Table Of Contents
- From Ancient Practices to Advanced Solutions: AI Assisting in Healthcare
- Deciphering the Power of AI in Drug Development
- Analyzing the Adoption of AI in Healthcare
- The Role of AI in Combating COVID
- AI Making its Mark in Diagnostics and Imaging
- AI Promoting Personalized Treatment and Precision Medicine
- Transforming Telemedicine with AI
- Conquering Challenges and Ethical Concerns
- Anticipating an Advanced Future with AI
- Mapping AI Journey into Future

Roshan Deshmukh

Akshata Tiwarkhede
Role of AI in Shaping Healthcare - The Quantum Leap

AI in healthcare refers to the use of ML algorithms, natural language processing, and robotics to simulate human intelligence in the analysis, interpretation, and comprehension of complex medical and health data. At a basic level, AI systems learn from large datasets, recognizing patterns and making predictions or recommendations based on that information.
AI in healthcare addresses critical user needs such as improved diagnostic accuracy, personalized treatment plans, efficient administrative processes, and enhanced patient care. Core potential use cases include medical imaging analysis, predictive analytics for patient outcomes, virtual health assistants, and robotic surgery. Although AI in healthcare is currently in the established stage, with widespread adoption across various domains, it continues to evolve rapidly.
From Ancient Practices to Advanced Solutions: AI Assisting in Healthcare
In the early stages, AI in healthcare was primarily limited to academic research and theoretical applications. Early innovations included rule-based systems such as MYCIN in the 1970s. MYCIN is an AI program, which works on the principle of backward reasoning. This expert system attempts to arrive at a probable diagnosis based on reported systems and medical tests, and recommends antibiotics. This technology also explains the reasoning that led to the diagnosis and recommendation. However, the use of this system was constrained by limited computational power and data availability. The focus was largely on creating databases and setting the groundwork for future AI applications. During the late 1990s and early 2000s, with advancements in ML and data science, more sophisticated AI applications began to emerge, though they remained experimental and isolated from specific projects. For instance, this period witnessed the development of expert systems for medical diagnosis and decision support. These systems utilized rule-based algorithms to analyze patient symptoms, medical histories, and diagnostic tests to assist healthcare professionals in diagnosing diseases and recommending treatment plans. In addition, AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants started to appear on websites, providing automated customer support and assistance with tasks such as booking appointments or answering FAQs. Thus, the integration of AI in healthcare holds immense potential, revolutionizing patient outcomes and transforming the way healthcare is practiced.
Deciphering the Power of AI in Drug Development
Traditionally, drug discovery processes were time-consuming and complex. Developing a new drug took up to 12 years with a success rate of less than 1%. Moreover, conventional drug discovery services were expensive, incurring costs up to $2 billion to $6.1 billion over a span of 12 years. The pre-clinical stage alone was estimated to cost around $700 million. However, the integration of AI is expected to streamline and accelerate various stages of the drug discovery process. With AI-driven approaches, researchers can identify potential drug candidates, which exhibit higher efficacy and lower toxicity. In addition, AI can minimize the risk of failure during drug development, which, in turn, is likely to reduce the expense of the pre-clinical stage to approximately $20 million. Alex Zhavoronkov—founder and chief executive of Insilico Medicine—says “AI provides a way to convert money into drugs. You can have luxury cars and everything but you can't live without drugs. You die without drugs and, in our case, we want to make sure people die late in life.” Thus, by reducing cost and enhancing efficiency, AI in healthcare is set to craft a better tomorrow by improving the drug discovery technologies and quality of life.
