Table Of Contents

Akshata Tiwarkhede

Yerukola Eswara Prasad
Submarine Batteries - The Powerhouse Beneath Waves

A submarine battery is specifically designed to power submarines. These batteries are critical for providing the electrical energy required to run various systems on the submarine, including propulsion, lighting, communication, and other onboard electronics. Submarine batteries are designed to operate under extreme conditions, including high pressure and corrosive seawater environments, and hence are required to be highly reliable and durable.
Navigating the Historical Depths: From Primitive to Present
Submarine batteries have undergone notable developments, which have enhanced the effectiveness and capabilities of underwater vessels. The earliest submarines relied on human power, using a crankshaft to drive an external propeller. It was soon realized that muscle strength did not suffice the purpose of propelling the submarines; hence, in 1800s, gasoline engine came into existence. However, they quickly consumed all the breathable oxygen and made it difficult to provide enough propulsion underwater. The advent of electric motors and rudimentary batteries helped to overcome this challenge. In 1888, Gymnote—a French-built, electric submarine was launched, which successfully completed around 2,000 dives suing 204-cell battery. The year 1954 was a game-changer for submarines with the launch of USS Nautilus nuclear-powered submarine. Using heavy lead-acid batteries, this submarine had the capacity to remain submerged underwater for months and travel long distances at high speed. However, these primitive lead-acid batteries were heavy and bulky and exhibited limited capability, thus restricting the endurance and range of submarines.
Naval engineers and scientists have been constantly focusing on R&D and innovation to improve the battery performance and reliability. With continuous advancements in engineering, material science, and chemistry, cutting-edge batteries have been developed to meet the modern requirements. With integration of smart batteries and advanced energy managements systems, the capabilities of submarines have improved significantly.

Deep Dive into the Details of Batteries
Submarines use various battery technologies such as lead acid batteries, lithium-ion batteries, nickel-cadmium (Ni-Cd) batteries, and silver zinc batteries. The usage of these batteries depends on the submarine applications which can be stated as below:
- Underwater Propulsion: Submarine batteries provide the primary source of power for propulsion when the submarine is submerged. Unlike surface ships that can rely on engines powered directly by fuel, submarines need a quiet and reliable power source that can operate underwater for extended periods.
- Stealth and Silence: Submarine batteries facilitate electric propulsion, which is significantly quieter than diesel engines. This reduced noise is critical for stealth operations, as it makes the submarine less detectable by enemy sonar systems.
- Operational Endurance: By using batteries, submarines can remain submerged for longer durations without the need to surface for air, which is essential for maintaining stealth and completing long missions.
- Safety and Reliability: Submarine batteries serve as a reliable backup power supply in case of main engine failure or other emergencies, ensuring that critical systems remain operational, and the crew can manage the situation safely.
- Environmental Conditions:Submarine batteries are designed to operate reliably under the extreme conditions found underwater, such as high pressure and corrosive environments, where other power sources might fail.
- Support for Various Systems:Batteries provide power for a wide range of onboard systems, including navigation, communication, weapons systems, sensors, lighting, and life support systems. This ensures the submarine can operate effectively and safely.
- Air-independent Power Source:Batteries are often used in conjunction with air-independent power systems, such as fuel cells, to extend the operational range of non-nuclear submarines. These systems generate electricity without the need for atmospheric oxygen, allowing the submarine to stay submerged for longer periods.
- Technological Advancement: Advances in submarine batteries, particularly with lithium-ion batteries, offer higher energy density, faster charging, and longer service life. This enhances the overall capabilities of submarines, making them more effective and efficient.
These use cases demonstrate the versatility and critical importance of submarine batteries in ensuring the success and safety of submarine missions. Submarine batteries are a vital component of submarine technology, offering a range of benefits from silent operation and high energy efficiency to enhanced safety and reliability. The ongoing advancements in submarine batteries, particularly with lithium-ion batteries and other metal ion batteries, continue to improve the capabilities and performance of submarines, supporting both military and research missions underwater.
