Green Diesel - Is It the Future Fuel?

Green diesel, also known as renewable diesel or hydrotreated vegetable oil (HVO), is a sustainable alternative to traditional petroleum-based diesel fuel. It is produced from renewable feedstocks such as vegetable oils, animal fats, and waste oils through hydrotreating. This process removes impurities and converts triglycerides into paraffin-based hydrocarbons, resulting in a fuel that is chemically similar to petroleum diesel.
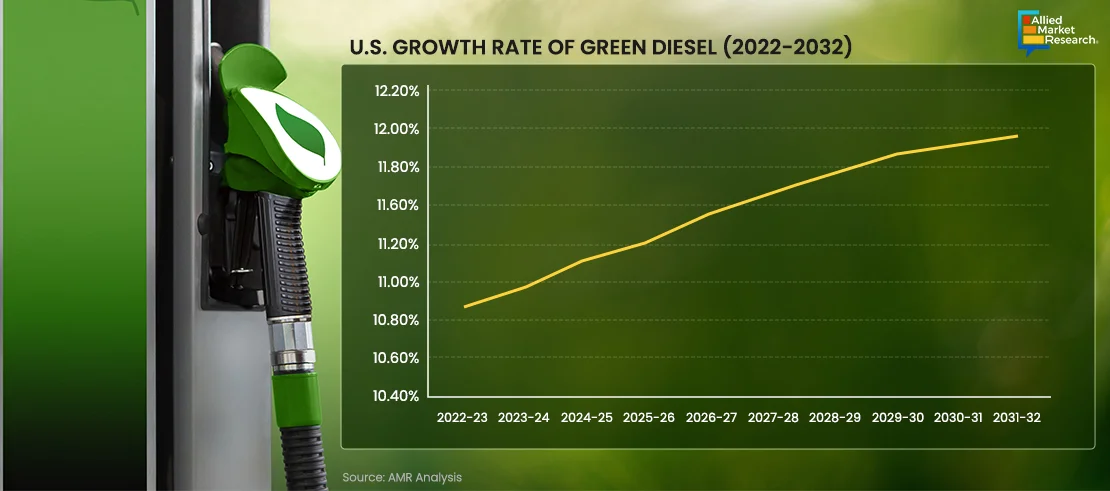
Rise in preference of eco-friendly fuels has led to the creation and adoption of green diesel. This alternative fuel has garnered interest for its ability to curb emissions and promote a greener, more sustainable tomorrow. The green diesel industry has gained momentum due to its environmental benefits and surge in interest of manufacturers & consumers in sustainable energy solutions. The diesel industry has witnessed advancements in green diesel production routes, catalysts, and fuel properties. These biofuels are progressively replacing fossil fuels to meet energy demands. In January 2023, Valero Energy Corporation commissioned and began production from Diamond Green Diesel Holdings LLC. In the fourth quarter of 2022, the operator's 395,000-b/d refinery in Port Arthur, Texas, produced 470 million gallons per year of renewable diesel.
Advantages of Green Diesel
This renewable diesel is derived from renewable sources such as vegetable oils, animal fats, & used cooking oil, and has several noteworthy advantages to offer.
Green diesel typically produces lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to petroleum diesel. Since it is derived from renewable feedstocks, it has the potential to significantly reduce carbon dioxide emissions, which contribute to climate change. This eco-friendly fuel produces fewer pollutants such as sulfur, particulate matter, and nitrogen oxides compared to conventional diesel, leading to improved air quality and reduced health risks associated with air pollution.
It is used in existing diesel engines and infrastructure without any modifications, making it a convenient drop-in replacement for petroleum diesel. This eliminates the need for costly engine upgrades or infrastructure investment. It has a high energy density, similar to petroleum diesel, which means it provides similar levels of performance and fuel efficiency in diesel vehicles & equipment.
It is produced from a variety of renewable feedstocks, including vegetable oils, animal fats, and waste oils. This versatility reduces dependency on any single feedstock and allows for greater flexibility in sourcing raw materials. Unlike finite fossil fuels, the feedstocks used to produce green diesel are renewable resources. This makes this diesel a sustainable alternative that helps reduce reliance on finite fossil fuels and promote energy security.
It typically has lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional diesel since it is derived from renewable feedstocks. It significantly reduces carbon dioxide emissions and produces fewer pollutants such as sulfur, particulate matter, and nitrogen oxides, leading to improved air quality. Some of the major players offering green diesel include Exxon Mobil Corporation, Cargill Incorporated, Marathon Petroleum Corporation, Total Energies SE, Chevron Corporation, Valero Energy Corporation, and Phillips 66.
Challenges in the Green Diesel Industry
The production of green diesel requires supply of feedstock such as vegetable oils, animal fats, and waste products. However, the availability of these materials is mostly inconsistent, which leads to fluctuations in production rates. The cost of producing green diesel is high due to the price of feedstock and the technology required in the process. This makes it challenging to compete with conventional diesel on a cost basis.

Despite its environmental benefits, green diesel industry faces challenges such as regulations & policies and consumer habits accustomed to traditional fuels. While green diesel is cleaner than fossil fuels, its production and use still have environmental impacts that need to be managed, such as the use of land for feedstock cultivation and emissions from production processes. Furthermore, the economic sustainability of green diesel is influenced by energy prices, government incentives, and competition from other renewable energy sources.
