The Promise and Potential of RNA-Based Therapeutics: A New Frontier in Medicine
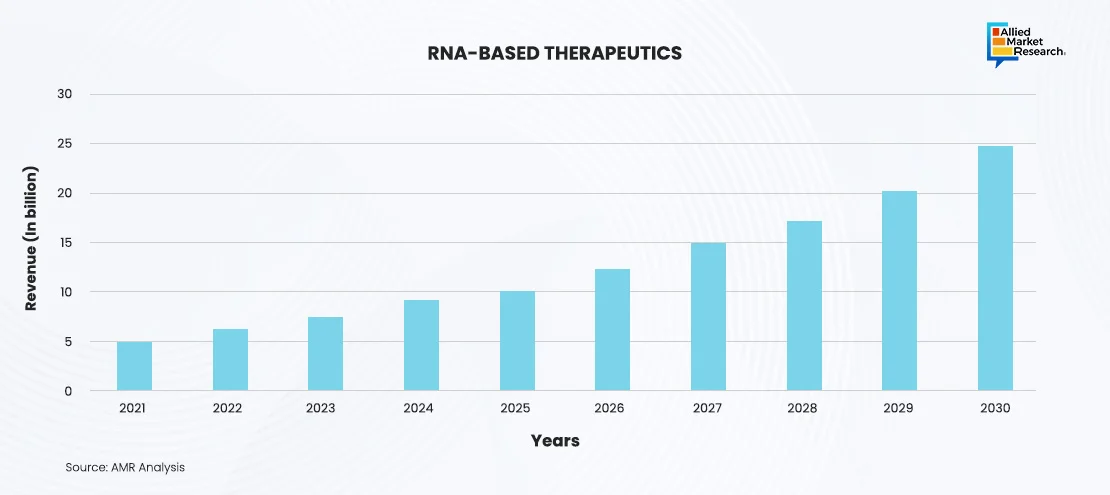
RNA-based therapeutics, including small interfering RNA (siRNA), antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), messenger RNA (mRNA) therapies, and RNA aptamers, offer precise, targeted treatments with fewer side effects than traditional drugs. They are being developed for a variety of conditions, such as genetic disorders, cancers, and infectious diseases, representing a significant development in personalized medicine. The global RNA-based therapeutics industry is experiencing remarkable growth, having generated $5.82 billion in revenue in 2021 and projected to reach $25.1 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 17.6%. This boom is driven by advancements in RNA technology, increased investment in research and development, and the successful deployment of mRNA vaccines during the COVID-19 pandemic, highlighting the transformative potential of RNA-based therapies in modern medicine.
Mechanisms of RNA-Based Therapeutics
RNA-based therapeutics can be classified into several categories based on their mechanisms of action:
RNAi involves the use of small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) to silence specific genes by binding to complementary mRNA sequences and inducing their degradation. RNAi is a natural process in cells where microRNAs (miRNAs) regulate gene expression by attaching to mRNA and preventing its translation into protein. This precise mechanism allows for the targeted silencing of disease-causing genes, offering a powerful tool for therapeutic intervention.
ASOs, on the other hand, are single-stranded DNA or RNA molecules designed to target specific mRNA sequences, inhibiting their translation into protein. ASOs can also modulate gene expression by binding to specific DNA sequences. This approach can be used to correct genetic mutations or alter gene expression patterns, providing a versatile method for treating various genetic disorders.
Ribozymes are catalytic RNAs that can cleave specific RNA sequences, allowing for the regulation of gene expression. Ribozymes are designed to pick out specific mRNAs, leading to their degradation. This mechanism provides a unique way to control gene expression at the RNA level, with potential applications in numerous diseases.
Simultaneously, aptamers are short, single-stranded RNA or DNA molecules that specifically interact with particular proteins or other molecules. Aptamers are used to regulate protein function or to deliver therapeutic molecules to specific cells. This specificity makes aptamers valuable tools for targeted therapy, potentially reducing side effects and increasing treatment efficacy.
