Table Of Contents

Sonia Mutreja

Pooja Parvatkar
Semiconductor & Electronics Spotlight: Industry Review 2023
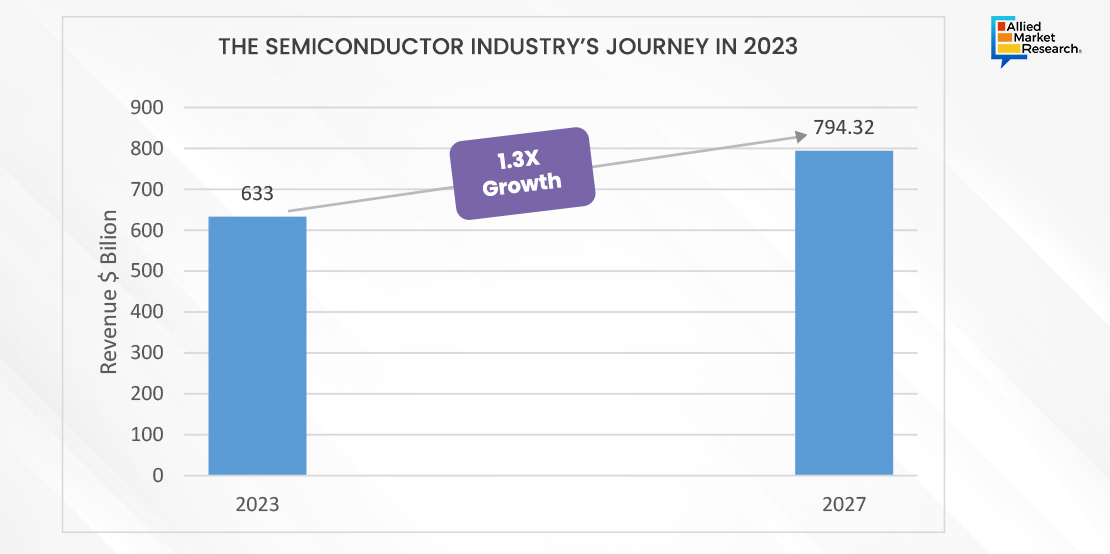
The semiconductor market reported a net revenue of $633 billion in 2023 and is projected to register 1.3X growth by the end of 2027.
In 2023, the semiconductor industry encountered formidable hurdles influenced by prevailing global macroeconomic and geopolitical dynamics. The landscape was marked by a confluence of factors, including increasing interest rates, inflationary pressures, and geopolitical tensions, culminating in a notable downturn in market capitalization. Notably, the top 10 global chip companies witnessed a substantial 34% decrease in their market value.
Amidst this turbulent backdrop, the industry grappled with significant fluctuations in high-end memory prices, which decreased by 50%. Despite this, average lead times remained persistently high at 25.5 weeks, posing operational challenges for market participants. Particularly impactful were the persistent shortages of certain chip types critical to industries like automotive, exacerbating supply chain disruptions, and hindering production capabilities.
The conflict in Ukraine served as an additional disruptor, further straining global supply chains and impeding access to crucial raw materials, with enduring repercussions expected to reverberate across the industry. Concurrently, regulatory actions undertaken by the US government to curb semiconductor technology exports to China exerted profound implications on the industry’s trajectory for 2023.
In response to these multifaceted challenges, chip companies adopted strategic measures aimed at mitigating financial strains, including cost-cutting initiatives, workforce reductions, and the deferment of capital expenditures.
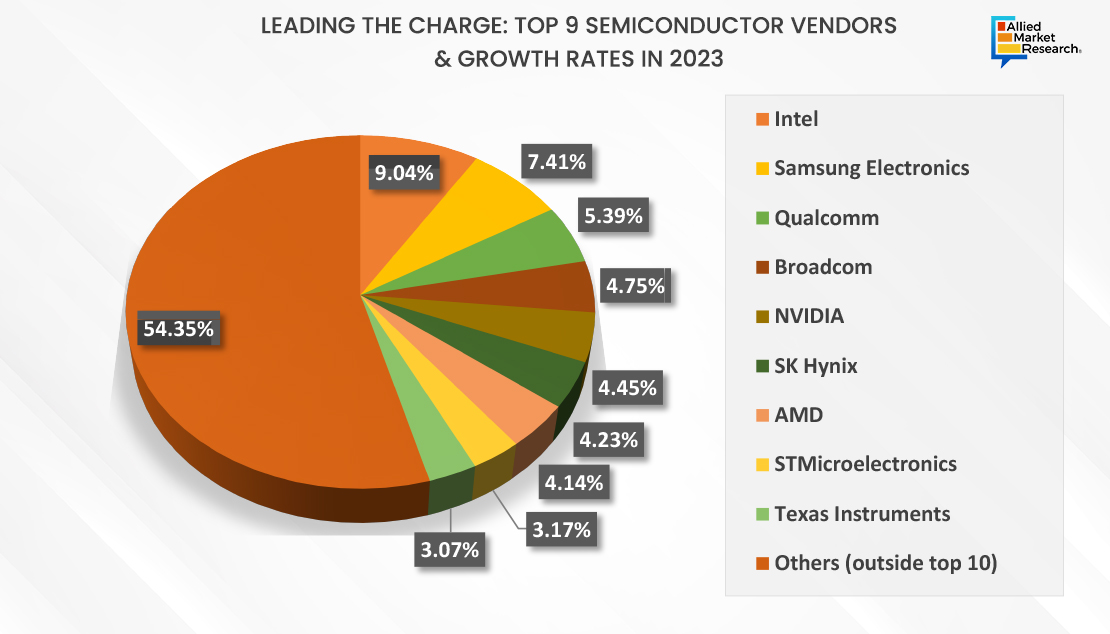
In 2023, leading semiconductor vendors experienced significant growth rates. Key players included Intel, Samsung, Nvidia, Broadcom, Qualcomm, AMD, and SK Hynix, among others driving innovation and market expansion.
