The Telemedicine Phenomenon: Deciphering the Virtual Health Frontier

Telemedicine, also referred to as telehealth or e-medicine, is the remote delivery of healthcare services, including examinations and consultations, through telecommunication technologies. It enables the healthcare providers to diagnose, evaluate, and cure patients without the need for in-person visits. The technology is catering to surge in demand for quick, effective healthcare delivery, especially for those with restricted mobility or residing in underserved areas.
The prospect of telemedicine market is rapidly evolving, with significant expansion since the COVID-19 pandemic. Cases of virtual consultations, remote patient monitoring, and telepsychiatry services have been observing noteworthy surge post pandemic. Telemedicine is currently being assimilated into several healthcare domains, transforming from a specialized idea to a developing technology.
Landscape of Telemedicine Market: Inviting Possibilities
The landscape of the market is evolving, with substantial technological improvements and broad use. Both pioneering startups and well-established healthcare providers are the major frontrunners in this field, striving to put forth innovative products & services. Telemedicine companies such as Teladoc Health Inc., Koninklijke Philips N.V., Siemens AG, Medtronic plc, and American Well Corporation have been at the forefront of telemedicine platforms. Improved telehealth infrastructure, increased connectivity, and creation of advanced platforms or services are among the key regions of focus for these firms.
Traversing its path since the pre-internet era, telemedicine services underwent a technological leap, with technology forming a basis for the expansion of the services. In recent times, evolved technologies, including artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, robotics, and 5G are playing a mainstream role in expanding the potential of telemedicine.
Telemedicine: Flourishing Across Multiple Domains
The genesis of mobile applications, wearable devices, and portable medical equipment has led to the applicability of telemedicine across multiple domains of healthcare. Tele-ophthalmology, tele-psychiatry, tele-dentistry, and tele-dermatology are among the verticals of telemedicine which are under practice in recent times. Tele-psychiatry is one of the most utilized domains of telemedicine. Tele-behavioral health platforms allow patients to get medication management, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and counselling sessions from licensed therapists or psychiatrists through video conferencing.
Telemedicine has extended its applications in cardiology, offering efficient treatment to patients in remote locations or regions with insufficient medical facilities. Wearable devices such as wearable ECG equipment and skin-surface patches are enhancing the possibilities in telecardiology domain. In addition, stakeholders are exploring possibilities in telemonitoring biosensors, which are anticipated to accelerate the decision-making in remote cardiology cases.
Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) published a report on the future of telemedicine after COVID-19 pandemic. According to the report, prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, governments of countries such as Hungary, Ireland, Mexico, and Korea, mandated physical presence for medical consultations. While usage of telemedicine services was increasing in countries such as Portugal and Canada, the share was only between 0.1 to 0.2% of the total services obtained. However, post the pandemic, several countries witnessed rise in inclination toward telemedicine services as individuals radically changed their lifestyle to limit infections. After March 2020, the U.S., Austria, and Türkiye dropped the requirement of physical presence to avail medical services.

In recent times, the U.S. is witnessing the highest cases of telemedicine as the services are now included under compulsory financial schemes by the government. Furthermore, residents in this developed country have access to cutting-edge technologies. The number of telehealth visits in the U.S. were about 22 million in 2013 and surged up to 46 million in 2022. The rapid development and enhanced accessibility of technology, such as smartphones, video conferencing software, and high-speed internet have increased the viability & convenience of telemedicine services for patients & healthcare professionals. Furthermore, technology has enabled healthcare practitioners to effectively manage their schedules and treat more patients virtually, while allowing patients to avoid the cost and time associated with travelling to a medical facility.