Initiatives from Government for Large-Scale Sequencing Projects
The surge in awareness of metagenomics sequencing for genetic disorders, viral diseases, and research projects, along with an increase in government initiatives for large-scale projects of RNA sequencing, are major factors contributing to the growing demand for RNA-based therapeutics. For instance, in December 2023, the National Institutes of Health announced the renewal of the National Human Genome Research Institute’s large-scale sequencing program. This program, crucial for mapping the human genome, aims to advance the understanding of genetics in health and disease. The renewal focuses on integrating advanced sequencing technologies, expanding research to diverse populations, and exploring complex genetic traits. Emphasizing collaboration, data sharing, and addressing ethical concerns, the program intends to enhance personalized medicine. It will assess funding and resource allocation to support its expanded scope, ensuring ongoing progress in genomic research and its clinical applications. These factors promote a healthy lifestyle and play an important role in fostering the growth of RNA-based therapeutics in the near future.
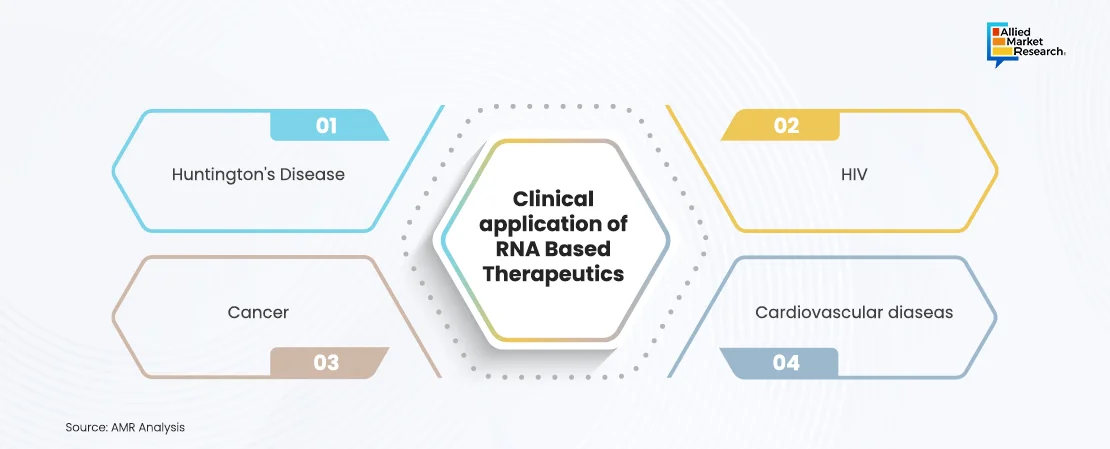
RNA-based therapeutics have been investigated for a variety of diseases, including genetic disorders, infectious diseases, and cancers. Some notable examples include:
Huntington's disease: According to the Huntington’s Disease Society of America, there are approximately 41,000 symptomatic Americans and over 200,000 at risk of inheriting the disease. Antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) have been utilized to target the huntingtin gene, which is mutated in Huntington's disease. These ASOs have demonstrated promise in reducing the production of the toxic huntingtin protein, offering hope for slowing disease progression and improving quality of life for patients.
HIV: RNA-based therapies have been explored for HIV treatment, employing siRNAs to target viral genes and reduce viral load, presenting a potential strategy for managing the infection. By targeting specific viral components, these therapies aim to control the virus more effectively and with fewer side effects than traditional treatments.
Cancer: RNA-based therapies have been developed to target specific cancer genes and enhance chemotherapy efficacy. For instance, siRNAs have been used to target oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes, while aptamers have been designed to deliver chemotherapy agents directly to cancer cells. According to the Global Cancer Society, the incidence rate for all cancers combined was 19% higher in men (222.0 per 100,000) than in women (186 per 100,000) in 2020. This highlights the need for innovative treatments that can address the diverse and complex nature of cancer.
Cardiovascular diseases: RNA-based therapies have shown promise in treating cardiovascular conditions such as hypertension and heart failure. siRNAs have been employed to target genes involved in blood pressure regulation, while miRNAs have been explored for their potential to regenerate cardiac muscle, offering innovative solutions for these prevalent diseases. The ability to target specific pathways involved in cardiovascular health presents a significant advancement in treating these conditions.
