Need for HPAPIs (Highly Potent Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients): Market Trends and Growing Interest Globally

HPAPIs (highly potent active pharmaceutical ingredients) are compounds used in pharmaceuticals due to their remarkable potency, even at minimal doses. These substances are commonly utilized in formulating drugs for addressing conditions such as cancer, autoimmune disorders, and specific viral infections. HPAPIs are distinguished by their capacity to yield substantial therapeutic benefits at exceedingly low concentrations, frequently quantified in micrograms or even nanograms.
HPAPIs address the need for more potent therapies, allowing pharmaceutical companies to develop drugs that target specific disease mechanisms more effectively. In addition, by requiring lower doses for therapeutic effects, HPAPIs help minimize adverse side effects associated with traditional treatments, improving patient safety and tolerance. Moreover, HPAPIs enable the creation of novel drug formulations with enhanced pharmacokinetic profiles, such as sustained-release formulations or targeted drug delivery systems, leading to better drug efficacy and patient compliance.
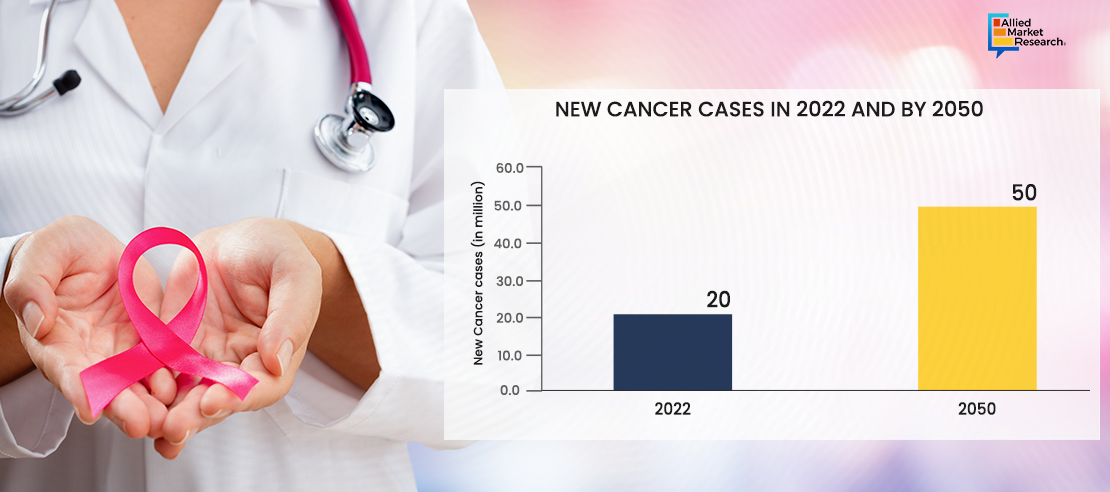
Rise in prevalence of chronic and complex diseases such as cancer, autoimmune disorders, and neurological conditions globally is driving the demand for advanced therapeutic treatments. HPAPIs are crucial in the production of cancer treatments, allowing for precise targeting of cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy tissues. It plays a significant role in the development of biologics and ADCs (Antibody-Drug Conjugates), expanding the therapeutic options for complex diseases. HPAPIs can be considered an established technology in the pharmaceutical industry. While ongoing research and development efforts may focus on improving formulations, delivery methods, and expanding the range of therapeutic applications, HPAPIs have been extensively utilized in drug development and manufacturing for many years. For instance, Seattle Genetics developed Adcetris (brentuximab vedotin), an ADC (Antibody-Drug Conjugate) utilizing HPAPIs. Adcetris is approved for the treatment of certain types of lymphomas, including Hodgkin lymphoma and systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma. The HPAPI component of Adcetris is monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE), a potent microtubule-disrupting agent.
Recent Developments in the Field of HPAPIs
Recent breakthroughs in HPAPI technology primarily focus on improving safety, efficiency, and manufacturing processes. Advances in containment technologies have enhanced worker protection during HPAPI handling and production. In addition, innovations in synthetic chemistry and biotechnology have led to the development of new HPAPIs with improved potency and selectivity. For instance, advancements in linker technologies and conjugation strategies have enabled the creation of next-generation ADCs with improved stability, efficacy, and selectivity. These ADCs incorporate novel HPAPIs that exhibit superior cytotoxicity against cancer cells while minimizing off-target effects. Examples include trastuzumab emtansine (Kadcyla) and enfortumab vedotin (Padcev), which employ innovative HPAPIs to target HER2-positive breast cancer and Nectin-4-expressing tumors, respectively.
Constraints and Opportunities in Market
Despite its advancements, HPAPI technology still faces several challenges. One significant challenge is the high cost associated with developing and manufacturing HPAPIs due to the specialized facilities, equipment, and stringent regulatory requirements. Ensuring worker safety during HPAPI handling remains a primary concern, requiring continuous improvements in containment technologies and operational practices. Also, there may be limitations in scalability and production efficiency for certain HPAPIs, impacting their widespread availability and affordability.
Moreover, HPAPI technology integrates with various existing technologies in the pharmaceutical industry, including drug formulation, drug delivery systems, and analytical techniques. For example, HPAPIs are often incorporated into novel drug formulations such as nanoparticles or liposomes to enhance drug delivery and efficacy. Analytical techniques such as HPLC (high-performance liquid chromatography) and mass spectrometry are utilized for HPAPI characterization and quality control purposes, ensuring the safety and efficacy of HPAPI-containing drugs. Moreover, advancements in synthetic chemistry and biotechnology contribute to the development of new HPAPIs with improved therapeutic properties.

