Table Of Contents

Roshan Deshmukh

Shivangi Jain
mHealth: Bridging Gaps in Healthcare Delivery

mHealth or mobile health, is the utilization of mobile & wireless communication technologies to improve healthcare approach, outcomes, and research. mHealth is expected to play a key role in engaging patients in self-care as smartphone ownership is rising across the globe.
One of the key factors boosting the popularity of mHealth among consumers is its convenience. Mobile technologies such as smart wearable devices permit consumers to continuously track and manage their health data without the need to visit their healthcare providers. For instance, mobile health apps, such as the Apple Health App, integrate with a patient's electronic health record (EHR), allowing users to access their health data on their apple products such as iPhone or iPad. In addition, the technology aids in bridging gaps in healthcare by facilitating the communication of patients with their doctor, without physical meeting.
Pre-Mobile Healthcare and the Solutions Offered by mHealth
Healthcare in earlier times was delivered through traditional methods such as in-person consultations, hospital visits, and paper-based records. Healthcare providers faced several barriers in delivering quality care, such as limited access to patient information, lack of real-time communication with patients, and ineffective processes. On the other hand, patients faced challenges such as restricted access to healthcare services, high costs, and longer wait durations.
The introduction of mHealth reformed healthcare delivery by enabling real-time communication between healthcare providers & patients, remote monitoring of patients, and access to patient information from anywhere at any time. The technology has shown promising results even with its limited adoption by enhancing access to healthcare, particularly for critical patients and people residing in distant locations.
The Current Landscape
In the medical device industry, companies such as Intuitive Surgical Inc. and GE HealthCare Technologies Inc. are actively driving innovation through mHealth technologies, with the U.S. leading in the adoption of technology within the global industry. These technologies provide patients with the tools to access health information & advice in real time, improve communication with doctors, manage & monitor their health, and engage deeply in their care. mHealth alerts lead to lower costs & improved outcomes as they reduce the need for costly episodic care by proactively notifying the individual and care team of incidences.
The adoption of mHealth technology has been increasing globally, with various factors influencing its acceptance and evaluation. According to a study executed in 2021 by independent researchers from countries such as China, Spain, India and Netherlands, users' digital literacy had the strongest impact on their willingness to use mHealth apps, followed by their habit of sharing personal achievements over the internet. Currently, users can choose from different applications, including Google Fit, Fitbit, Samsung Health, and BlueStar. According to The Daily Guardian, a British daily newspaper, as of 2023, approximately 305,000 mHealth apps are available for download from app stores.
How is mHealth Transforming Healthcare Delivery?
In recent times, mHealth is making its way to strengthen the healthcare system around the globe and encourage individuals to get involved in their wellness. mHealth offers diverse digital solutions for wellness, including programs for weight & stress management, chronic condition self-care, remote monitoring, and diagnostics. It provides behavior change interventions, virtual care, and telemedicine services for convenient healthcare access. Moreover, the technology enables physicians to diagnose the symptoms faster during in-person visits, with minimal possibility of errors.
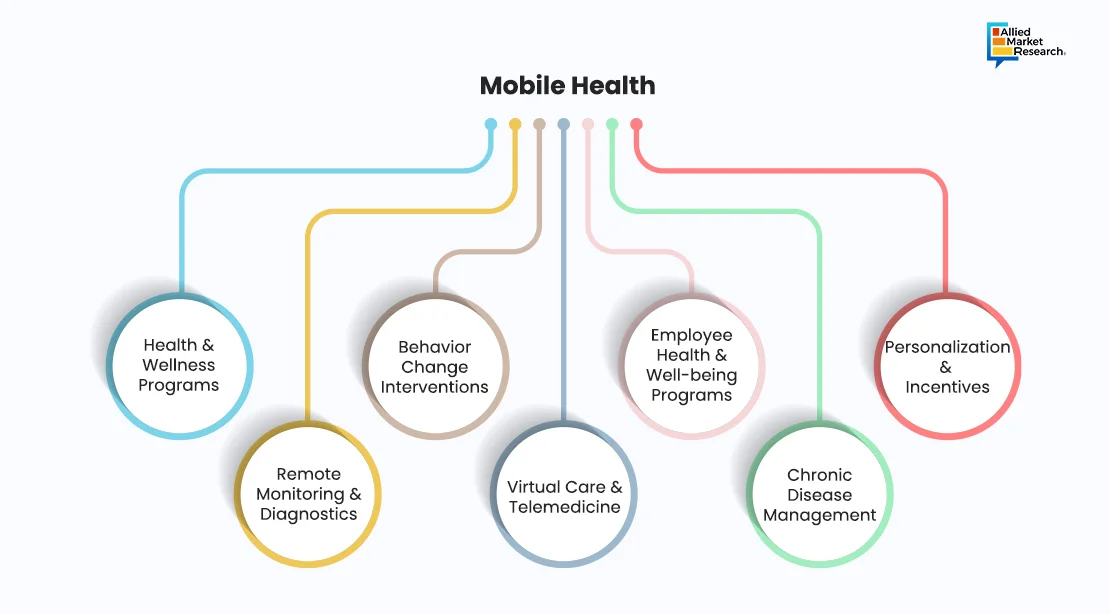
The stakeholders of mHealth technology have adopted a patient-centric approach by empowering patients to take charge of their fitness. The apps proficiently monitor the behavioral change of a person and offer different services such as personalized goal setting, individualized dosing reminders, & scheduling appointments. These services are boosting the convenience & engagement of users and leading to cost savings.
Therefore, the diverse offerings of mHealth are intended to revolutionize healthcare delivery, support individuals in managing their health, elevate access to medical advice, and enhance overall well-being through mobile devices.
Frontrunners: Leading the Charge
Key manufacturers and companies operating in the mHealth market include AirStrip, AliveCor, Apple, AT&T, Athenahealth, Boston Scientific, CardioNet, Cerner, Epocrates, Fitbit, Honeywell, Jawbone, Motion Computing, Nike, Qualcomm, Sanofi, Telcare, Vodafone, and Voxiva. These companies are engaged in developing innovative mHealth solutions, including mobile apps, wearables, and remote patient monitoring systems, to improve healthcare delivery, patient outcomes, and reduce costs. In addition, researchers and innovators in the mHealth market are contributing significantly to the development of new technologies and solutions. For instance, the digital health pilot program by Food and Drug Administration (FDA) includes companies such as Apple, Fitbit, Pear Therapeutics, and Tidepool, emphasizing the growing role of mHealth in digital health. The aim of this program is to offer pre-certification to the digital health technologies and move them under the realm of Software as a Medical Device (SaMD).
Recent Breakthroughs and Progress in mHealth Technology
The deployment of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and data analytics is transforming mHealth apps, enabling accurate diagnoses, enhanced patient engagement, and personalized treatment plans. AI in healthcare is analyzing vast amounts of data, including medical records, genetic information, and personal health metrics; to generate meaningful insights & predictions. In addition, blockchain technology ensures secure and transparent data management. The advancement of current wearable electronics, such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, and smart glasses is expected to be a significant factor in the development of mHealth. These devices currently provide continuous real-time monitoring of health metrics, enabling early prediction of various health conditions.

