Table Of Contents

Roshan Deshmukh

Akshata Tiwarkhede
VR and AR in Healthcare - Once a Distant Dream of Science, Now a Reality

AR and VR, Beyond Technological Advancements
AR and VR in healthcare have outweighed traditional methods, offering enhanced precision, immersive training environment, and improved patient care solutions, which were previously unattainable. VR produces a fully realistic digital environment that users can interact with through the use of headgear and specialized gear. AR improves a user's perspective of their surroundings by superimposing digital information over the real world using gadgets such as smartphones or AR glasses. Numerous consumer demands in the healthcare industry are addressed by these technologies, including patient education, improved rehabilitation therapies, real-time help during surgeries, and immersive teaching environments for medical students. Surgical simulation, diagnostic imaging, pain treatment, and mental health therapy are among the primary potential use cases. VR and AR in healthcare are currently in varying stages of development, from nascent to increasingly established. VR is being used widely for surgical simulation and training. Immersive, hands-on training offered by platforms for surgeons enhance their abilities in a risk-free virtual environment, thereby improving their precision, confidence, and readiness for real-life surgical procedures. Due to its ability to provide high fidelity, interactive training that improves surgical accuracy and results, this technology is growing in popularity, while AR applications for patient education are still in the early stages of development.
Achieving Unrealistic Dreams in Healthcare with AR and VR
At present, AR and VR in healthcare are applied to improve imaging methods, patient treatment programs, and surgical training. Among the most revolutionary uses of AR and VR in healthcare are surgical planning and simulation. However, the landscape of the industry is evolving, with notable technological improvements and broad use of AR–VR healthcare equipment.
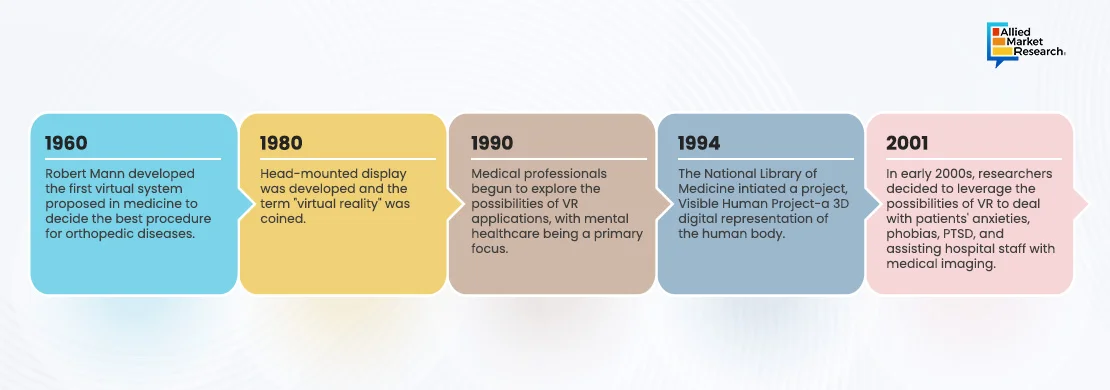

The planning and performance of intricate surgical procedures, as well as the training of medical professionals, are greatly improved by immersive and interactive settings of these technologies. Surgeons may practice procedures in 3D settings created by VR that are realistic and immersive, all without putting patients at danger. Surgeons can improve their skills and decision-making processes by using these simulators, which can recreate a variety of circumstances, including uncommon and challenging instances.