Major Applications in the Pharma Sector
In the pharmaceutical sector, including oncology, immunology, and infectious illnesses, the use of HPAPIs is growing gradually. Rise in demand for tailored treatments, improvements in medication delivery systems, and the growth of personalised healthcare are some of the factors generating interest and adoption. Regulatory obstacles pertaining to safety and environmental issues, together with the high costs of handling and producing HPAPIs, slow down the adoption, restricting the market growth. Pharmaceutical businesses that treat cancer, with a specific demand for strong chemicals, are among the early adopters of HPAPIs.
The field of HPAPIs (highly potent active pharmaceutical ingredients) is now changing quickly due to advances in safety procedures, containment technologies, and synthesis techniques. Leading developers in the field include specialized manufacturers such as Lonza and Cambrex, as well as pharmaceutical corporations including Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche. The production of highly potent substances while guaranteeing the safety of workers and the environment has been made possible by recent advancements in synthetic chemistry and containment technology such as advanced isolation and containment systems, Advanced cleaning and decontamination technologies including VPHP (vapor-phase hydrogen peroxide) sterilization and dry fogging systems.
Future Landscape of HPAPI Market
In the future, HPAPIs have the potential to completely transform therapeutic approaches and medication development. The creation of innovative treatments for uncommon illnesses, focused cancer therapy, and improved drug delivery methods are some examples of future capabilities. Experts predict that containment technology, synthetic chemistry, and regulatory requirements will continue to progress to facilitate the safe and effective manufacture of HPAPIs. More innovation is required in fields like manufacturing automation, process optimization, and risk assessment approaches if HPAPIs are to reach their full potential. Through enhanced safety procedures and environmentally friendly production techniques, concerns about dangers to workers’ health and the environment must also be addressed.
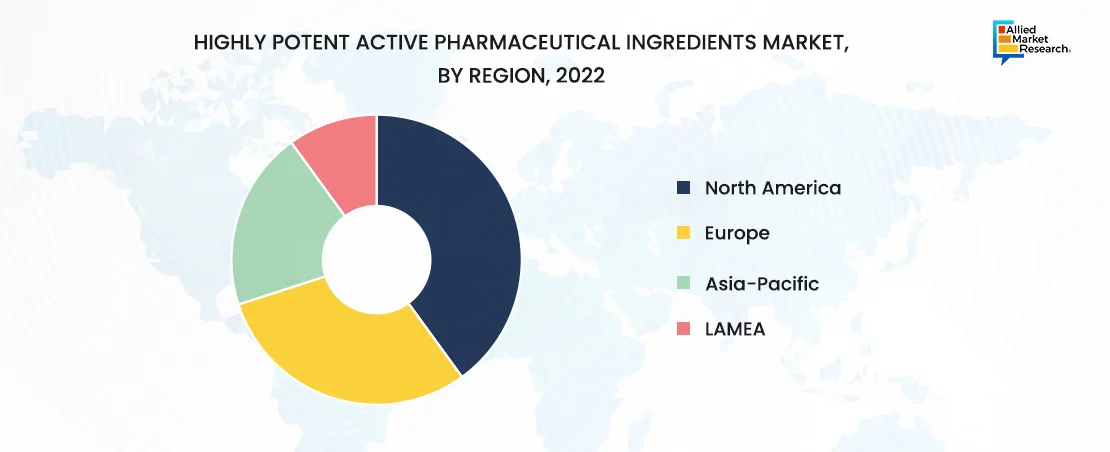
The North America market for HPAPIs (highly potent active pharmaceutical ingredients) is driven by several key factors, catalyzing its growth and significance within the pharmaceutical industry. Rise in prevalence of chronic diseases such as cancer, autoimmune disorders, and cardiovascular diseases in North America has propelled the demand for advanced and targeted therapies. HPAPIs play a crucial role in the development of these therapies, as they enable the precise targeting of diseased cells while minimizing adverse effects on healthy tissues.
In addition, emerging markets such as Asia-Pacific and LAMEA provide lucrative opportunities for market participants, as these regions are distinguished by rapid economic growth, cost-effective manufacturing, and rise in healthcare expenditure. Thus, emerging economies are progressively evolving into pivotal centers for pharmaceutical innovation and production, thereby fueling the broader adoption of HPAPIs.
Strategies Adopted for Development
Several pharmaceutical companies specialize in the development and manufacturing of HPAPIs. Some key innovators and companies in this field include Pfizer, Novartis, Lonza Group, Teva Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer Ingelheim, AbbVie, and others.
In addition, collaborations and partnerships between indigenous pharmaceutical enterprises and global corporations have streamlined knowledge transfer and technology exchange, driving the advancement and acceptance of HPAPIs in emerging markets. These alliances not only augment the technical prowess of local manufacturers but also facilitate entry into global markets and regulatory authorizations. For instance, Biocon, an Indian biopharmaceutical company, collaborated with Mylan, a global pharmaceutical company, to develop and commercialize a portfolio of biosimilars, including oncology drugs. This partnership leveraged Biocon's expertise in biologics manufacturing and Mylan's global reach and regulatory experience.
Market Overview and Future Prospects
In conclusion, potent therapeutic effects with low side effects are provided by highly potent active pharmaceutical ingredients, which mark a paradigm shift in drug development and manufacturing. Even though the HPAPIs are still in their early stage, recent advancements and rise in usage indicate that HPAPIs will have a bright future in terms of improving patient outcomes and fulfilling unmet medical needs. To overcome current obstacles and guarantee the safe and sustainable manufacturing of these transformational molecules, continued innovation and cooperation are necessary in the market. For further insights, get in touch with AMR analysts.