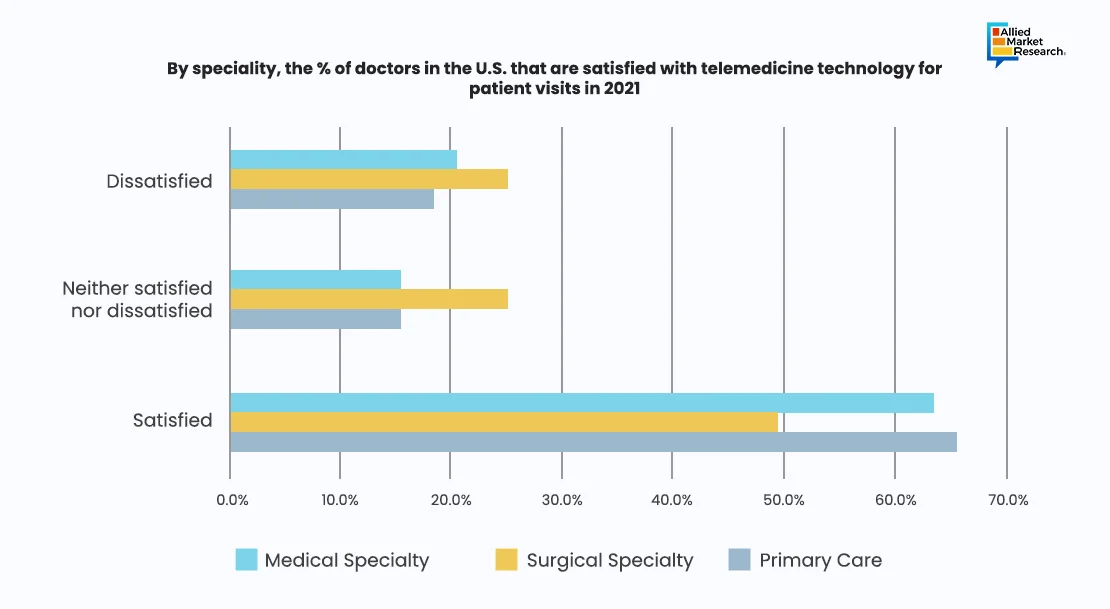
Distinctive Opinions: Analyzing the Satisfaction Ratio
In a study conducted in the U.S. in 2021, doctors' opinions regarding telemedicine technology for patient visits were analyzed depending on their profession. Of the primary care physicians who offered general and family practice services, 18.5% were not happy with the technology, 15.6% were neither satisfied nor unsatisfied and the majority 65.5% were content with it. In addition, out of the total surgical experts, nearly half were satisfied with telemedicine technology for patient visits, while the other half was split between those who were unsatisfied (25.2%) and those who were neither satisfied nor dissatisfied (25.1%).
Furthermore, for the medical specialists who offered services across various verticals such as tele-radiology, tele-psychiatry, tele-dermatology, and tele-cardiology; the satisfaction levels for the use of the technology were 63.6%, 15.6% were ambivalent, and 20.6% were unsatisfied. Thus, telemedicine technology comparatively had a high satisfactory rate among the primary care physicians and medical specialists.
Telemedicine: In the Age of AI and IoT
The current era of artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) devices is a privilege for the expansion of telemedicine. High speed connectivity enables real-time exchange of data, thereby boosting the speed and quality of remote care. The assimilation of devices with cloud servers ensures intermittent transmission of patient’s vitals to the healthcare provider. In addition, the data remains stored in the cloud, thereby eliminating the hassle of managing the reports in the future. Some of the IoT devices being used in telemedicine include oximeters, digital stethoscope, sleep monitors, blood sensors, and hearing aids.
Furthermore, AI is playing a noteworthy role in enhancing the effectiveness of telemedicine. Apart from real-time data sharing, the technology is aiding healthcare providers to predict future health trends by assessing the history of medical records. This predictive healthcare is serving as an asset as it helps to obliterate future emergencies and cuts down on unnecessary expenses. Furthermore, the predictive model of AI is assimilating telemedicine and precision medicine. By analyzing the vitals, the AI model can predict a patient’s current & future health conditions and suggest specific treatment and medication. Moreover, after the COVID-19 pandemic, ingenious data-driven AI algorithms are being developed. These algorithms will be able to analyze new data without previous statistical modeling and develop diagnostic solutions for diverse populations.
