Table Of Contents

Yerukola Eswara Prasad

Shraboni Sen
Transformer Core Growth Potential

Transformer core is a structure made using thin ferrous metal laminated sheets that are stacked together around which the primary and secondary windings are wrapped. The core serves as a magnetic pathway to guide the flow of magnetic flux generated by the transformer's primary winding to the secondary winding. Transformer cores were primarily made of iron or steel laminations, stacked, and insulated to minimize eddy current losses. However, research and technological innovations have led to the introduction of new core materials, such as amorphous alloys and nanocrystalline materials, which incur even lower losses and offer improved magnetic properties. In addition, advancements in core design, including optimized shapes and configurations, have further enhanced the efficiency and reliability of transformers. Furthermore, innovations in manufacturing processes, such as laser cutting and precision assembly techniques, have enabled the production of cores with tighter tolerances and superior performance.
Advantages of Transformer Core
Designed and manufactured in a wide range of sizes, transformer core facilitates voltage regulation. An efficient transformer requires a core, and some of the advantages that a transformer core offers are -
- Efficiency: Transformer cores are highly efficient in transferring electrical energy from one circuit to another through electromagnetic induction. They ensure efficient power transmission with minimal energy loss.
- Compact Design: Transformer cores enable construction of compact and lightweight transformers, making them suitable for various applications where space is limited.
- Scalability: Transformer cores are designed and manufactured in a wide range of sizes and capacities, from small voltage regulators to large electrical power transformers, making them adaptable to different power requirements.
- Reliability: When designed and maintained properly, transformer cores offer high reliability and longevity. They operate continuously for several years with minimal maintenance, providing stable and reliable power distribution.
- Isolation: Transformer cores provide electrical isolation between primary and secondary windings, ensuring safety and preventing electrical hazards such as electric shocks and short circuits.
- Voltage Regulation: Transformer cores facilitate voltage regulation by adjusting the turns ratio between primary and secondary windings. This helps transform voltage levels to meet specific requirements in power distribution systems.
- No Moving Parts: Unlike some other power conversion devices, transformer cores have no moving parts, which reduces the risk of mechanical failure and eliminates the need for lubrication & maintenance of moving components.
- Low Noise: Transformer cores operate silently, without generating noise or vibration, making them suitable for use in noise-sensitive environments such as residential areas or office buildings.
- Compatibility: Transformer cores are compatible with various power sources and loads, including AC and DC systems, making them versatile for use in different electrical systems and applications.
The vital component of a transformer is its core. It is primarily classified into shell type and core type. They are designed for specific applications. For instance, core type configuration is used for high voltage applications, while shell configuration is used for low voltage applications. Shell configuration transformer core has better energy efficiency due to closure windings and restricted magnetic flux path.
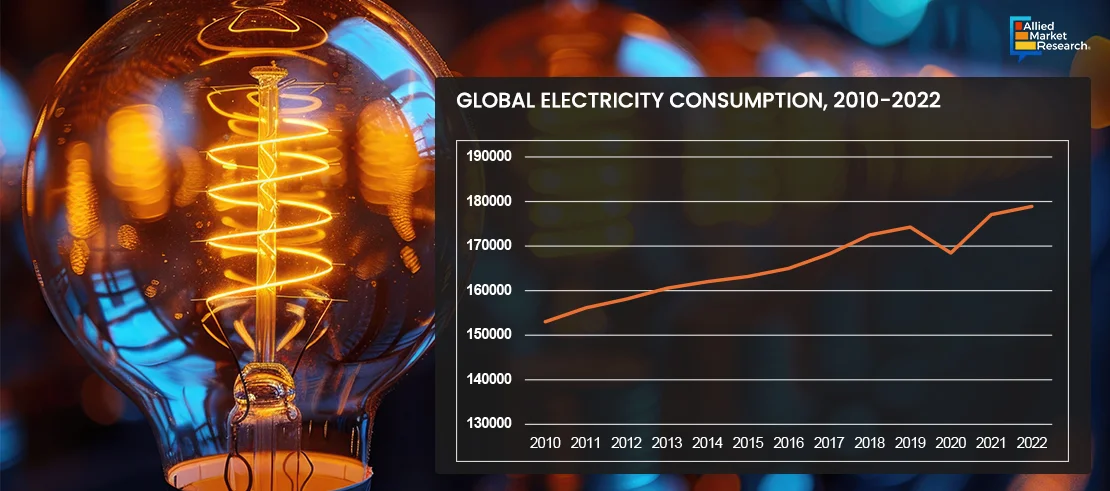
Electricity Consumption Outlook
The demand for electricity has increased exponentially with rapid industrialization and rise in population. Transformers facilitate a link between energy consumers and energy providers, such as power plants or substations by permitting voltage change from transmission stage to consumer stage. This allows for better transmission and distribution of electricity over long distances, thus minimizing loss of electricity. According to a study by CHINT Group, almost 4% electricity is lost during transmission stage, which can be reduced using the chain insulators. Moreover, surge in demand for smart transformers for various purposes such as better power services, improved air quality, and enhancement in energy security are expected to augment the demand of transformers in the power industry. The growth of the transformer market is correspondingly anticipated to increase the demand of transformer core in the coming years.
In 2020, the utility-scale (power plant) sector accounted for 36% of the total U.S. end use energy consumption. Moreover, rapid industrialization across the region is expected to increase the demand for electricity. For instance, numerous electronic and semiconductors industry related manufacturing facilities are expected to be established in India, Taiwan, Thailand, Vietnam, and other countries. With the launch of these projects, the demand for uninterrupted electricity is expected to increase considerably. Several industry leaders have shifted toward green energy sources such as solar energy and wind energy to fulfil the increase in demand for electricity. Rise in environmental concerns due to strict laws to reduce GHG emissions have forced many companies to adopt an effective energy conservation measure.
The implementation of stringent government regulations to control carbon footprints has encouraged industries to opt for an integration with effective energy conservation methods. For instance, according USEPA Clean Air Act 111(d), “the proposed new source performance standards (NSPS) and emission guidelines reflect the application of the best system of emission reduction (BSER) that, taking into account costs, energy requirements, and other statutory factors, is adequately demonstrated for the purpose of improving the emissions performance of the covered electric generating units”. Upgradation of existing grid network, rise in demand for electricity, and surge in number of power companies across the globe are few of the reasons that are expected to be responsible for the growth of the smart transformers and transformer core market in the coming years. Transformers cores are extensively used in renewable energy, electric vehicles, energy storage, and other smart devices.
Market Players and their Strategies
The key players operating in the market includes:

- Arteche
- Corefficient S.R.L.
- Eilor Magnetic Cores
- Foshan Juli Electromechanical Co., Ltd.
- KRYFS
- Megger
- Metglas, Inc.
- Nicore Magnetic Cores
- Power Core Industries
- Vilas Transcore Ltd.
Various companies in the transformer core market are engaged in different strategic approaches such as mergers & acquisitions, expansion, agreements, joint ventures, and new product launches. Comprehensive analysis of recent developments and growth curves of various companies helps to understand the growth strategies adopted by them and their potential effect on the market. Below are some of the prominent examples of various approaches undertaken by these major players to remain competitive in the market:
- In May 2023, JFE Shoji Power Canada announced plans to expand its production capacities for distribution transformer core components by 40%, and production capacity of large power transformer core components by more than 50% as compared to 2023 production rates. This expansion by the company is projected to be beneficial to cater to the increase in demand of transformers in renewable energy sector mainly in Canada and the U.S.
- In March 2024, Wilson Power Solution (U) launched Wilson e4 Ultimate Low Loss Amorphous Transformer. This distribution transformer utilizes amorphous metal with random molecular structure, which results in reduced friction during the magnetization and de-magnetization of the core with low heat dissipation leading to overall high efficiency of the transformer. This new transformer launched by the company serves applications such as industrial, supermarkets, retail, education, healthcare, food & beverage, water, renewables, MOD, ports, and EV.
Future Outlook and Growing Market Scope
The development of transformer cores has undergone significant advancements over the years, driven by the constant quest for higher efficiency, reduced losses, and improved performance. As stakeholders navigate these shifts, a proactive approach that incorporates innovation and regulatory compliance is expected to be essential for maintaining competitiveness and meeting the evolving needs of the market. By embracing emerging trends and leveraging opportunities for sustainable growth, stakeholders position themselves effectively.