Key Trends in the Semiconductors & Electronics Sector: 2023
Technological innovations, changing consumer demands, and market dynamics thrived the expansion and development of the industry. Several trends reshaped the industry’s landscape, making it essential for professionals in the field to adapt and innovate.
1. The Realm of Advanced Process Technologies
Semiconductor manufacturing facilities invested heavily in advanced nodes, such as 7nm, 5nm, and even 3nm processes. These smaller transistor sizes enabled the creation of more powerful and energy-efficient CPUs, essential for applications like artificial intelligence, data centers, and high-performance computing. Modern manufacturing techniques greatly focused on accuracy and efficiency; for instance, robotics and automation technologies reduced errors and increased throughput. Techniques such as 3D chip stacking and extreme ultraviolet lithography (EUV) were deployed to enhance chip density and overall performance, ushering in an era of unprecedented semiconductor innovation.
2. Rise of 3D Packaging
The development of 3D packaging semiconductors and heterogeneous integration techniques marked a paradigm shift in the pursuit of smaller, more effective electronics. These advancements enabled multiple semiconductor components to be stacked within a single package, resulting in lower power consumption, higher performance, and more compact designs, particularly in mobile and data center applications. On the other hand, heterogeneous integration focused on combining various semiconductor materials and parts into a single package, encompassing CPUs, memory, sensors, and power management units. This approach paved the way for highly specialized, multipurpose chips, enhancing the performance and capabilities of electronic systems.
3. Revolutionizing Automotive Transportation
The automotive sector underwent a profound transformation, and the semiconductor & electronics industry played a pivotal role in enabling this shift. The increased complexity of modern vehicles demanded a growing need for semiconductor components, which propelled the expansion of the global automotive semiconductor market. From chips powering advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) to autonomous driving, in-car entertainment systems, and electric vehicles (EVs), semiconductors have always been the backbone of automotive innovation. Specialized automotive-grade chips that can withstand extreme temperatures, vibrations, and electromagnetic interference were being developed to integrate electronics seamlessly into automobiles.
4. Rise of Sustainable Semiconductors to Pave the Way for Green Electronics
The semiconductor industry emphasized the creation of energy-efficient components due to an increasing emphasis on sustainability. For both electronic gadgets and data centers, energy-efficient semiconductors became crucial since they used less power and had less of an impact on the environment. The development of renewable energy technologies like solar cells and energy storage systems also became a priority for semiconductor producers. These technologies supported a greener, more sustainable future by using cutting-edge semiconductor materials and production techniques. Environmentally friendly semiconductor materials and methods were on the rise as a means to minimize the environmental impact of manufacturing.
5. Redefining the Limits of Computation with Quantum Computing
Various firms and organizations were racing to develop usable quantum computers, with the potential to revolutionize computing by executing complex computations at speeds unattainable by traditional computers. As quantum computing services moved closer to becoming more publicly available, semiconductor companies were at the forefront of this paradigm-shifting technology, promising to bring in innovation across numerous industries, including finance, healthcare, and artificial intelligence.
Technologies That Accelerated the Growth of the Semiconductor & Electronics Industry
In 2023, semiconductor and electronics advancements accelerated, driven by breakthroughs in AI chips, quantum computing, 5G integration, and sustainable materials, fueling transformative applications across industries worldwide.
- AI: Artificial intelligence (AI) was a significant driver of semiconductor demand in 2023, requiring high-performance computing and specialized chips. Additionally, AI facilitated chip design automation and optimization, reducing costs and time-to-market.
- IoT: The Internet of Things (IoT) connected billions of devices and sensors in 2023, generating vast amounts of data and requiring edge computing capabilities. IoT applications spanned various domains, including smart homes, smart cities, industrial IoT, and healthcare.
