evolve, defense cybersecurity remains imperative in safeguarding the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of sensitive information and assets in an increasingly vulnerable cyber landscape.