EVITE, an interactive mHealth app, has recently proved to be effective in improving the health and lifestyle of coronary heart disease patients who had undergone percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). The app constantly motivates patients to adhere to the modified lifestyle through its multiple components, including calls, messaging, website, and emails.
Current Challenges to Overcome
While mHealth technology has made substantial advances in recent years, there are still a few technical limitations and challenges restraining its development. This involves integrating new technologies with existing systems, overcoming regulatory & legal barriers, addressing interoperability issues, and the existing gaps in educating healthcare professionals & patients regarding the utilization of technology. Investment in R&D is vital for advancing technology and making it more accessible and user-friendly. Developments in machine learning and digital applications used for health management & decision-making are expected to offer favorable opportunities for improving healthcare outcomes and patient engagement. In addition, collaborations among stakeholders, including technology firms, healthcare providers, and governments & nonprofit organizations allows for pooling resources and expertise which is anticipated to address the challenges effectively. Regular training programs are crucial for equipping healthcare professionals with the skills needed to utilize digital resources efficiently.
Moreover, adopting mHealth solutions comes with risks such as ensuring data privacy and security. According to a report released by Approov, a Scottish software company, on February 2021, the 30 most popular mHealth apps were highly vulnerable to API attacks, offering unauthorized access to the complete data of patients’ records. To address such concerns, it should be mandated for the mHealth app developers to implement encryption strategies and audit trails for the confidentiality of the health records. By addressing the existent challenges, providers can pave the way for successful implementation of mHealth solutions and unlock a new frontier in healthcare delivery.
Future of mHealth: Innovative and Preventive
The potential future capabilities and applications of mobile health (mHealth) technology are vast and varied, with experts anticipating significant developments in the coming years. Immersive technologies such as augmented reality (AR) are projected to redefine the engagement of users into the mHealth apps by enhancing their knowledge regarding health. For instance, AR can educate users about body organs or any medical procedure, using 3-dimensional models. Moreover, wearable sensors are being developed body different parts of the body which can be assimilated with the mHealth apps. These sensors are expected to play a crucial role in preventive healthcare by detecting early signs of different health conditions. These sensors will shift the role of mHealth beyond data collection to personalized healthcare.

A research team at Johns Hopkins Medicine is currently testing a smartphone-based eye tracking application. The goal of this app is to prevent the incorrect diagnosis of strokes occurring at the back of the brain. One of the methods of diagnosing brain strokes is examining eye movements. These movements are very subtle which can be misinterpreted easily. The success of the app is expected to ensure timely diagnosis and treatment. This development depicts tremendous potential of mHealth in transforming healthcare delivery.
In conclusion, continuing as a trend, mHealth is predicted to establish its firm essence in the healthcare industry due to the constant integration of technological advances. The journey of mHealth toward the future is more patient-centric, efficient, and undeniable. Moreover, as the stakeholders continue to explore the potential of mHealth, it is projected to lower healthcare discrepancies and offer improved health outcomes.
For further insights, get in touch with AMR analysts!