- 5G: In 2023, 5G emerged as the next generation of wireless communication, offering faster speeds, lower latency, and higher bandwidth. It unlocked new use cases like autonomous vehicles, virtual reality, and cloud gaming, demanding more advanced and power-efficient chips.
- Advanced Packaging: Advanced packaging techniques integrated multiple chips or components into a single package in 2023, enhancing performance, functionality, and reliability. It enabled heterogeneous integration, chiplet-based design, and 3D stacking.
- In-house Chip Design: In 2023, companies embraced in-house chip design to cater to specific needs and differentiate themselves from competitors. This trend fostered customization, innovation, and cost savings.
Automotive Electronics: The trajectory of semiconductor growth in 2023 was poised to be significantly influenced by the automotive electronics sector. Projections indicated a substantial expansion, with the automotive electronics market forecasted to generate $382.16 billion by 2026. Anticipated demand dynamics revealed a compelling outlook for advanced automotive chips, characterized by enhanced processes and functionalities.
Industry 4.0 solutions: In 2023, the semiconductor industry experienced a notable transformation propelled by the widespread adoption of Industry 4.0 solutions. These cutting-edge technologies, including digital twins and advanced analytics, reshaped traditional manufacturing paradigms by unlocking unprecedented levels of efficiency, quality control, and predictive maintenance. The integration of Industry 4.0 principles empowered semiconductor companies to leverage virtual simulations and real-time data analytics, facilitating agile responses to dynamic market conditions and mitigating potential disruptions across the supply chain.
Facing 2023’s Challenges and Risks: Preparedness for the Road Ahead
Every transformative endeavor faces hurdles and unforeseen circumstances. As the semiconductor industry navigated the promising terrain of 2023, it was aware of potential obstacles along the way.
Consumer Electronics Faced Low Demand
The consumer electronics sector, which includes tablets, PCs, and cell phones, saw a decline due to weak demand. International Data Corporation (IDC) revised its worldwide smartphone forecast due to a slower market recovery than previously expected. According to the latest Worldwide Quarterly Mobile Phone Tracker forecast, shipments of smartphones declined 1.1% in 2023 to 1.19 billion units, down from the 2.8% growth in the prior forecast as the market continues to suffer from weak demand and ongoing macroeconomic challenges. There were 967.7 million units that were Android devices, while the rest were IOS.
The US-China Chip War: A Major Roadblock
China and the US are engaged in a furious chip war, key data revealed that the US allocates approximately USD$ 52 billion to support companies like Nvidia, Intel, TSMC, and Samsung in investing in American semiconductor production, with a restriction on expanding advanced chip manufacturing in China for five years. With tensions lingering, companies faced a challenging dilemma between aligning with the US or China in 2023, impacting industry efficiency amidst deglobalization.
Resilience in Supply Chain: The global semiconductor supply chain faced problems from pandemics, natural disasters, and tensions between countries, which caused delays and shortages. To manage these risks, it was important to make the supply chain stronger and more diverse. This could be done by having multiple sources for materials, making things in different places, and having plans for emergencies.
Counteracting Counterfeit Components and Ensuring Authenticity: The proliferation of counterfeit semiconductor components posed significant threats to device quality, performance, and security. Implementing stringent measures to authenticate products and mitigate the risks associated with counterfeit components was crucial for maintaining industry standards and consumer trust.
Looking Forward: Welcoming Change and Shaping the Future
The upcoming years ahead signifies a pivotal moment for the semiconductor sector, offering an opportunity to embrace change, foster innovation, and collaborate towards a promising future. Prioritizing technological advancements, sustainability efforts, and workforce development will empower semiconductor firms to navigate forthcoming challenges and shape the trajectory of technology. Here are key aspects to monitor:
- Fostering Innovation: The adoption of a culture of continuous innovation is crucial for maintaining a competitive advantage and exploring new opportunities. Companies need to be receptive to new ideas, invest in research and development, and promote risk-taking to stay at the forefront.
- Strategic Partnerships for Technological Advancements: Partnering with tech leaders, academic institutions, and startups accelerates progress in vital areas like AI integration, quantum computing, and material science. These collaborations facilitate idea exchange, resource sharing, and expedited innovation.
- Prioritize Sustainability: Sustainability must transcend mere rhetoric and become a guiding principle in industry decisions. Companies should devise comprehensive sustainability strategies encompassing environmental stewardship, ethical sourcing, and conscientious waste management. By adopting a holistic sustainability approach, the sector can contribute to a cleaner and more equitable future.
The outlook for the global semiconductor market in 2023 was challenging, with subdued demand in consumer electronics, ongoing tensions in the US-China chip conflict, and a backdrop of rising inflation. However, automotive chips are expected to drive growth momentum in the coming years. Despite 2.5% decline in the semiconductor market for 2023, prospects are brighter for 2024. Reach out to us as we navigate through the complex terrain of the semiconductor and electronics industry, offering a comprehensive perspective on the key factors shaping its trajectory in the years ahead.