Current Barriers
RNA-based therapeutics encounter significant challenges, particularly in terms of delivery, stability, and safety. RNA molecules are naturally unstable and need to be efficiently delivered to target cells, which has led to the development of various delivery systems, including liposomes, nanoparticles, and viral vectors. Additionally, RNA molecules can trigger immune responses, leading to inflammation and other adverse effects. Although chemical modifications and synthetic carriers have mitigated some of these issues, ongoing research is needed to develop RNA-based therapies that minimize immune activation. Furthermore, chemical modifications to RNA can alter their structure and function, potentially causing off-target effects. This highlights the need for meticulous design and testing of RNA-based therapeutics to ensure they specifically target intended sites, enhancing both safety and efficacy

Strategies Adopted by Businesses
Key players in the RNA-based therapeutics industry are advancing through strategic collaborations and acquisitions. In July 2021, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals and PeptiDream establighed a license and collaboration agreement to create peptide-siRNA conjugates, aiming to advance RNAi therapeutics for targeting tissues outside the liver. Sanofi's acquisition of Tidal Therapeutics enhanced its research capabilities in immuno-oncology and inflammatory diseases by integrating a novel mRNA-based approach for reprogramming immune cells in April 2021.
Later, in September 2021, Sanofi completed its acquisition of Translate Bio, furthering its mRNA technology efforts for transformative vaccines and therapies. Additionally, Sarepta's AMONDYS 45 (casimersen), an antisense oligonucleotide for Duchenne muscular dystrophy, received FDA approval, highlighting the industry's ongoing commitment to advancing RNA-based therapeutics through innovative partnerships and regulatory achievements.
Future Directions
Future research in RNA-based therapeutics are expected to focus on:
Improved delivery systems: The development of more efficient and targeted delivery systems is highly important for the success of RNA-based therapies. Novel delivery platforms, such as lipid nanoparticles and viral vectors, are being explored to enhance the delivery of RNA molecules to specific cells and tissues. Advances in delivery technologies are essential to the effectiveness of these therapies.
Chemical modifications: Chemical modifications to RNA molecules have been refined to enhance their stability, specificity, and efficacy. This includes the use of locked nucleic acids (LNAs) and 2'-O-methylated RNAs, which have shown promise in reducing off-target effects. These modifications are essential for creating more robust and reliable RNA-based therapeutics.
Novel RNA Molecules: The discovery of new RNA molecules and mechanisms provides additional tools for therapeutic applications. For instance, the use of miRNA mimics to regulate gene expression and the development of RNA-based gene editing technologies are promising areas of research. These innovations will expand the therapeutic potential of RNA-based treatments.
Combination Therapies: Combination therapies that integrate RNA-based therapeutics with small molecule drugs or immunotherapies are being explored to improve their efficacy and safety profiles. Combining different therapeutic approaches can provide synergistic effects, leading to better patient outcomes.
Wrapping up
RNA-based therapeutics represent a transformative approach to treating a wide range of diseases, offering precision, versatility, and the potential for personalized medicine. Ongoing advancements in delivery technologies, RNA modifications, and manufacturing processes are paving the way for the next generation of RNA-based treatments. RNA therapeutics have the potential to transform healthcare, offering new hope for patients and tackling medical challenges that currently go unmet. RNA-based treatments are likely to become a key part of modern medicine, offering targeted and effective solutions for diseases.
Allied Market Research highlights the potential of these therapeutics in transforming the healthcare landscape. AMR’s commitment to provide comprehensive market insights, trends, and forecasts enables vendors to make informed decisions that drive growth and success. Through tailored reports, custom consulting services, and ongoing support, AMR equips vendors with the knowledge and tools needed to capitalize on the inherent advantages of RNA-based therapeutics. Our team of experts specializes in this specific branch of medicine, offering valuable insights to help you identify emerging trends, assess market entry strategies, and optimize product portfolios. Contact us today to explore how our actionable recommendations can advance your business in this innovative field.