Analyzing the Adoption of AI in Healthcare
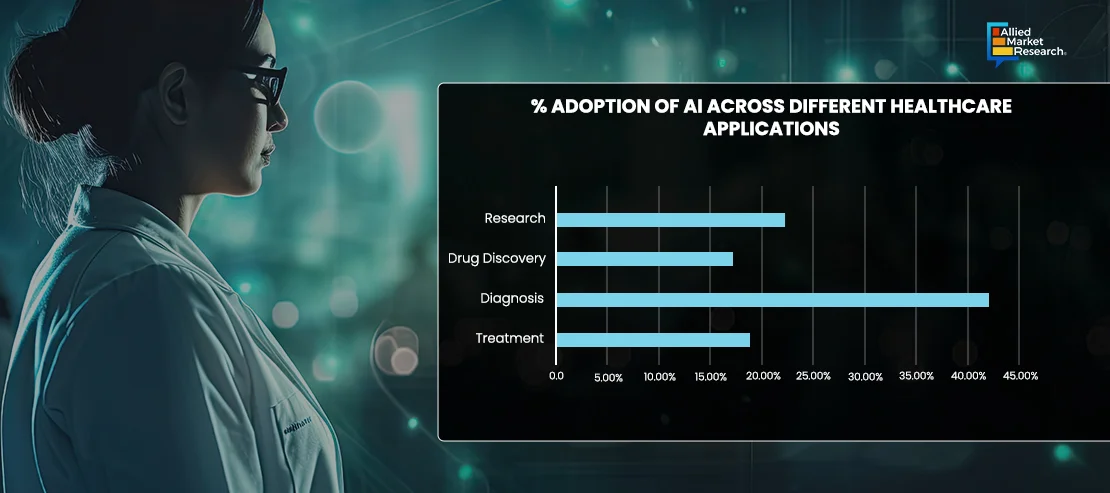
Currently, AI is integrated into a multitude of healthcare applications and services. For instance, ML algorithms are extensively used for analyzing medical images, enabling radiologists to detect anomalies such as tumors with high accuracy. In addition, AI-driven predictive analytics helps in forecasting disease outbreaks, patient admissions, and treatment outcomes, thus improving resource allocation and patient management. Furthermore, natural language processing is utilized in electronic health record systems to streamline documentation and extract actionable insights from unstructured data. Moreover, virtual health assistants provide patients with 24/7 support, managing appointments, medication reminders, and health inquiries. Robotic systems powered by AI assist in minimally invasive surgeries, offering precision and reducing recovery times. For instance, the da Vinci Surgical System, widely used in procedures such as prostatectomies and cardiac valve repair, allows surgeons to perform complex operations through small incisions with enhanced vision, precision, and control. This system uses advanced robotics and AI to translate the surgeon's hand movements into smaller, more precise movements of tiny instruments inside the patient's body. As a result, patients experience less pain, minimal scarring, and quicker recovery times compared to traditional open surgery, highlighting the transformative impact of AI-powered robotic systems in modern medicine.
The Role of AI in Combating COVID
During the pandemic, advancements in AI have particularly benefited the sectors such as retail, education, and healthcare.Despite expectations of a slowdown due to the pandemic, the penetration of AI was already underway before 2020, and its trajectory has remained unhindered. According to Appen's State of AI 2020 Report, rather than decelerating, 41% of companies have accelerated their AI strategies amid COVID.
Organizations have been heavily investing in AI-driven automation to facilitate remote work, improve user and customer experiences, and reduce costs in response to the pandemic. For instance, in April 2024, Microsoft announced a significant investment in AI and cloud technologies to support remote work through its Azure platform. This includes the development of AI-powered tools such as Microsoft Teams, which integrates features like virtual meeting assistance, real-time transcription, and intelligent task automation. These advancements have enabled businesses to maintain productivity and enhance collaboration during the pandemic, demonstrating the critical role of AI-driven automation in adapting to new work environments and improving operational efficiencies. In addition, the State of AI Report reveals that three quarters of surveyed organizations consider AI crucial to their success in 2020, and many are already reaping the benefits of these efforts.
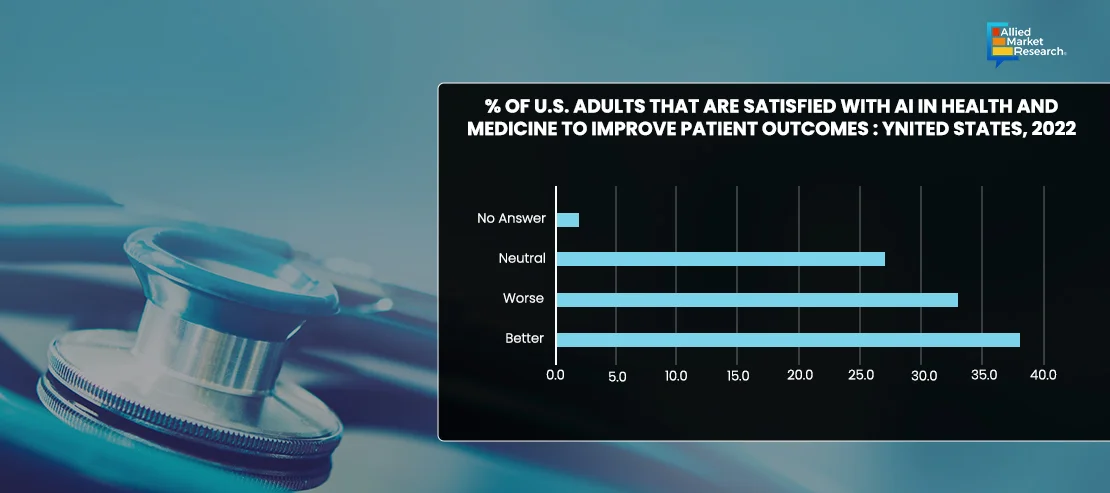
According to a survey conducted by the Pew Research Center from December 12-18, 2022, among 11,004 U.S. adults, only 38% believe that the utilization of AI for tasks such as diagnosing diseases and suggesting treatments would result in overall better health outcomes for patients. Conversely, 33% express the belief that it would lead to worse outcomes, while 27% indicate that it would have minimal impact.