Strategic Developments in the Green Diesel Industry
Phillips 66 (U.S.), in April 2024, converted its San Francisco refinery in Rodeo Renewable Energy Complex only for the commercial production of green diesel. The facility currently produces 30,000 barrels of renewable diesel per day, which is slated to increase to 50,000 barrels per day by June 2024. The facility currently processes only renewable feedstock for green diesel production and is expected to be the industry leader with the completion of the undertaking. Apart from green diesel, renewable jet fuel, i.e., sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) is projected to be produced in the same facility. SAF is anticipated to act as a substitute for aviation turbine fuel (ATF) for use in different aircraft. With the completion of this expansion, Phillips 66 is projected to position itself as one of the leading players in the green diesel industry on a global level.
In September 2023, Mitsui & Co., Ltd. (Japan) and Galp SGPS S.A. (Portugal) entered into a joint venture for the development and production of green diesel and sustainable aviation fuel in Sines Refinery. Galp is expected to own 75% of this new entity and Mitsui is expected to own 25% of it. For green diesel production, feedstock is anticipated to be sourced from waste residue oil such as hydrotreated vegetable oil, cooking oil, and animal fats .
ExxonMobil owned affiliate, Imperial Oil Ltd., in January 2023 started with the construction of its new refinery facility in Canada. Imperial’s Strathcona refinery is expected to produce 20,000 barrels of renewable diesel per day from locally sourced feedstock. The facility is expected to utilize low carbon hydrogen, which is produced with carbon capture technology to meet Canadian regulations for low emission fuel standards. The green diesel produced from this facility is anticipated to be primarily utilized in the transportation end-use industry.
The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS, GoI), in September 2023, developed 9 standards for biofuels, which also includes green diesel. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) proposed Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) volumes and percentage standards, which includes renewable fuel for 21.87 billion RIN (One RIN is equivalent to one ethanol-equivalent gallon of renewable fuel)
End-use Industry Demand
Green diesel is predominantly used as fuel in various industries such as transportation, manufacturing, and power generation. Growth witnessed in these end-use industries is expected to increase the demand for green diesel globally. Various advantages offered by green diesel as compared to conventional diesel makes it one of the most preferred choices among end users. The manufacturing sector utilizes large volumes of diesel mainly for power generation and other related tasks. Below are some of the major countries having large scale manufacturing output on a global scale -
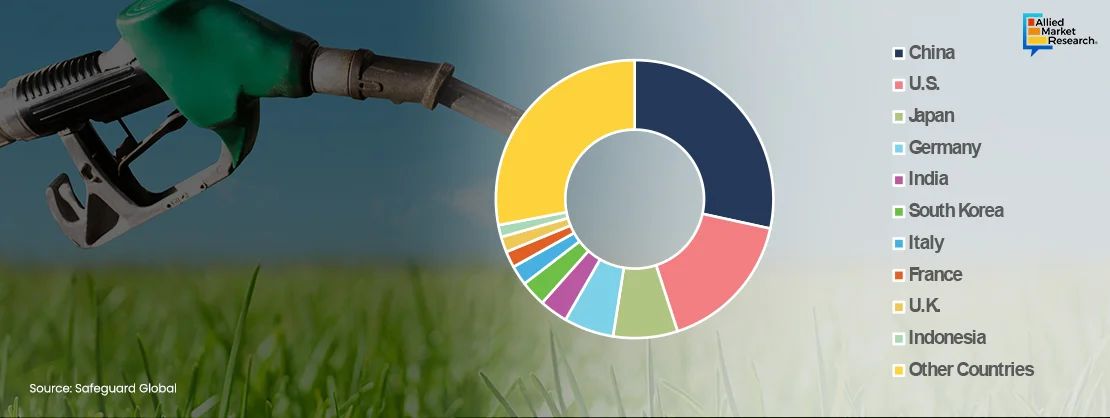
The demand for electricity increases considerably with an expansion of the manufacturing sector of a country. Currently, most of the global energy requirements are met through non-renewable sources. Power generated through biofuels such as green diesel instead of coal is projected to reduce GHG emissions and help in reducing landfill waste. The incorporation of green diesel has increased many folds by meeting these power generation requirements mainly in the manufacturing sectors. Therefore, with the growing manufacturing sector (automotive, oil & gas, chemical, fertilizers, electrical & electronics, marine, semiconductors and so on) mainly in economies such as China, U.S., India, Vietnam, Brazil, Indonesia and others, the demand for green diesel will increase considerably in the coming years.
Future Insights into the Green Diesel Industry
The future outlook of the green diesel industry is quite promising, with several key trends and projections indicating robust growth. The industry is expected to benefit from ongoing technological advancements, particularly in the areas of feedstock processing and fuel production, which will likely lead to more efficient and cost-effective green diesel production methods. Government initiatives and policies are anticipated to support the growth of the green diesel industry, with many countries aiming to reduce their carbon footprint and promote renewable energy sources.
The demand for renewable diesel is projected to be substantial, which suggests that the green diesel industry is projected to play a critical role in the transition to more sustainable fuels.
Outlook and Growth Scope
Green diesel is a sustainable alternative to conventional diesel, as it is derived from renewable resources that are anticipated to be replenished over time. Overall, the environmental, economic, and regulatory advantages of green diesel make it a preferred choice over conventional diesel for reducing emissions, improving air quality, enhancing energy security, and promoting sustainability in various sectors. The demand for green diesel is expected to grow steadily in the coming years with new technological innovations and increase in product incorporation.
For further insights, get in touch with AMR analysts.