Global Military Submarine Fleet Outlook (2023)
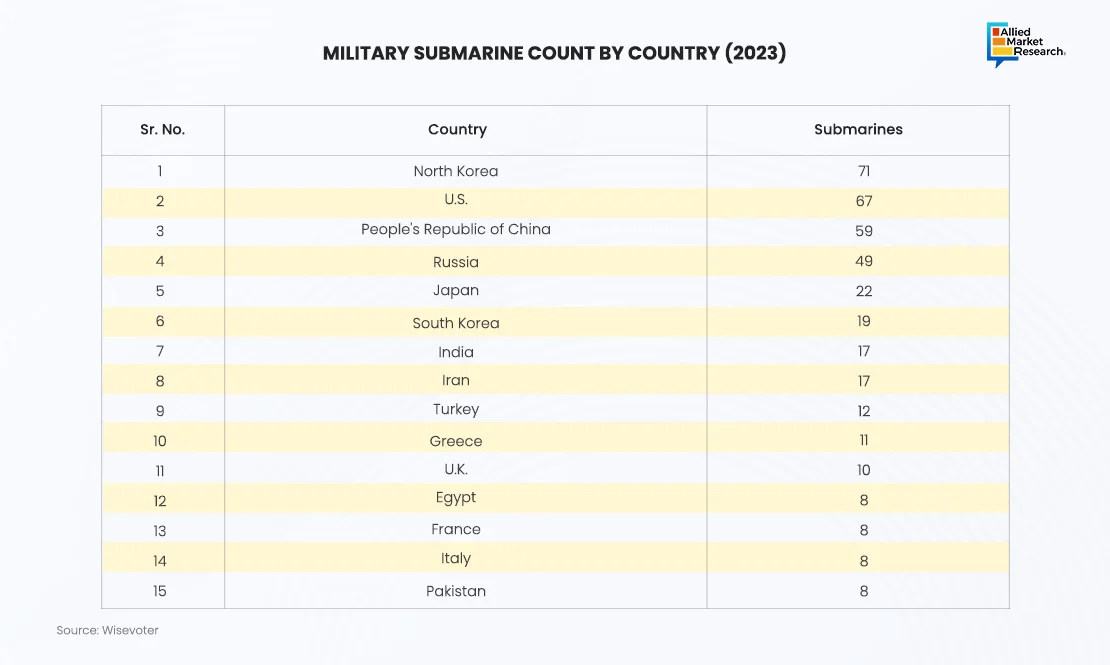
Various countries globally with a coastline and their corresponding navy employ maritime vessels and submarines for different purposes. Submarines are majorly used in military applications for surveillance activities. Currently, there are more than 42 countries that have submarines as a part of their naval fleet. Some of these countries are among the global superpowers who have invested vastly in their naval capabilities to maintain their dominance in the maritime domain. Below table showcases the submarine fleet of different countries.
As seen in the above figure, North Korea, the U.S., China, and Russia have had the largest military submarine fleets on a global level. These countries also account for some of the largest functional submarines in active duty. Batteries are mostly used in diesel-powered submarine as they are silent and help in better surveillance. Operating and maintaining a diesel-electric submarine is usually less costly than a nuclear submarine. Nuclear submarines require specialized facilities and highly trained personnel for maintenance, handling nuclear fuel, and managing radioactive waste. For instance, Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd. in October 2023 launched RAIGEI (fourth Taigei class submarine). The submarine supports lithium-ion battery systems for increased underwater endurance. The submarine exhibits improved surveillance capabilities, increased stealth capabilities, and enhanced safety measures as it is equipped with a variety of automated systems, high-performance sonar, and powered by lithium-ion battery.
Lithium-ion Battery as a New Power Source
Submarine batteries are used for several crucial reasons, primarily centered around their role in providing power for various systems on the submarine. Batteries are often used in conjunction with air-independent propulsion systems, such as fuel cells, to extend the operational range of non-nuclear submarines. Air-independent propulsion systems generate electricity without the need for atmospheric oxygen, allowing the submarine to stay submerged for longer periods. Also, advances in battery technology, particularly with lithium-ion batteries, offer higher energy density and faster charging. This enhances the overall capabilities of submarines, making them more effective and efficient. Moreover, lithium-ion batteries require low maintenance and exhibit prolonged service life as compared to lead-acid batteries. Dr. Rolf Wirtz—CEO of thyssenkrupp Marine Systems—says “The use of the new battery technology has enormous tactical advantages. We are entering a new era of submarine construction.”