Ingestible Sensors: The Smart Pills
The technology of ingestible sensors is gaining substantial traction among healthcare providers and patients due to its non-invasive nature. These sensors are diagnostic devices, similar to the size of a capsule medicine. Comprising of biocompatible materials, they assess the conditions inside patient’s body and transmit data to the connected device, such as smartphone. The amount of information which can be extracted through this technology is immense. The technology is especially benefiting the elderly patients who tend to forget their medicine intake. The sensor monitors the medicine dosage of patients and notifies about the missed dosage on mobile. This is a developing technology with several future capabilities. For instance, the same technology can be utilized in the form of camera pills, to capture images of patients’ interna organs, like in X-ray or CT scan.
Brewing Barriers: A Ground to Cover
While the advantages of telemedicine are multifold, its journey is accompanied by several impediments. The threat of data theft, lack of trust, telehealth licensure, patient confidentiality, and technical errors are among the most prominent factors preventing the widespread adoption of telemedicine. Being internet-predicated technology, maintaining stringent security and encryptions over the platform is necessary to prevent data theft. These platforms are further supported by multiple government laws which ensure data security and patient confidentiality.
While the healthcare providers can offer their services beyond the geographical barriers, a legal procurement of interstate of international telehealth licensure is critical for their practice. While obtaining these licenses is a laborious procedure, it is pivotal for the globalization of medical facilities and offers multiple advantages to the practitioners.
Failure of medical equipment or emergence of technical glitches is a major hazard for the telemedicine market. It can lead to incorrect diagnosis, risking the patient’s health. This area of telemedicine requires thorough research and concrete solutions. Digital twin is a technology which can help to lower the chances of equipment failure. It monitors and simulates electronic equipment and sensors from a long distance, thereby preventing their chances of failure or allowing early replacement.
Telesurgery Through Robotics: A Bright Future Ahead
Efforts are underway for the deployment of robotics into telemedicine. This integration is anticipated to redefine the meaning of remote care. Along with virtual consultations and monitoring patients’ vitals, robots will be able to perform surgeries and administer medicines. This field of telemedicine, called telesurgery, is projected to be a groundbreaking advancement owing to the exceptional benefits it is expected to deliver. Addressing the absence of skilled surgeons, robots will be able to perform surgery with high precision and less invasive procedures. These surgeries will be performed with the assistance of human surgeons. 3-dimensional vision systems will guide the surgeons distant apart to view the anatomy of the patient and instruct the robot surgeon to perform the surgery.
Along with surgical operations, the robots are being designed to offer psychological care to patients. The robots will address the concerns of patients and help them in reducing their anxiety before surgery. With its diverse benefits, telesurgery is at the forefront to revamp the landscape of telemedicine. Companies such as InTouch Health, Intuitive Surgical, and TytoCare are the leading players in the field of AI-powered robotic telemedicine.
Transformation in Telemedicine Services
Telemedicine has a bright future ahead, with many potential uses that reach beyond the current possibilities. Moreover, the popularity of telemedicine is projected to rise, propelled by changes in healthcare delivery models, regulatory changes, and technological developments. AI-driven virtual diagnostics, wearable sensor integration for real-time monitoring, and immersive telepresence using augmented reality (AR) & virtual reality (VR) technologies for surgical consultations are a few potential future capabilities. In addition, automation of the technology is projected to synchronize the administrative activities of healthcare, thereby increasing the focus on patient care. Despite the ethical and legal difficulties, the expansion of telemedicine indicates that geographical boundaries will not be a restraint for access to high quality healthcare. With all the efforts and advancements, the goal of telemedicine is to change healthcare systems for the betterment of individuals and the care providers.
In conclusion, telemedicine is an exemplary change in the delivery of healthcare that offers unprecedented opportunities to boost patient outcomes, expand access to care, and make the most use of available resources. Telemedicine is serving as a key factor in determining how healthcare is delivered globally in the future, as technology and societal needs continue to evolve.
For further insights, get in touch with AMR analysts!