Customers have a cautiously favorable opinion of AI in healthcare. Although there is a lot of excitement about the possible advantages of AI, this is countered by real worries about ethics, privacy, and trust. The healthcare sector should promote more acceptance and trust in AI technology by proactively and transparently addressing these concerns. This will eventually improve patient experiences and healthcare results. To ensure that AI is applied in a way that is ethical, safe, and advantageous to everyone, regulators, consumers, healthcare providers, and technology developers must work together in the future.
AI Making its Mark in Diagnostics and Imaging
One of the most significant areas where AI is massively penetrating is diagnostics and medical imaging. ML algorithms can analyze vast amounts of medical data, including images from X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, to identify patterns and anomalies with remarkable accuracy. For instance, AI-powered systems can assist radiologists in detecting early signs of diseases such as cancer, enabling earlier interventions and improving patient outcomes.
AI-driven diagnostic systems have gained widespread acceptance among healthcare providers due to their ability to enhance accuracy and efficiency in disease detection. For instance, a study published in Nature Medicine in 2020 found that an AI algorithm developed by Google Health outperformed radiologists in detecting breast cancer from mammograms, demonstrating the potential of AI to improve diagnostic accuracy in medical imaging. Similarly, AI-based diagnostic tools have shown promising results in other areas such as pathology, dermatology, and ophthalmology, aiding clinicians in making more accurate and timely diagnoses.
Moreover, AI is increasingly being integrated into clinical decision support systems to assist healthcare providers in selecting optimal treatment strategies for individual patients. Research published in The Lancet Oncology in 2022 highlights the utility of AI in guiding treatment decisions in cancer care, where AI algorithms analyze patient data to predict treatment responses and identify personalized therapeutic options. Moreover, AI-powered virtual health assistants and chatbots are becoming increasingly prevalent, providing patients with personalized treatment recommendations, medication reminders, and lifestyle advice, thereby improving treatment adherence and patient outcomes.
AI Promoting Personalized Treatment and Precision Medicine
AI is revolutionizing the approach to treatment by developing personalized medicine. AI algorithms can predict individual responses to medications and therapies by analyzing genetic data, medical history, and other relevant information. This allows healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans to suit each patient's unique characteristics, maximizing efficacy while minimizing adverse effects. Precision medicine holds great promise for improving patient care and advancing medical research.
One of the key applications of AI in precision medicine is in the interpretation of genomic data. By analyzing an individual's genetic makeup, AI algorithms can identify specific genetic mutations or variations associated with disease risk, treatment response, and prognosis. This genomic profiling enables healthcare providers to develop personalized treatment plans tailored to the molecular characteristics of each patient's disease, maximizing treatment efficacy while minimizing adverse effects.
In addition to diagnosis and treatment planning, AI in precision medicine plays a crucial role in therapeutic development and drug discovery. By analyzing large-scale genomic and clinical datasets, AI can identify novel drug targets, predict drug responses based on individual patient characteristics, and optimize drug dosages for maximum efficacy and safety. This approach, known as pharmacogenomics, holds the potential to revolutionize drug development by enabling the development of targeted therapies tailored to the genetic profiles of specific patient population.
Transforming Telemedicine with AI
The integration of AI into remote patient monitoring systems and telemedicine platforms is another significant development in healthcare. AI algorithms can continuously analyze patient data collected from wearable devices and other remote monitoring tools to detect deviations from normal health parameters. This enables early intervention and timely adjustments to treatment plans, particularly for patients with chronic conditions. Furthermore, AI-powered virtual assistants and chatbots are enhancing the delivery of healthcare services by providing patients with personalized medical advice and support, regardless of their location.