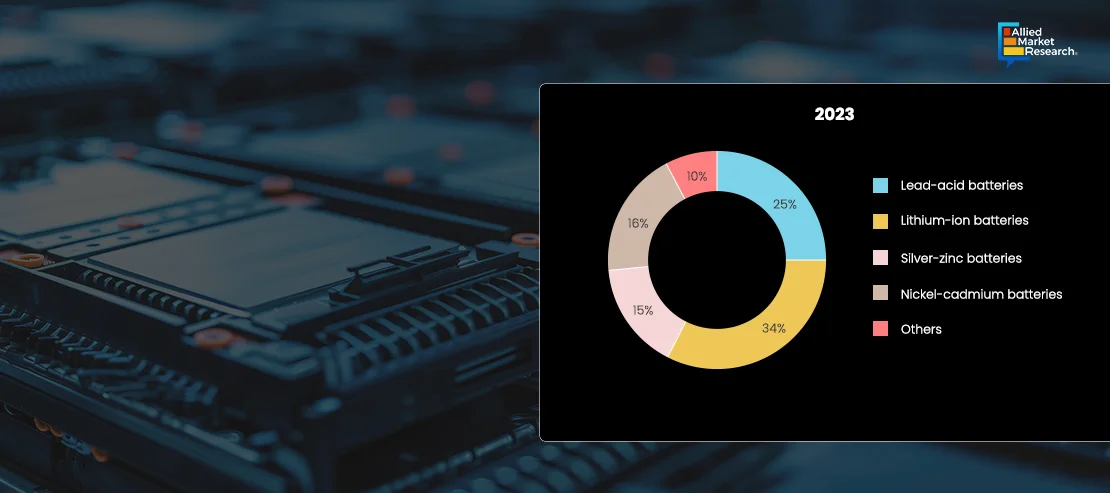
As seen in the figure above, the lithium-ion battery is the most widely used technology in submarines in 2023. Due to their higher energy density, lithium-ion batteries require less space and weight to store the same amount of energy. This can free up space and reduce the overall weight of the submarine, allowing for more flexibility in design and additional payload capacity. When operating on battery power, diesel-electric submarines with lithium-ion batteries can remain silent for extended periods, enhancing their stealth capabilities. This is particularly important for covert operations and avoiding detection by enemy forces. In addition, these batteries provide a more stable voltage output throughout their discharge cycle, ensuring consistent performance of the submarine's systems. Modern Li-ion battery systems are designed with advanced safety features and require less maintenance compared to traditional lead-acid batteries. This reduces the operational burden on the crew and enhances overall safety. Lithium-ion batteries provide significant advantages for diesel-electric submarines, including higher energy density, faster charging, longer battery life, improved stealth, operational flexibility, efficiency, performance, and safety improvements. These benefits enhance the overall capabilities and effectiveness of diesel-electric submarines, making them more competitive and versatile in modern naval operations.
For instance, in September 2023, North Korea launched SINPO-C Class, a newly built submarine No. 841 Hero Kim Kun Ok, which is a diesel-powered submarine. Also, in March 2024, France and Brazil launched a diesel-powered submarine built in Brazil with French technology as part of a Prosub program. Brazil in 2008 collaborated with France for transferring naval manufacturing technology. With this, Brazil obtained the manufacturing rights for the production of diesel and nuclear submarines. Also, with new submarine programs announced by various countries globally for maritime activities, the demand for diesel-powered submarines is bound to increase considerably. Parallelly, with advancements in battery technology, the usage of lithium-ion battery, sodium-ion battery, and other battery types will increase gradually in the coming years.
Future Perspective
The submarine battery industry is witnessing tremendous R&D activities in diversifying its product offerings and innovations. New product offerings based on ion technology such as lithium-ion battery and sodium-ion battery are expected to gain high traction in the coming years. In addition, with new submarine programs being announced by various countries, the overall demand for submarines is anticipated to increase simultaneously, thus paving the way for more advanced submarine batteries.
For further insights, get in touch with AMR analysts.