Virtual reality fosters the development of muscle memory and procedural familiarity by allowing surgeons to perform surgical methods repeatedly. Surgery can be performed by trainees repeatedly until they reach a high degree of proficiency. The COVID-19 pandemic has further increased interest in and investment in remote and immersive healthcare technologies by highlighting their significance.
Early adopters are mostly found in fields like physical therapy, where AR can assist patients through exercises with real-time feedback and medical education, where VR offers safe and reproducible training scenarios. As costs decline and technology becomes more widely available, adoption may extend to more clinical uses.
A Comprehensive Case Study of a Ground-breaking Surgery
In 2022, with the assistance of VR-enabled surgical procedure, a pair of conjoined twins, Bernardo and Arthur Lima—three-year-olds from Brazil—were successfully separated. As these twins were born joint at the head with their brains interconnected, medical experts were of the opinion that it was impossible to separate them and ensure there was no loss of life. However, the surgery was accomplished successfully with the help of VR technology in a hospital in Rio de Janeiro that was directed live by Dr. Noor ul Owase Jeelani from a hospital in London. Initially, 3D models of the boys’ brains were built from the data gathered from CT scan and MRI. Using these 3D models, the surgery was virtually practiced for months among the medical teams to get a hand over it and ensure it was error-free. A series of seven surgeries was required to separate the boys, which was carried out wearing VR headsets to coordinate the activities of the UK and Brazil teams, with Dr. Jeelani directing the procedure live. It was reported that boys were recovering well seven weeks post surgery.
This extraordinary surgical intervention stands as a benchmark in enhancing surgical precision and patient outcomes.
Empowering Healthcare with VR and AR
New developments in software have made it possible to create realistic simulations and exact overlays of medical data, while hardware improvements have led to more accurate tracking and higher resolution displays. The functionality of VR and AR in healthcare is improved through integration with other technologies, such as AI and big data analytics, which offer more individualized and efficient healthcare solutions. Companies, such as Surgical Theater, integrate VR with AI and big data to enhance pre-surgical planning and intraoperative navigation. Medical imaging data from patients can be used to create VR simulations that surgeons can utilize. Anatomically accurate 3D models of patients are produced by AI algorithms analyzing this data. By optimizing surgical methods based on the unique anatomy and condition of each patient, surgeons can practice intricate procedures in a virtual setting. Surgical accuracy and recovery times are improved by this combination. Furthermore, Augmedics Xvision system is one example of a platform that combines AR with big data analytics and AI to provide better surgical aid. During surgery, the device superimposes important patient data and 3D anatomical information in real time on the surgeon's perspective. This technology enhances operation safety and precision, especially in difficult surgeries.
Highlighting the Hurdles
A lot of technological obstacles are yet to overcome, such as the expense of the gadget, the requirement for a lot of processing power, and guaranteeing user satisfaction and safety. Furthermore, a number of developments are required to fully utilize VR and AR in healthcare. These include hardware cost reductions, improved user interface design, and strong regulatory frameworks to guarantee efficacy and safety. In addition, it will be essential for healthcare workers to have proper training and social acceptance. However, data privacy problems, the possibility of being overly dependent on technology, and guaranteeing fair access to cutting-edge medical care are some of the risks and issues surrounding these technologies. It will necessitate comprehensive initiatives of stakeholders from the technology, healthcare, and regulatory organizations to address these problems.
The data on user replies highlights many major barriers to the adoption and use of VR and AR in healthcare. Around 65% of the respondents have experienced concerns about comfort, usability, and the immersive nature of AR and VR devices, indicating these as the most common barriers faced among users. Thus, improving the practicality and usability of these technologies is essential for their wider acceptance. In addition, about 27% of the respondents mentioned about the cost to consumers. Many potential consumers are put off by the high price of AR and VR experiences and gadgets. Expanding the user base of these technologies will require lowering their cost. Thus, overcoming the above obstacles will increase the adoption of AR and VR in the industry.
Bypassing the Barriers
Although the integration of AR and VR in healthcare offers promising growth prospects, challenges such as protection of sensitive patient data and complying with regulations need to be addressed. However, the use of blockchain technology, implementation of strict access rules, frequent audits, and cutting-edge encryption can help overcome the challenges in the future. Moreover, demonstrating clinical efficacy and safety may also restrain the utilization; however, by conducting rigorous clinical trials, collecting real-world evidence, publishing peer-reviewed research, and establishing collaborative research networks can provide solution for the same. Thus, recognizing the full potential of AR and VR in healthcare can be achieved by addressing these issues through technological innovation, regulatory cooperation, and stakeholder collaboration.
Expanding Influence Across the Globe
According to Statista, the above table presents the projected number of users of VR and AR from 2020 to 2027. The number of AR and VR users has shown a consistent upward trend, from 2020 and expected to surpass 100 million users by 2027. This growth reflects increasing adoption across various sectors, including entertainment, education, and healthcare. Future capabilities might include more complex surgical navigation systems, completely immersive telemedicine consultations, and real-time adaptive rehabilitation programs. Furthermore, in the upcoming years, experts predict that AR and VR will play a major role in mainstream healthcare due to ongoing technology improvements and increasing acceptability in the medical community.
Fostering the Future
The healthcare sector is undergoing a massive change with increasing penetration of VR and AR by offering cutting-edge approaches to patient engagement, treatment, and training. Although there are some adoption and technical obstacles to overcome, the rate of innovation and growing uptake point to a time when these technologies will be widely used in medical procedures. VR and AR have the potential to greatly improve the standard and accessibility of healthcare globally provided they are developed further and existing constraints are addressed.
For further insights, get in touch with AMR analysts!