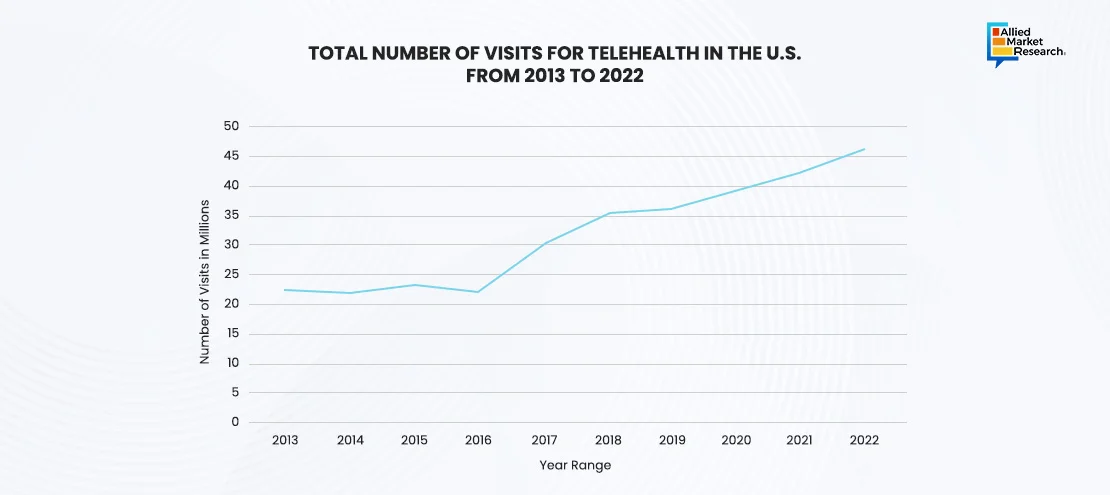
In recent times, the U.S. is witnessing the highest preference for telemedicine as the services are now included under compulsory financial schemes by the government. Furthermore, residents in this developed country have access to cutting-edge technologies. The number of telehealth visits in the U.S. were about 22 million in 2013 and surged up to 46 million in 2022. Rapid development and enhanced accessibility of technology such as smartphones, video conferencing software, and high-speed internet have increased the viability & convenience of telemedicine services for patients & healthcare professionals. Furthermore, AI is playing a noteworthy role in enhancing the effectiveness of telemedicine. Apart from real-time data sharing, the technology is aiding healthcare providers to predict future health trends by assessing the history of medical records. This predictive healthcare is serving as an asset as it helps to obliterate future emergencies and cuts down on unnecessary expenses.
Conquering Challenges and Ethical Concerns
While the potential of AI in healthcare is vast, its widespread adoption is not without challenges. Data privacy and security concerns are increasing at an alarming rate, especially given the sensitive nature of medical information. Ensuring the ethical use of AI in healthcare, including transparency, fairness, and accountability, is paramount to build trust among patients and healthcare professionals. Moreover, there are concerns about the potential for algorithmic bias, where AI systems may produce biased outcomes, particularly in diagnostic algorithms trained on imbalanced datasets. Addressing these challenges requires collaboration among policymakers, healthcare providers, technologists, and ethicists to establish robust regulatory frameworks and guidelines for AI deployment in healthcare.
Anticipating an Advanced Future with AI
The future of AI in healthcare is promising, with advancements expected in precision medicine, genomics, and personalized treatment. AI's capability to analyze massive volume of genetic data will lead to more tailored therapies, minimizing side effects and improving efficacy. The integration of AI with the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) will enable real-time monitoring and proactive management of chronic diseases through connected devices. Emerging technologies such as quantum computing could further enhance AI's ability to process complex biological data, leading to breakthroughs in drug discovery and development. Moreover, AI is anticipated to play a crucial role in addressing global health challenges by providing scalable and cost-effective solutions, particularly in underserved regions.
Mapping AI Journey into Future
AI is reshaping the landscape of healthcare, offering unprecedented opportunities to improve patient care, enhance operational efficiency, and advance medical research. From diagnostics and personalized medicine to remote patient monitoring and drug development, AI is permeating every aspect of healthcare. However, realizing the full potential of AI in healthcare requires addressing challenges related to data privacy, algorithmic bias, and ethical considerations. By leveraging AI responsibly and ethically, healthcare systems can harness its transformative power to create a healthier future.
For further insights, get in touch with AMR analysts!

